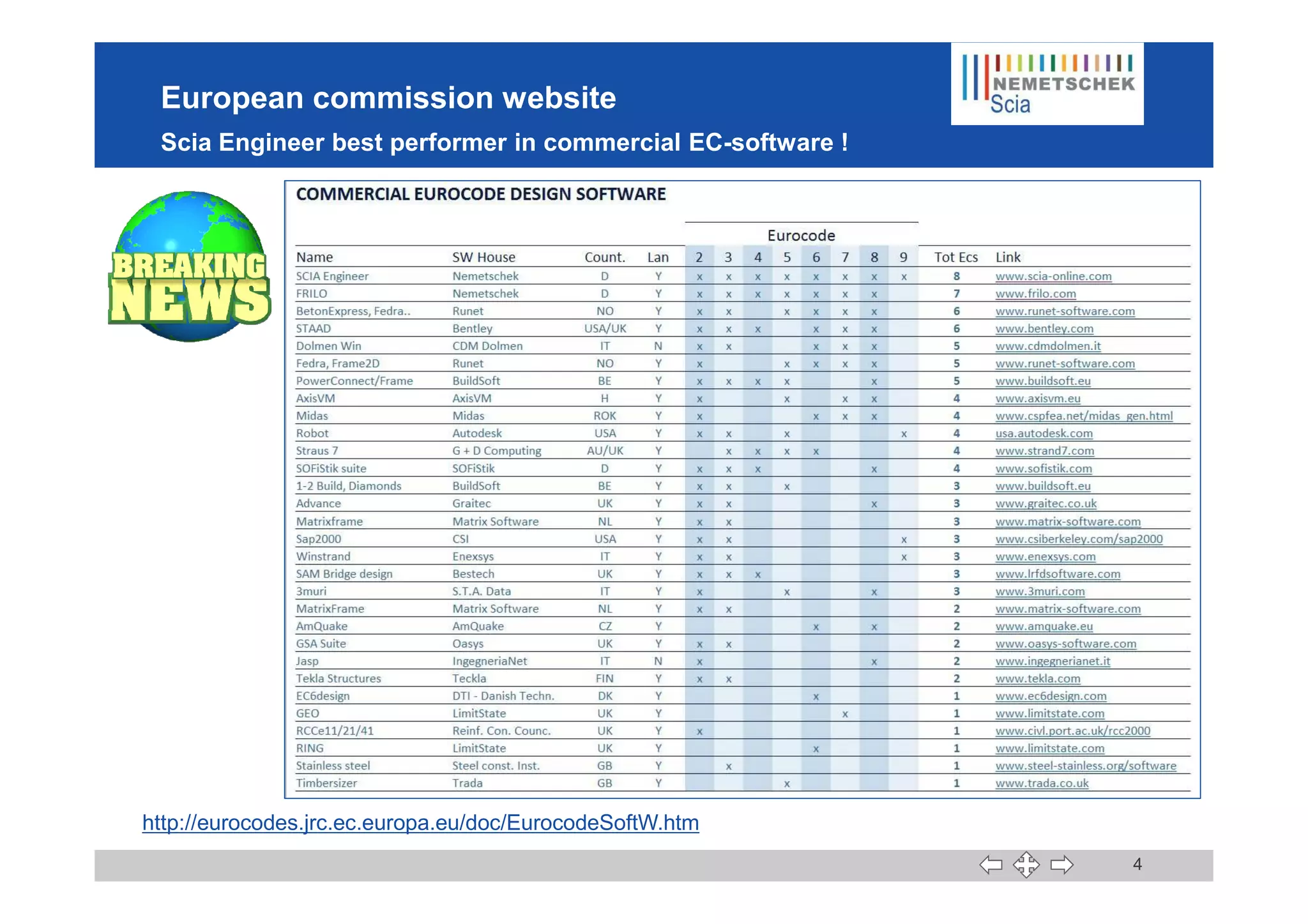
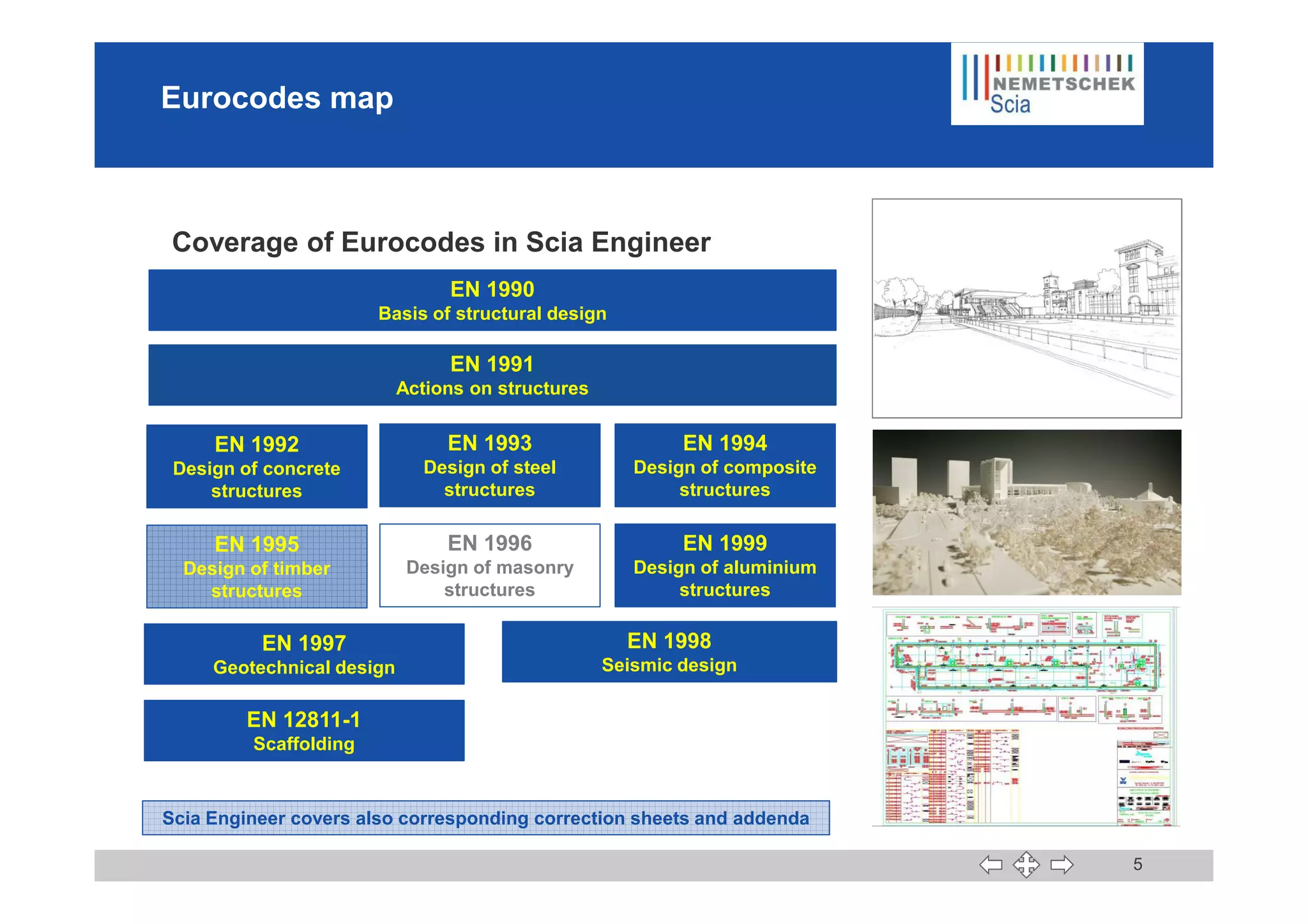
