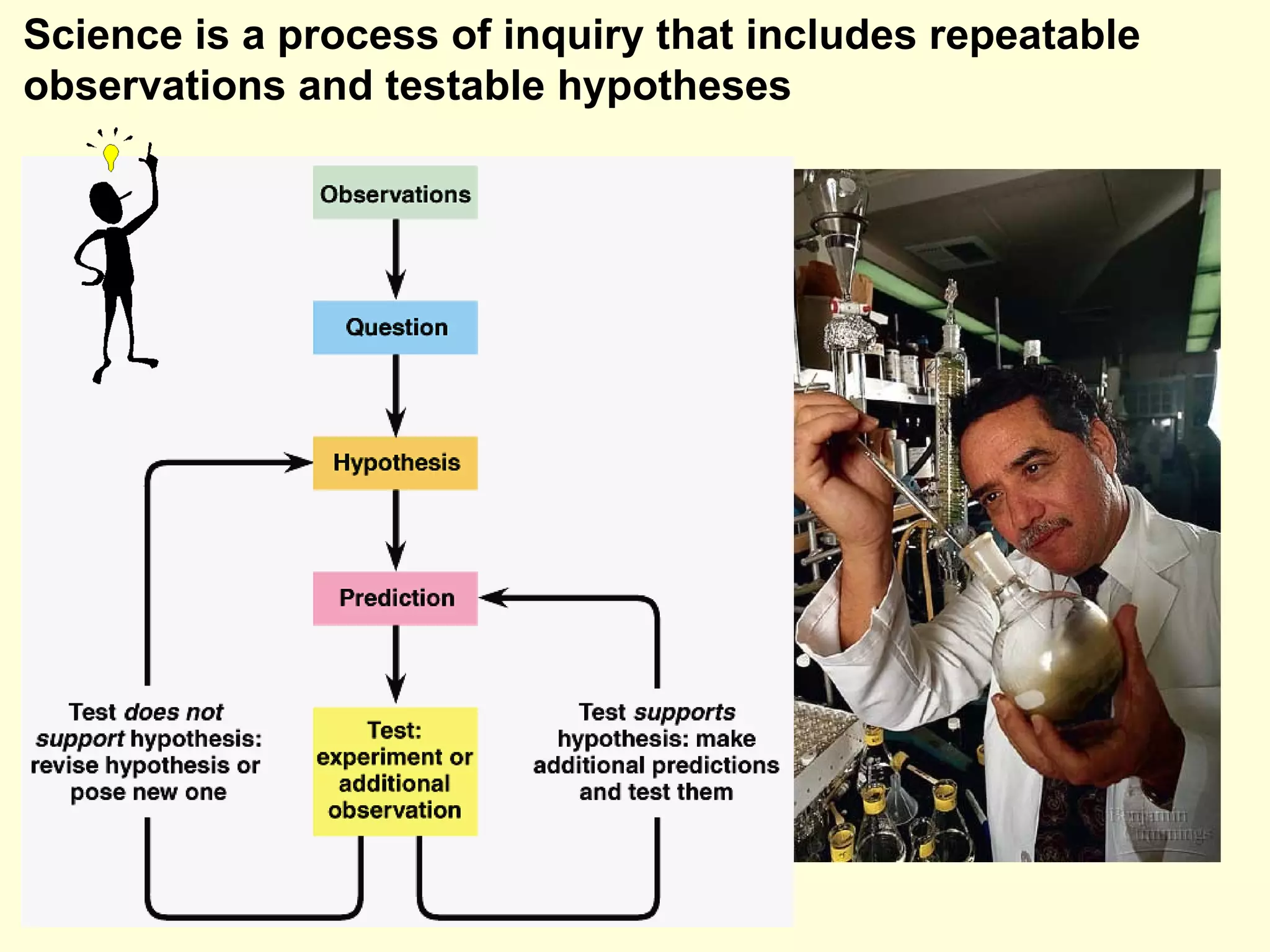
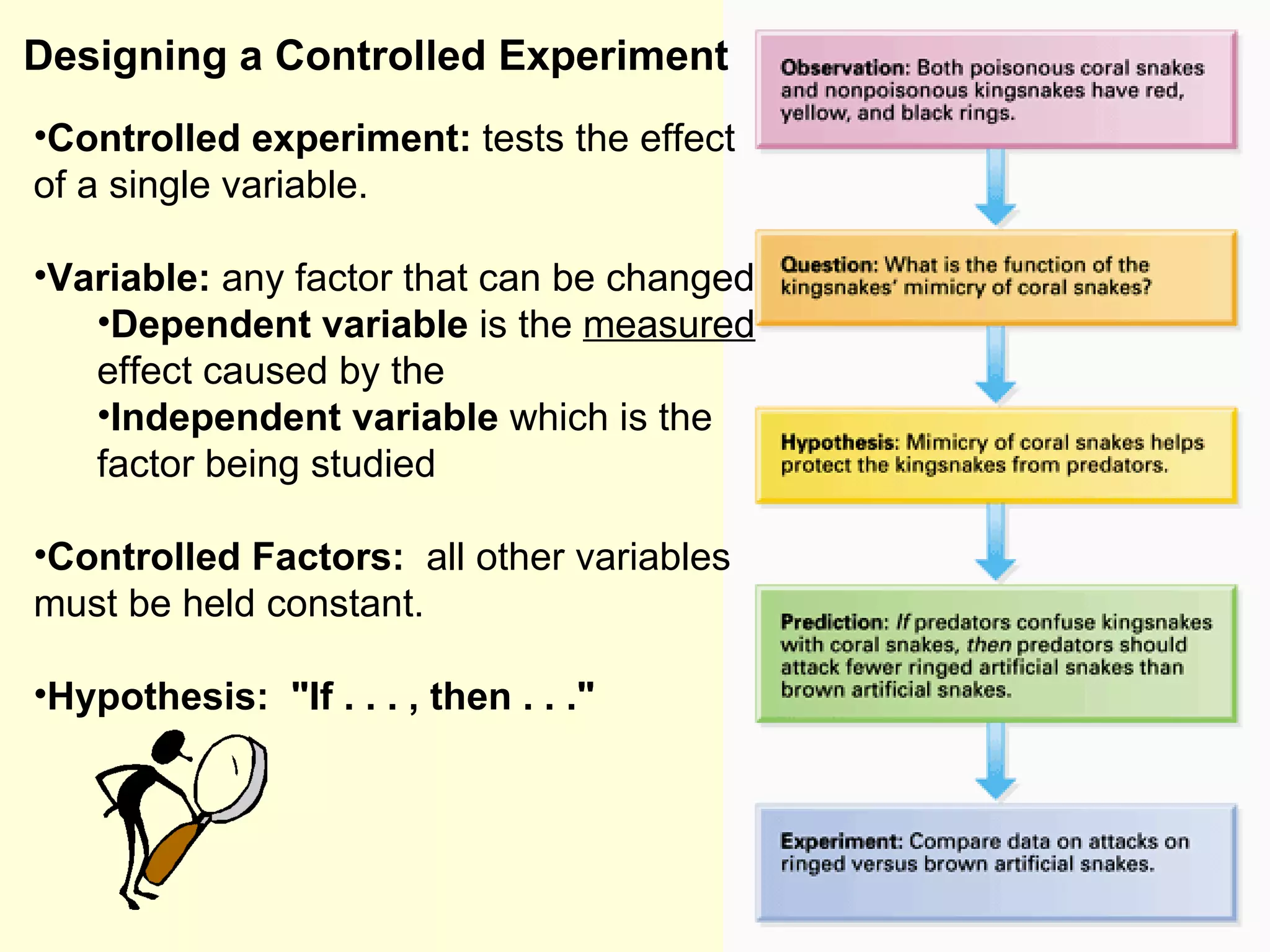
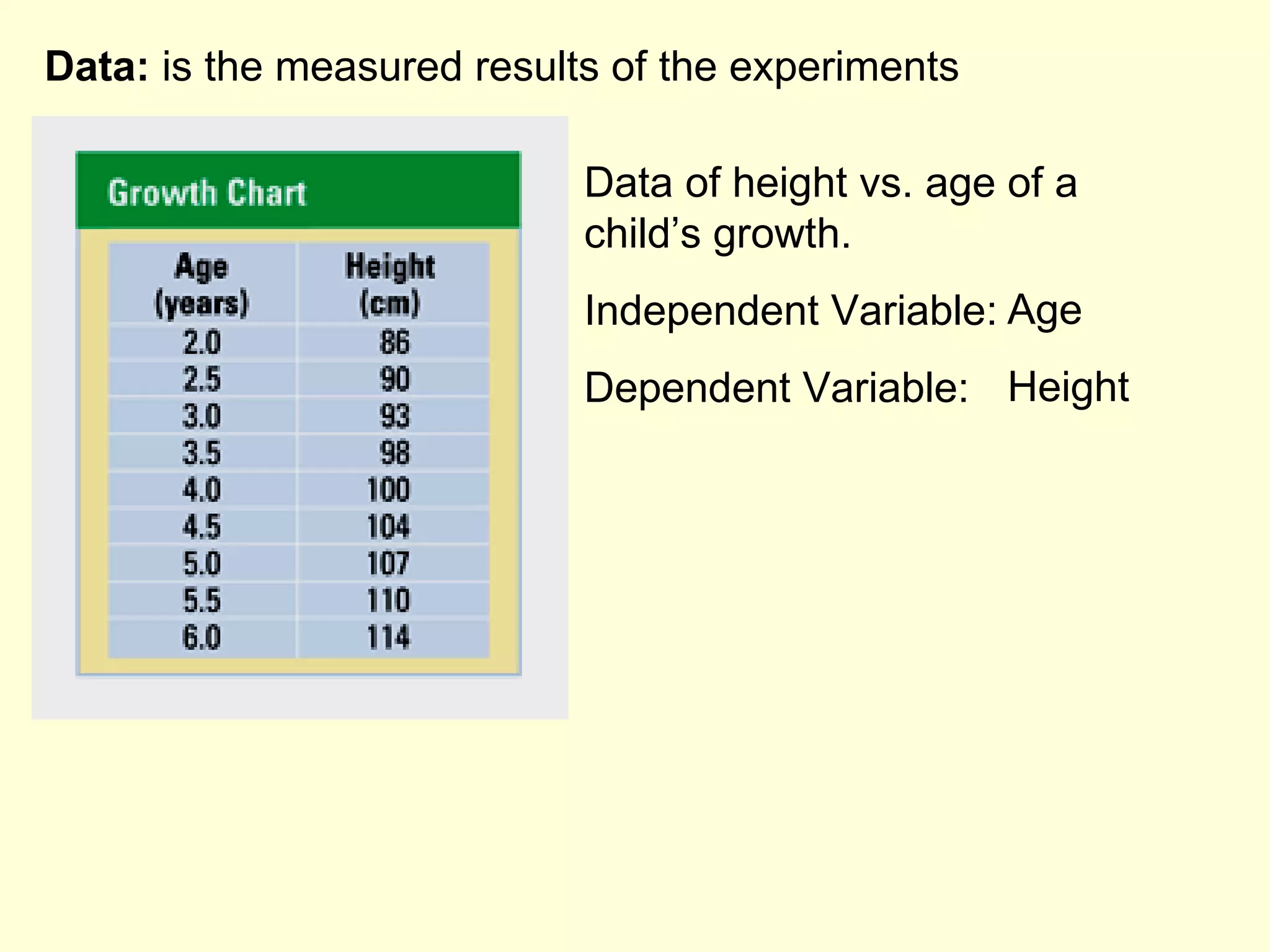
