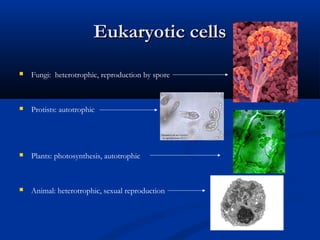
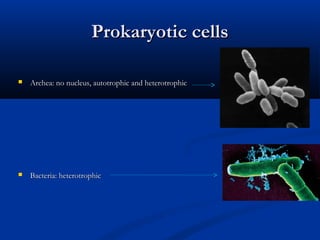
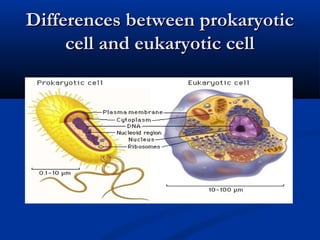
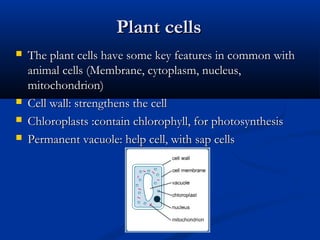
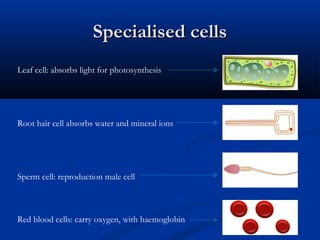
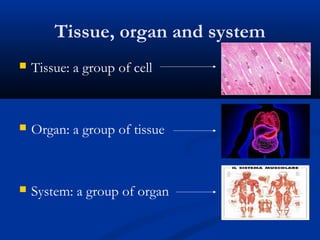
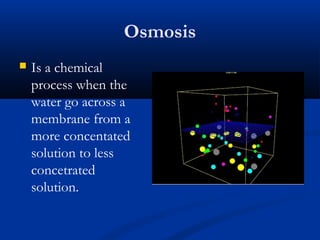
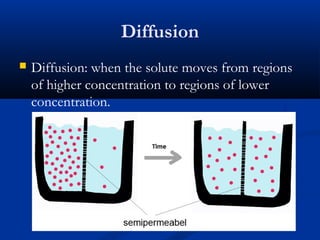
There are two main types of cells: eukaryotic and prokaryotic. Eukaryotic cells include plant, animal, fungi and protist cells which have a nucleus and organelles, while prokaryotic cells like bacteria and archaea lack a nucleus. Key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells include the presence of organelles like mitochondria and the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. Both plant and animal cells share features like the cell membrane, cytoplasm, and mitochondria but plant cells also have a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a permanent vacuole. Specialized cell types perform functions like photosynthesis, reproduction and oxygen transport.