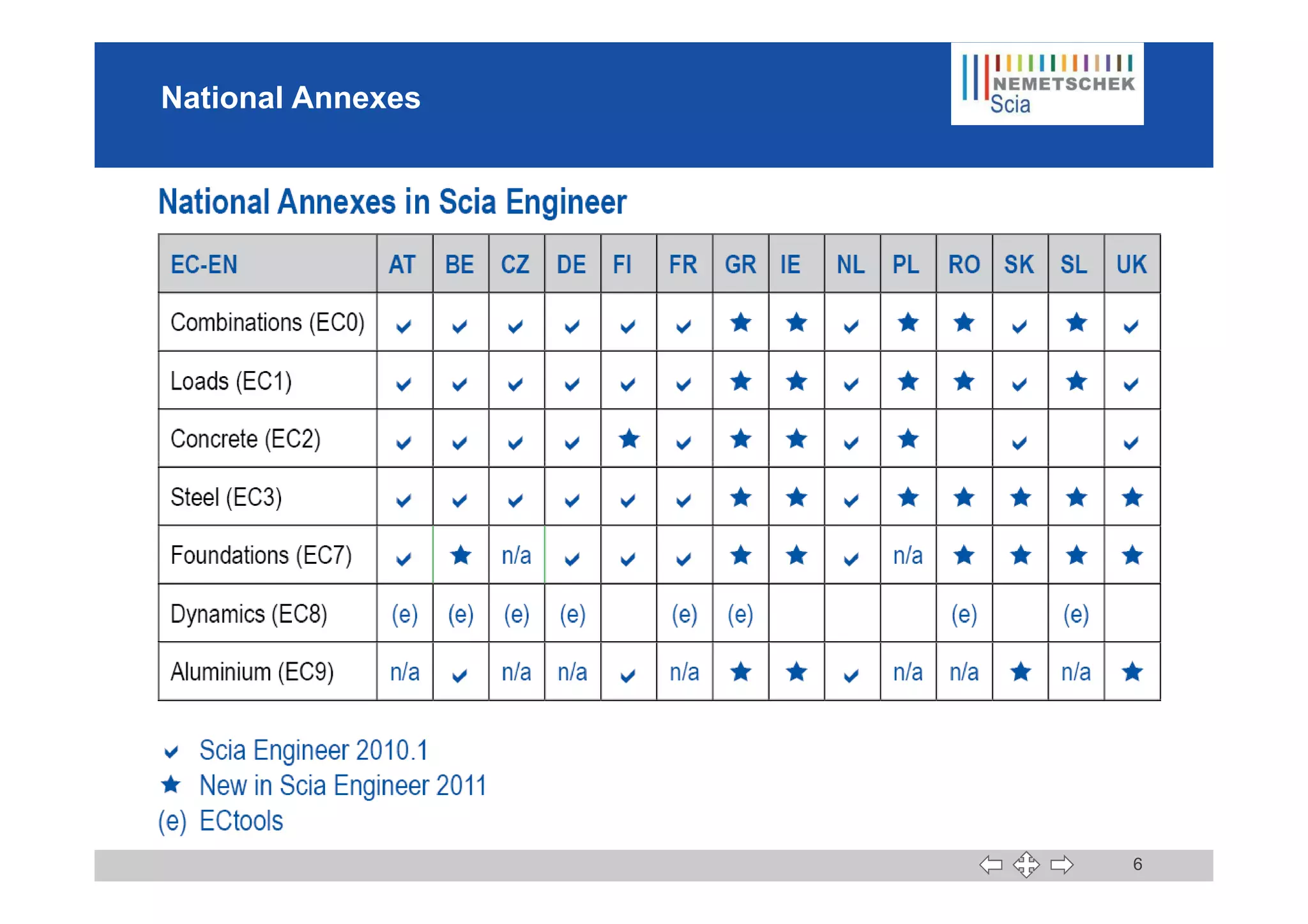