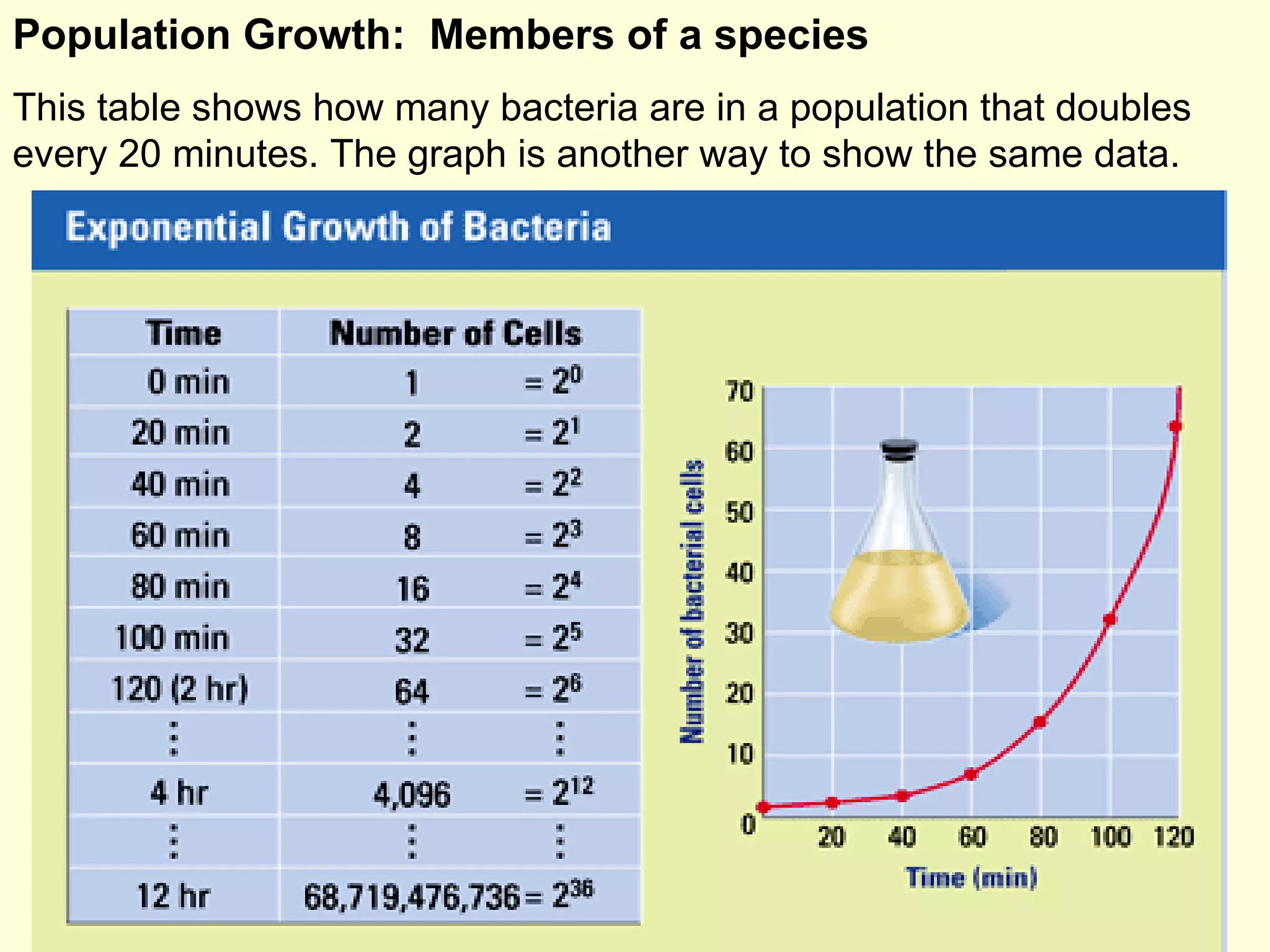
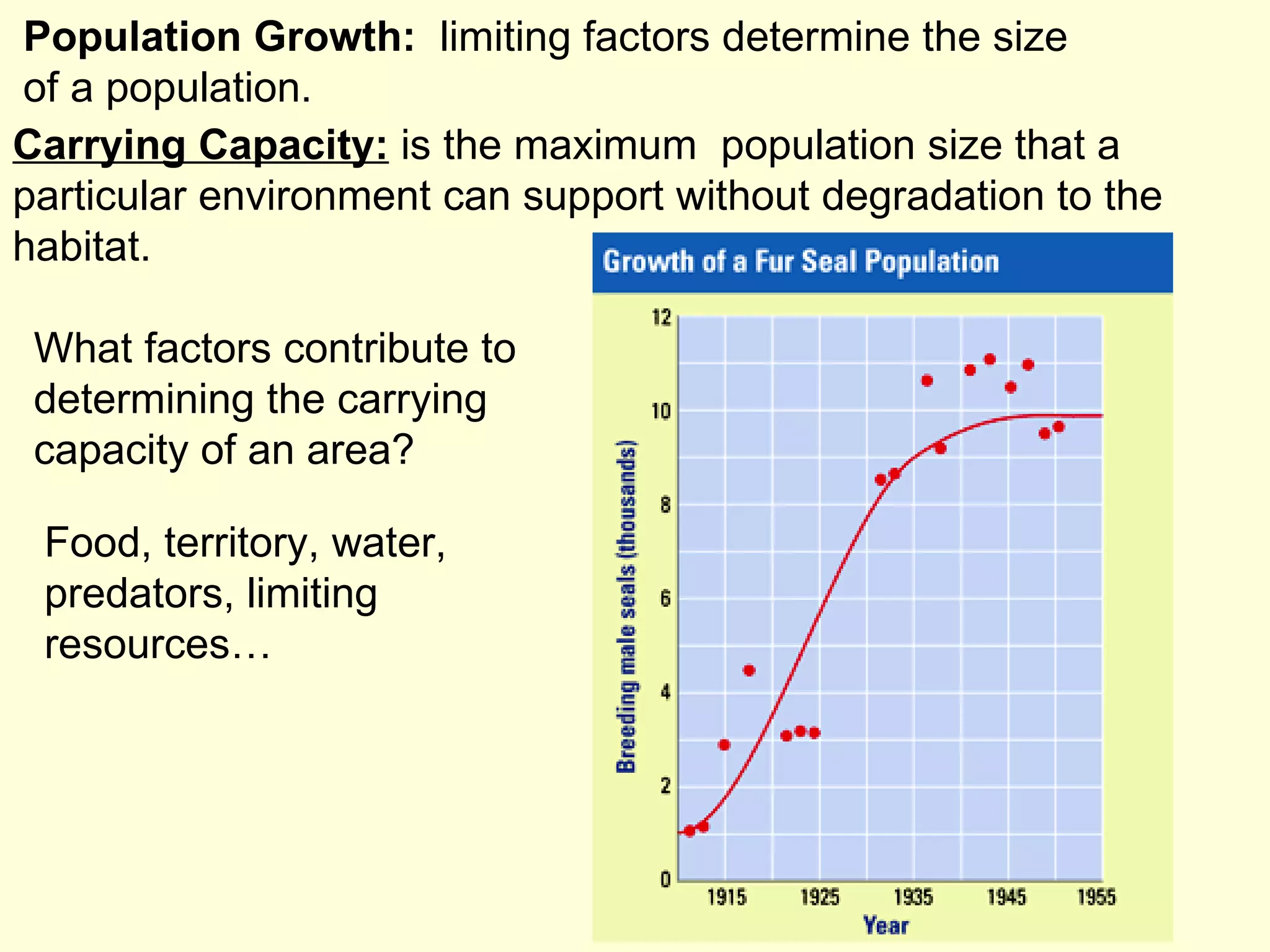
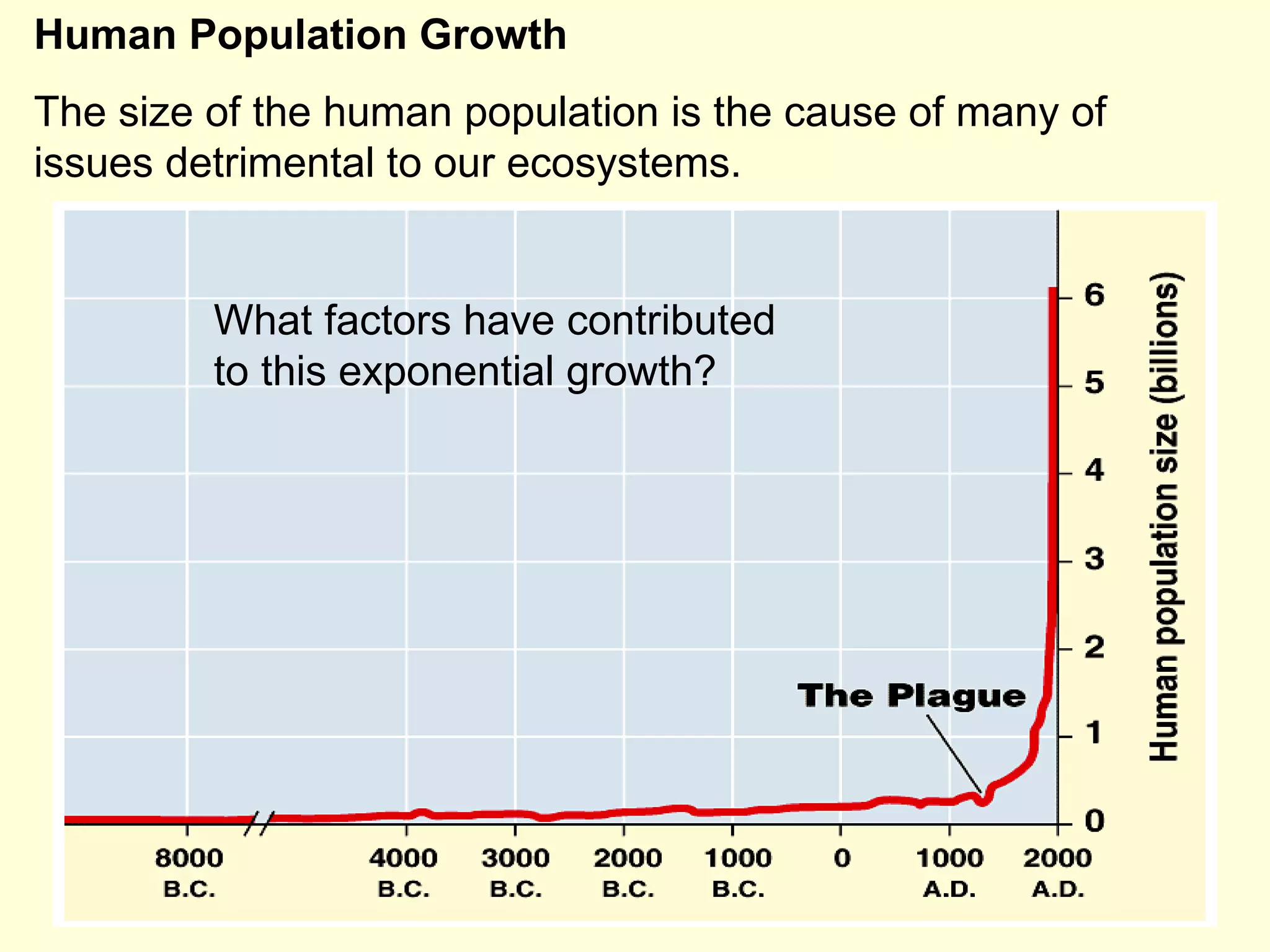