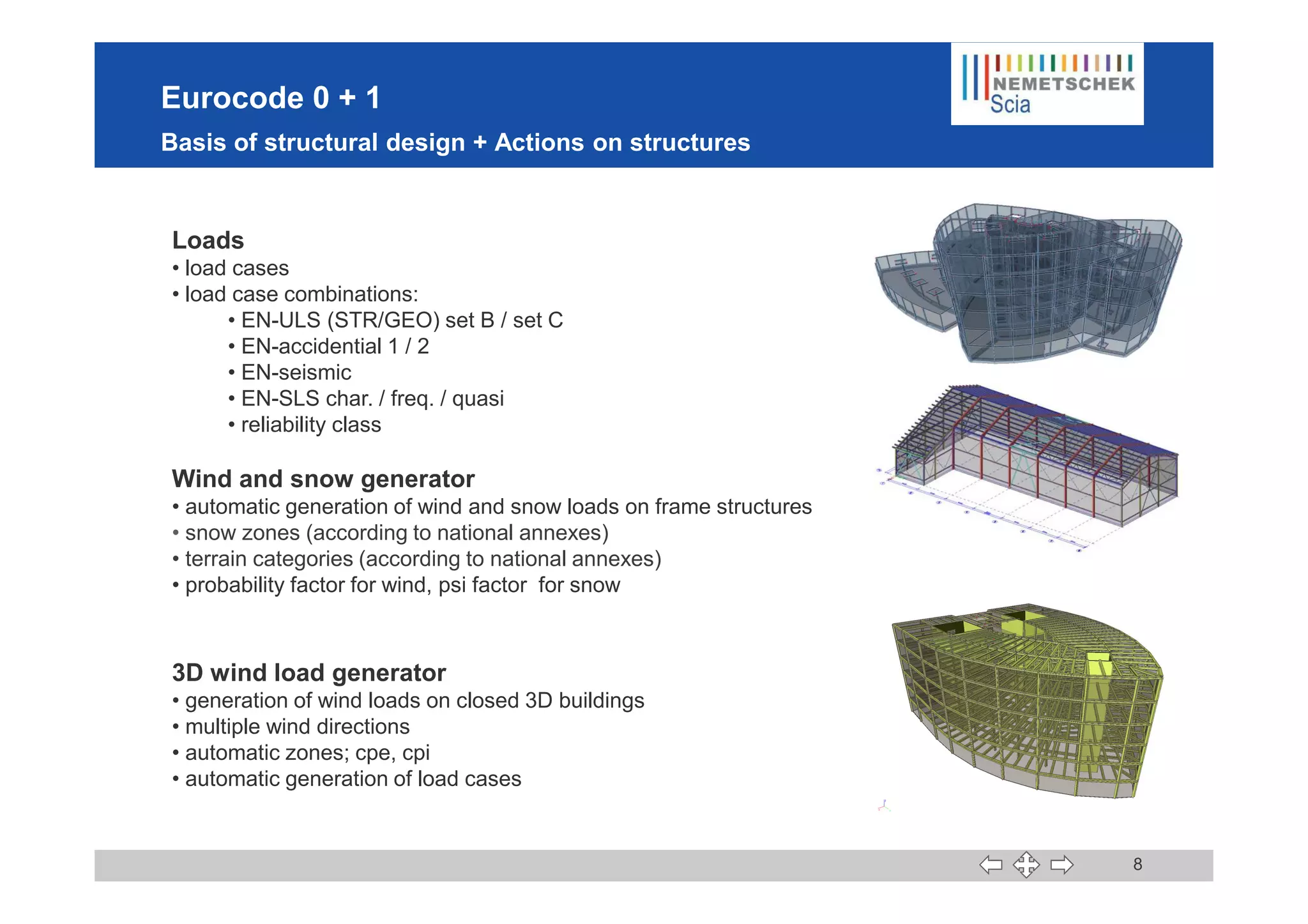
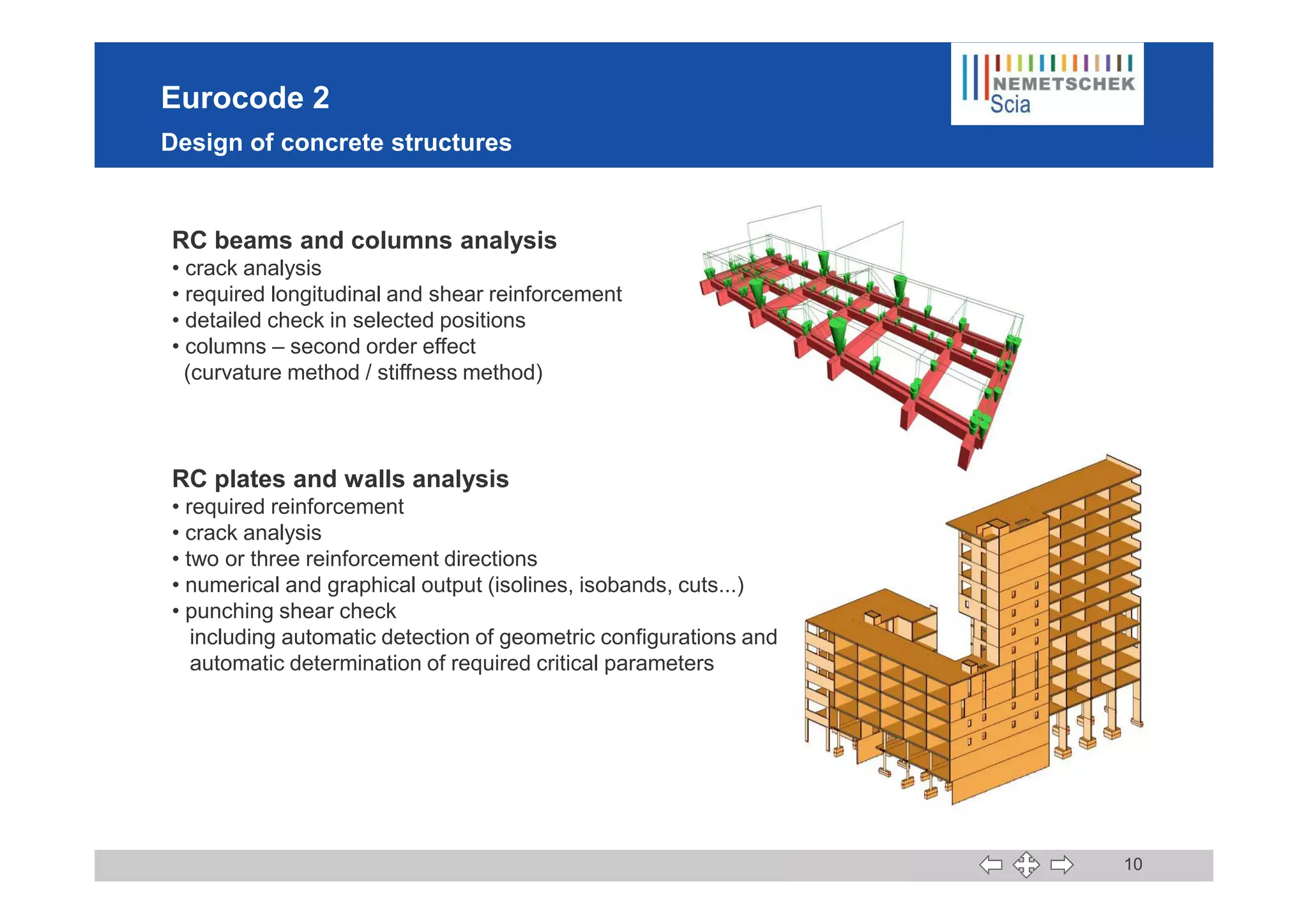
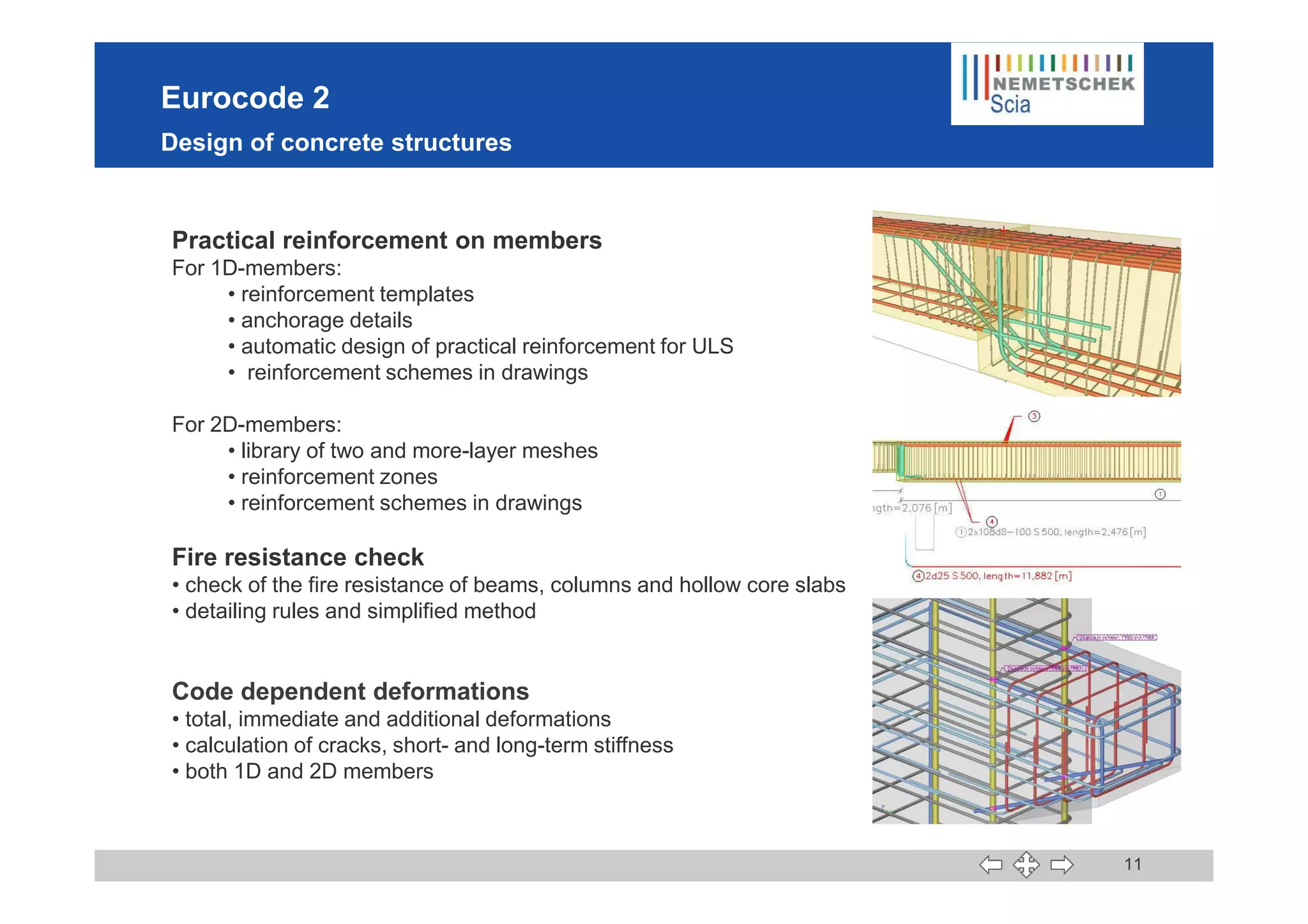