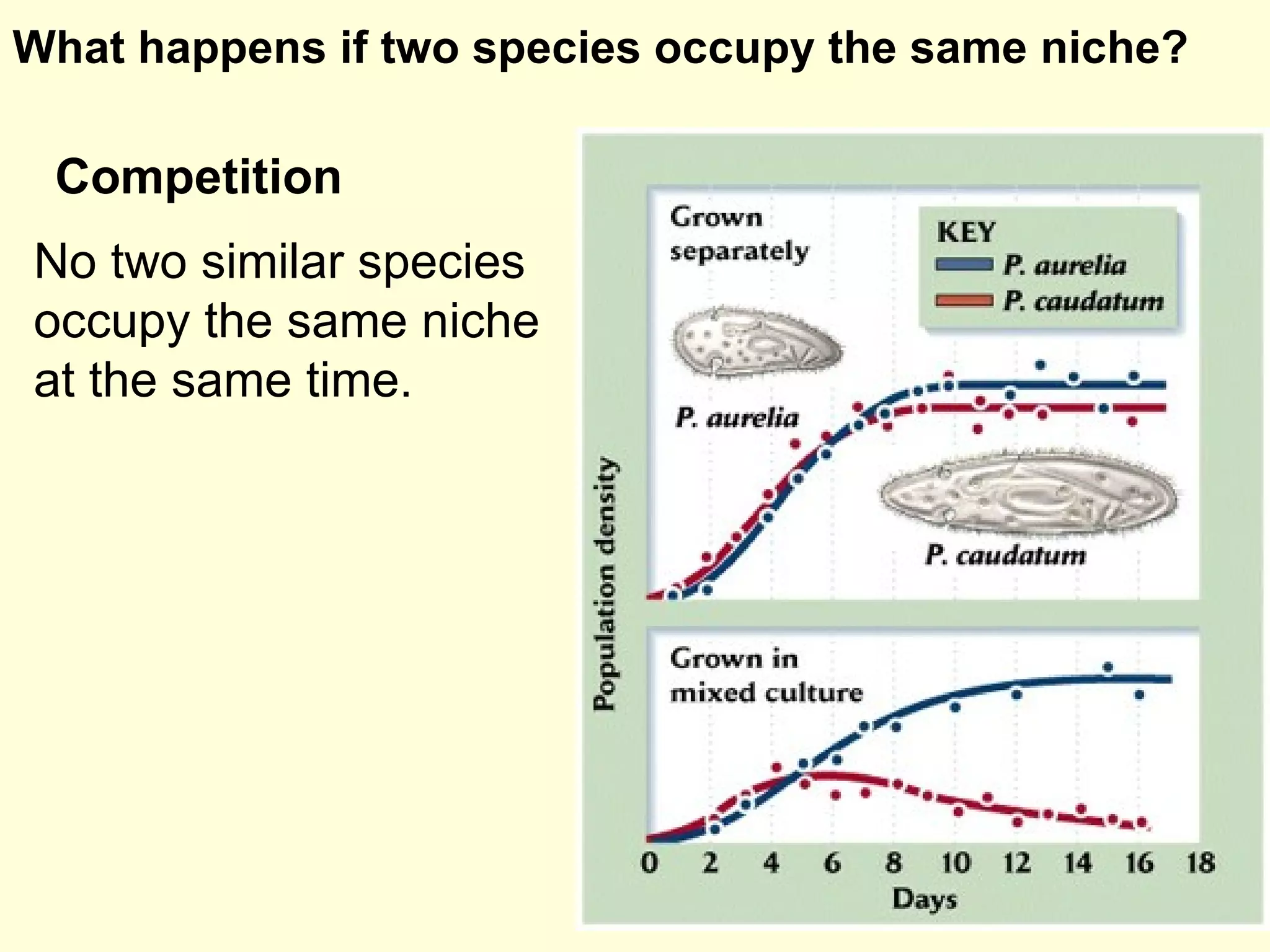
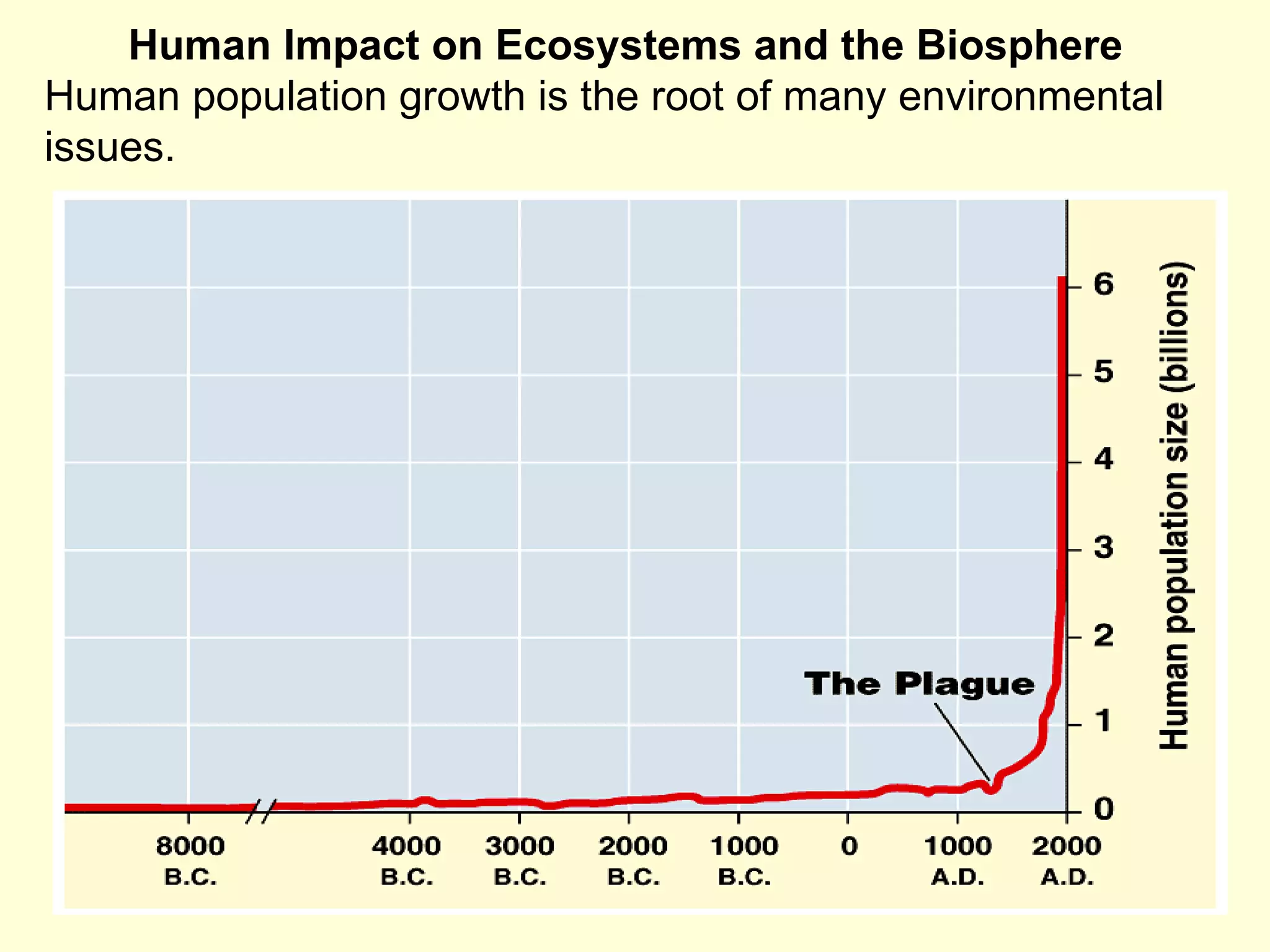