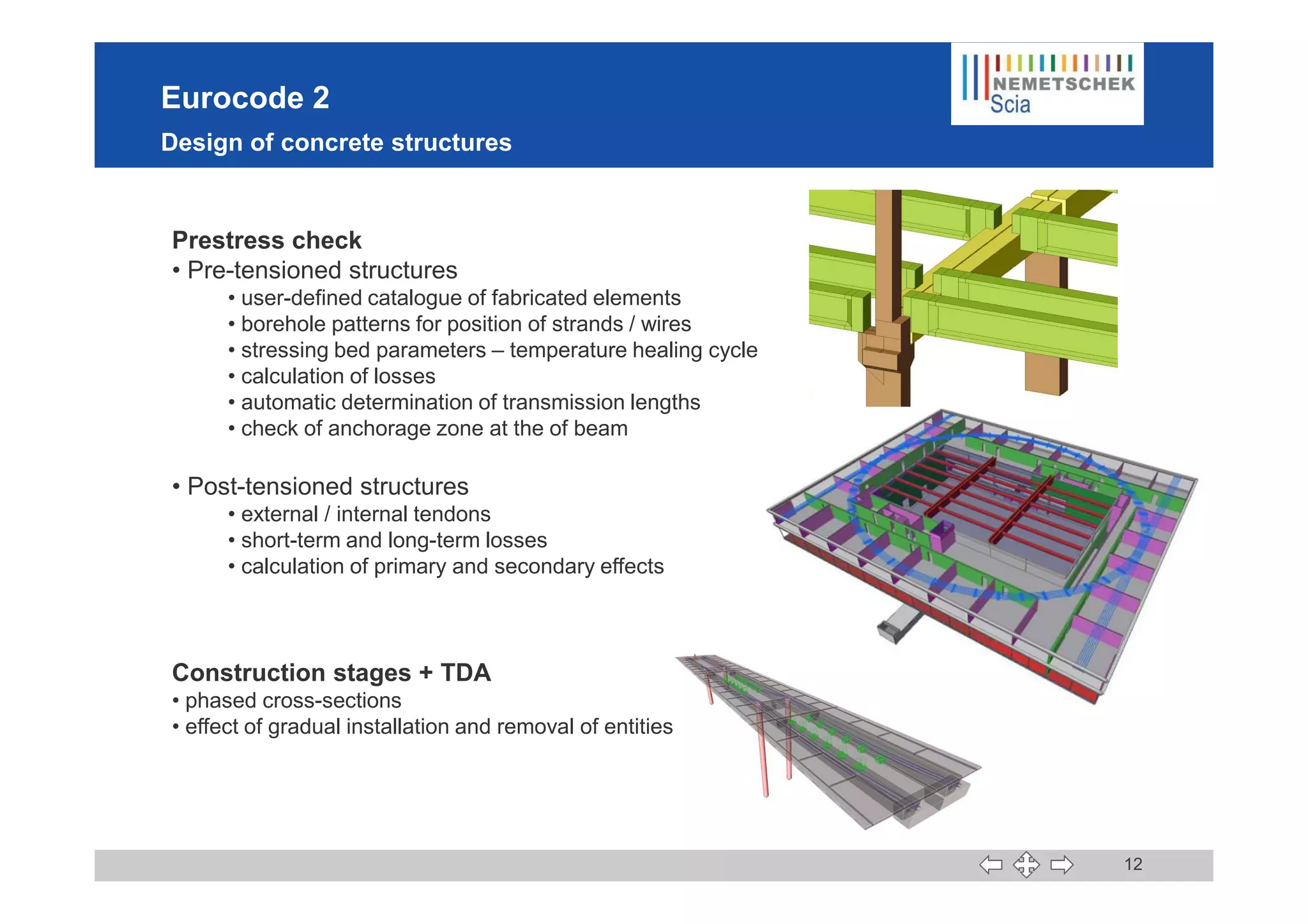
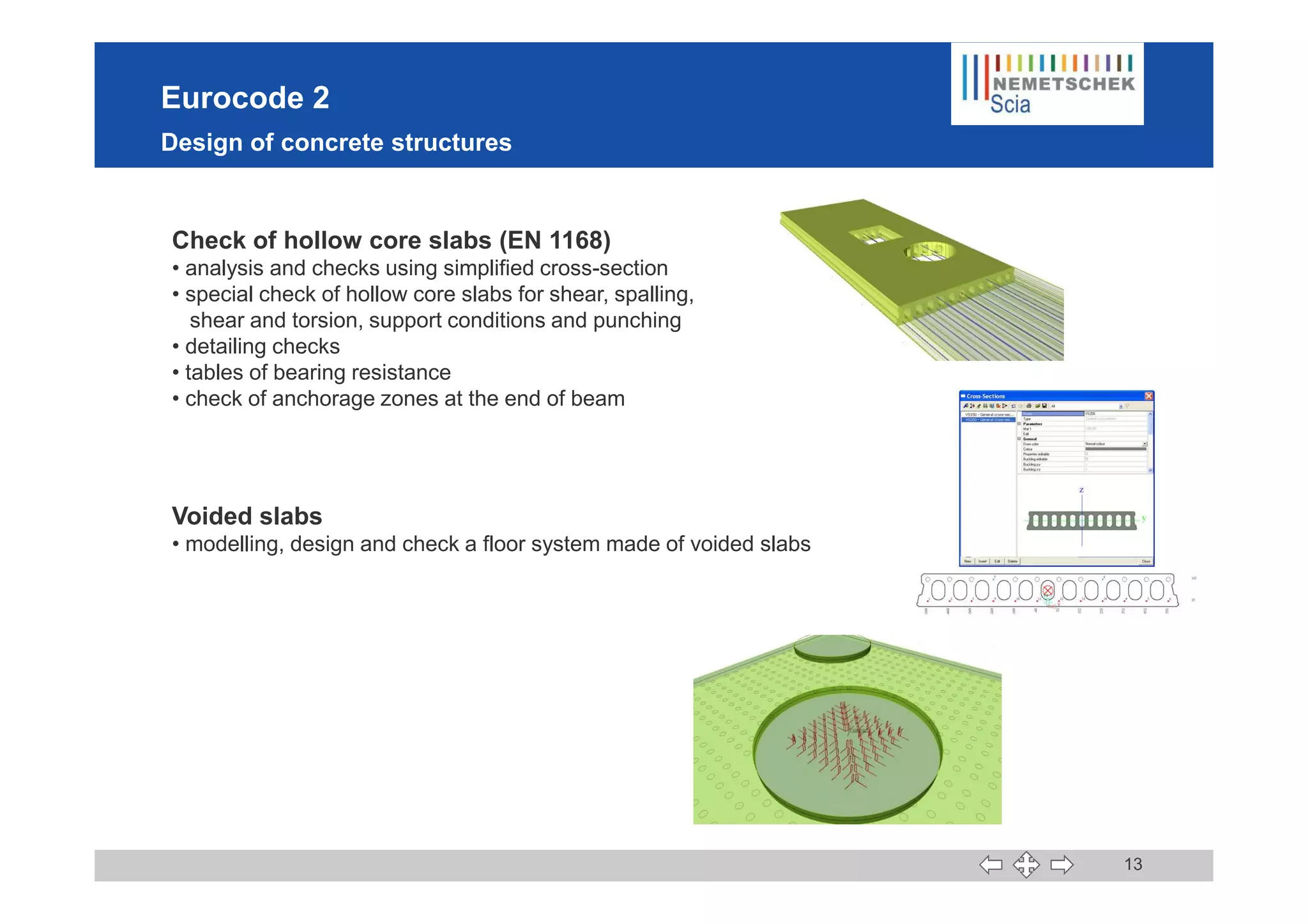
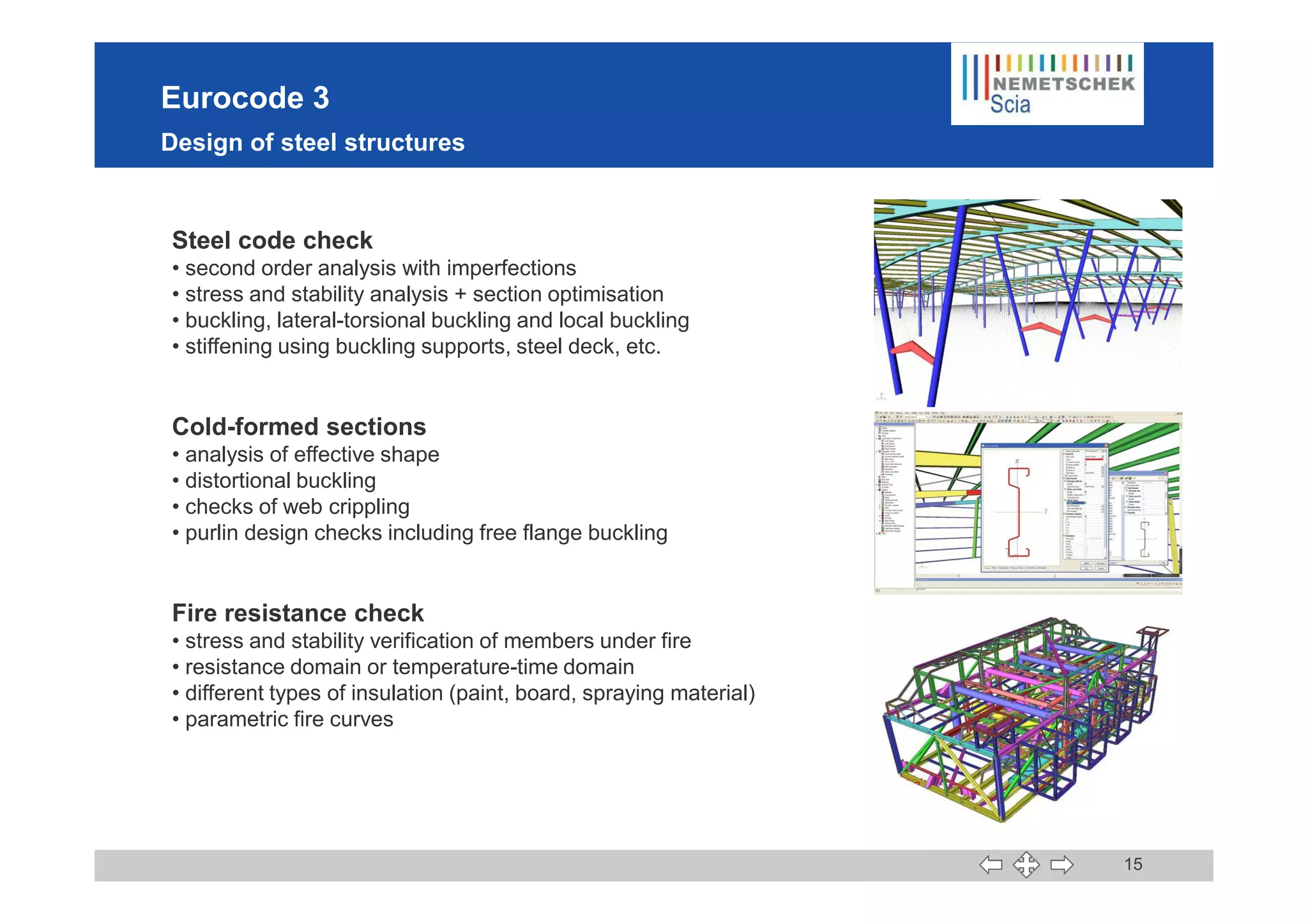