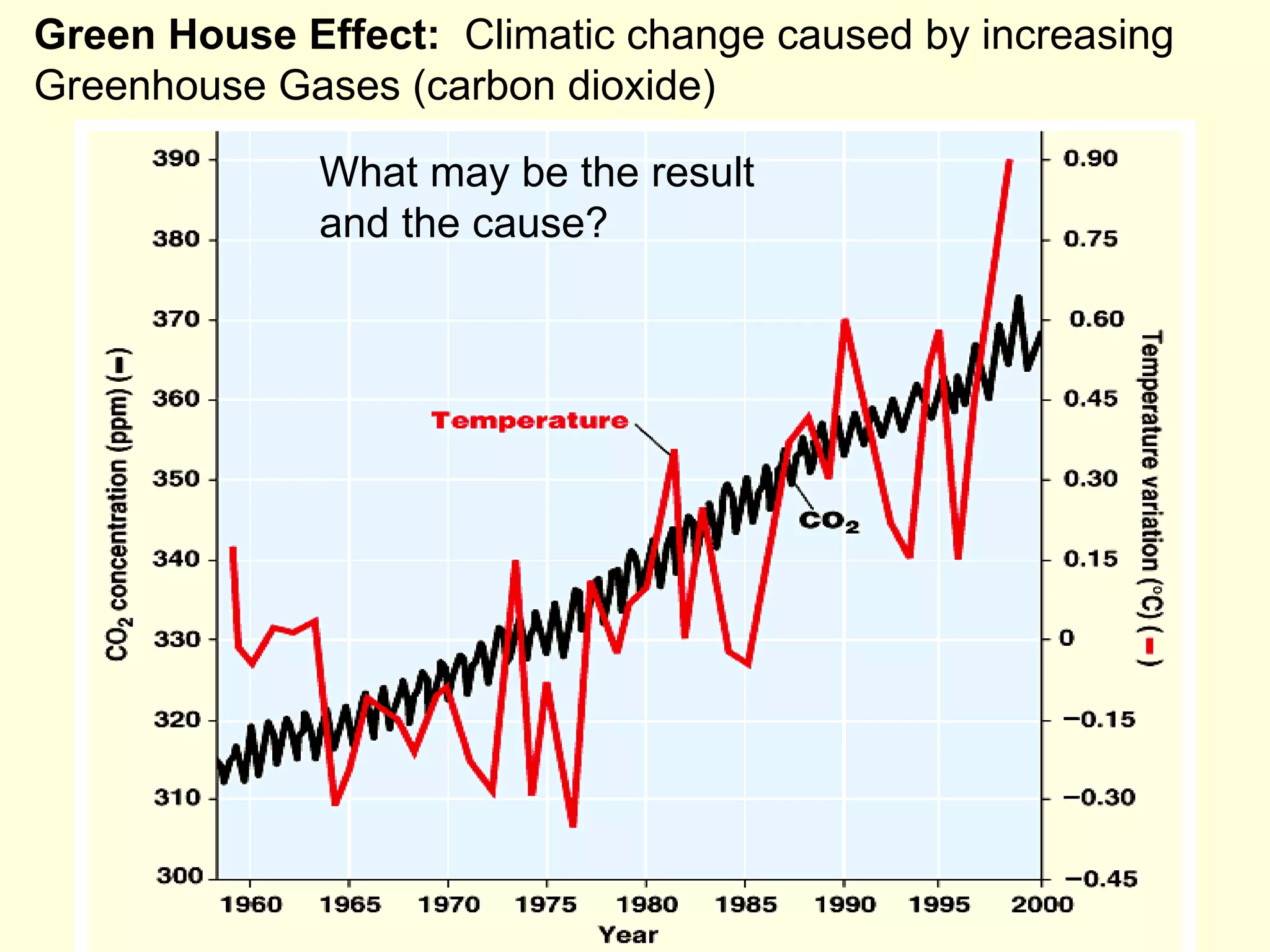
This document discusses the scientific process and principles of controlled experiments. It defines key terms like independent and dependent variables, and how to design experiments to test hypotheses. For example, an experiment could test if a new fertilizer increases plant growth by applying the fertilizer as the independent variable and measuring plant height as the dependent variable while controlling other factors. The document also covers topics like population growth, carrying capacity, human impacts on ecosystems, and the greenhouse effect.