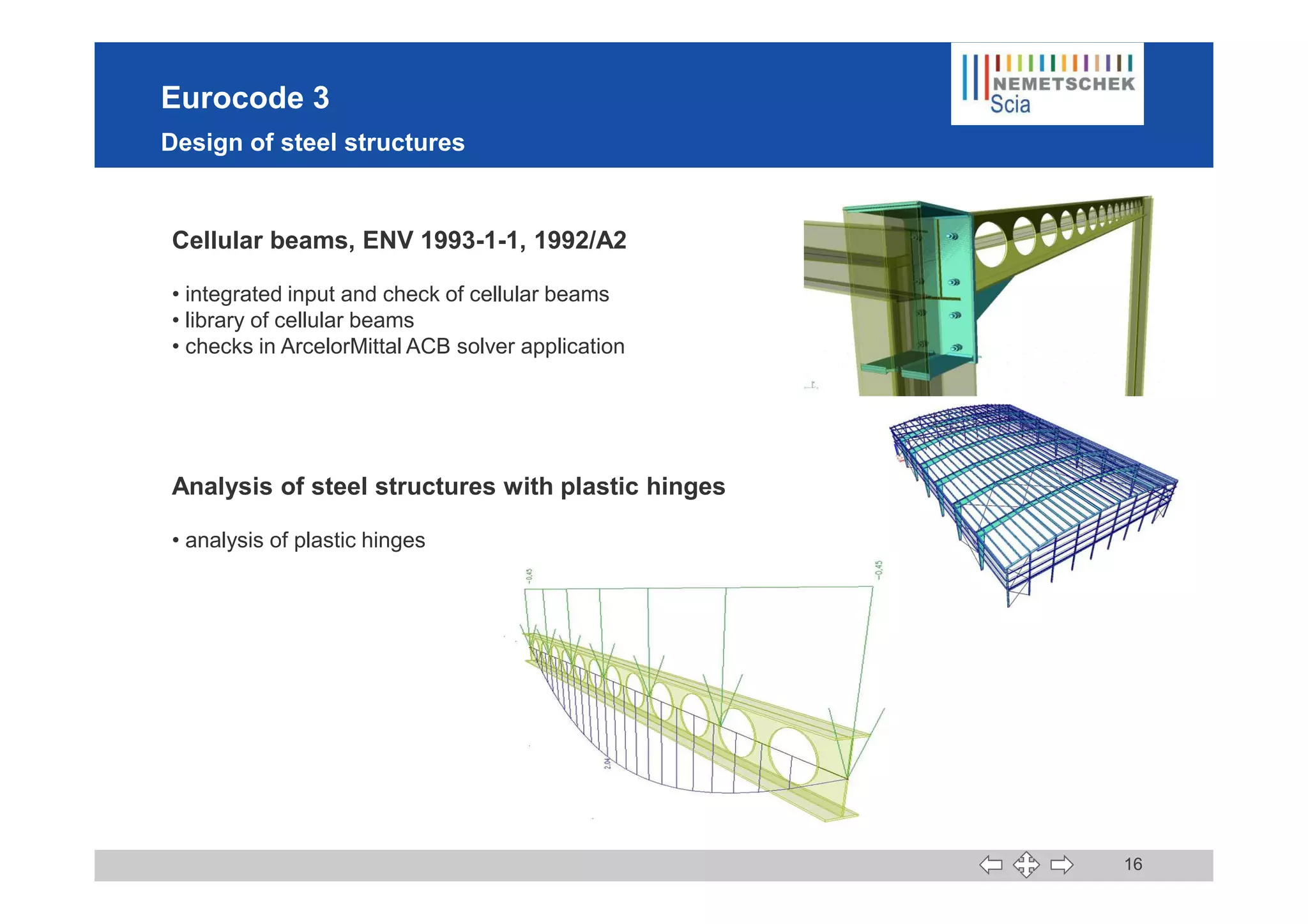
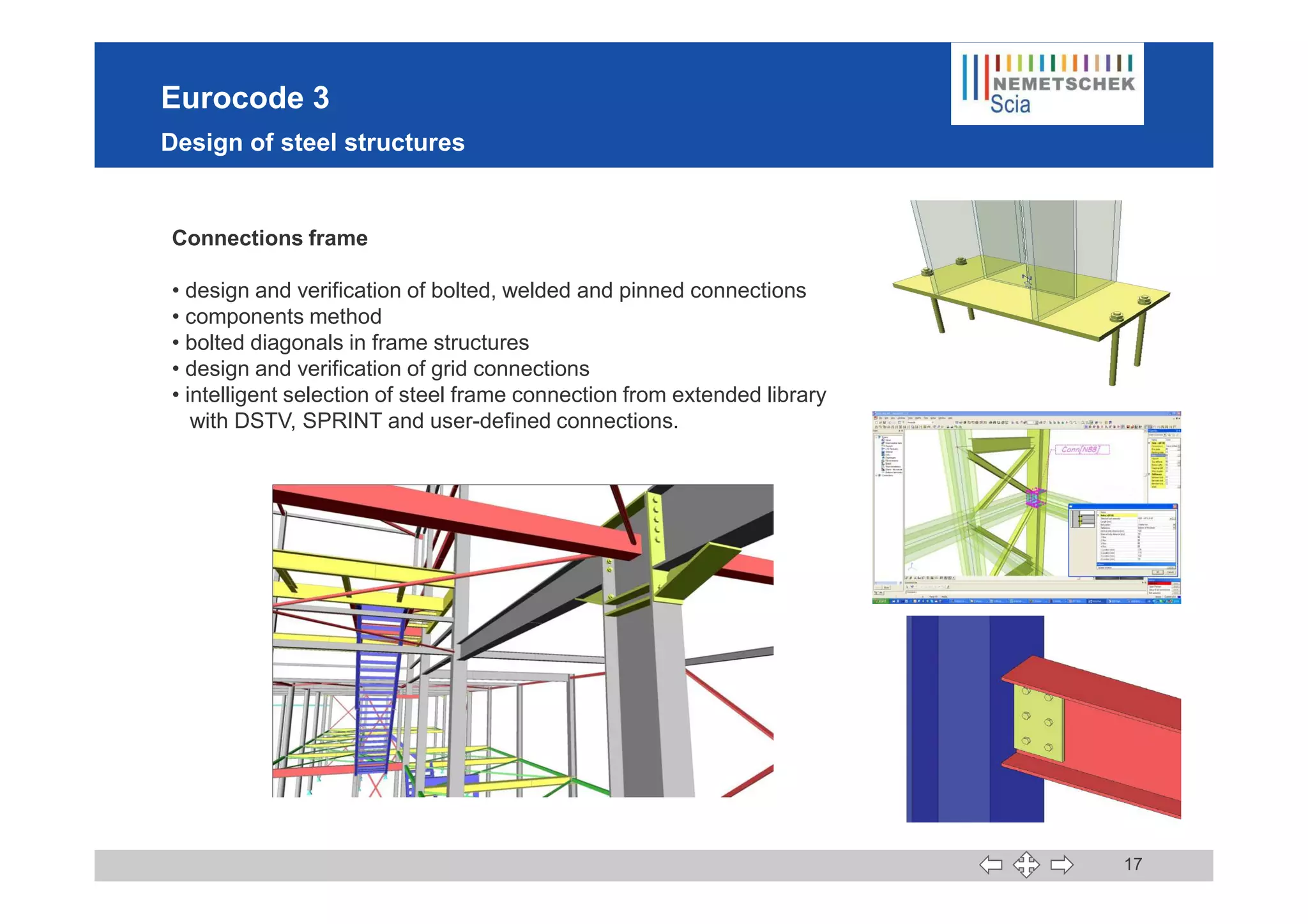
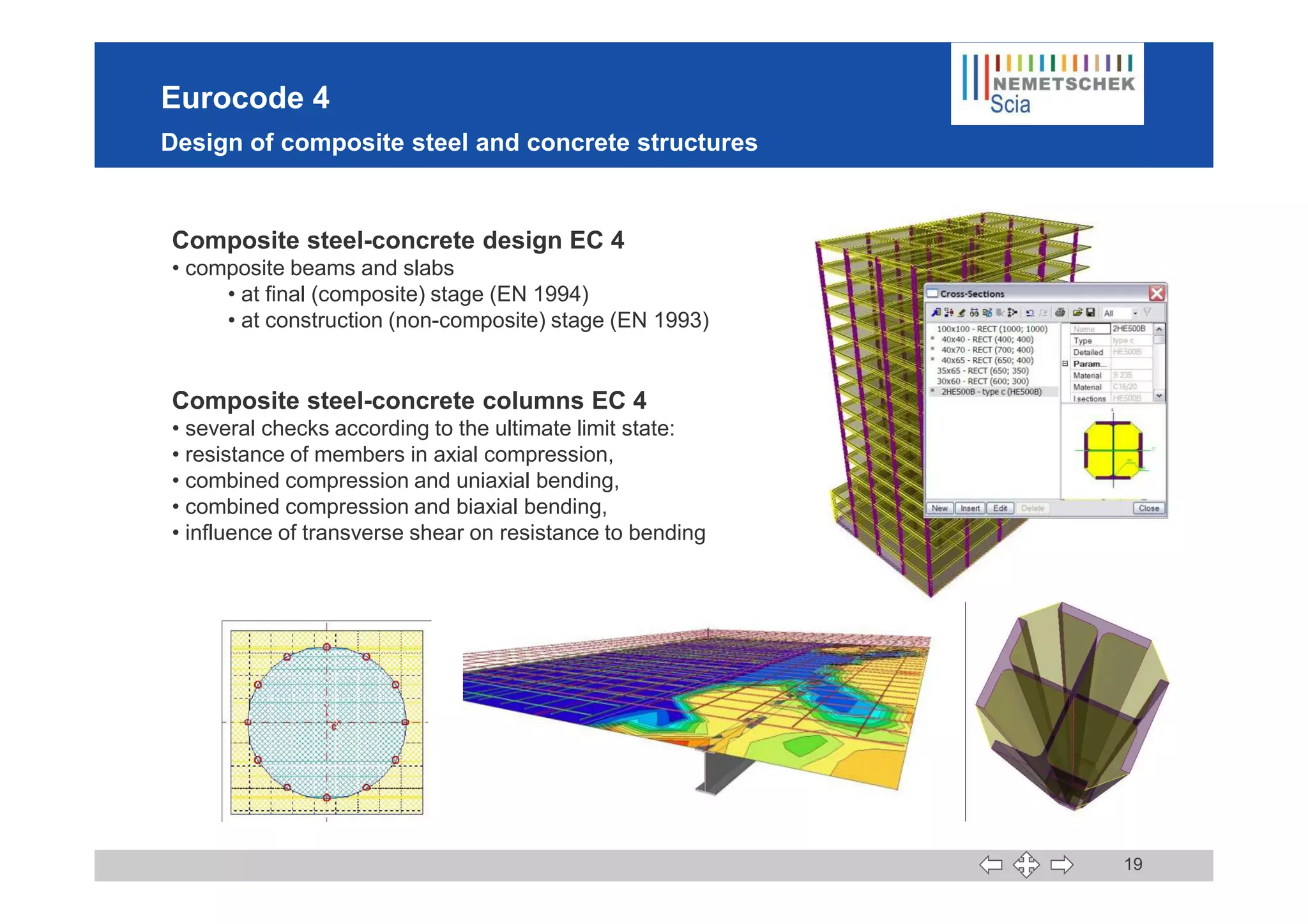
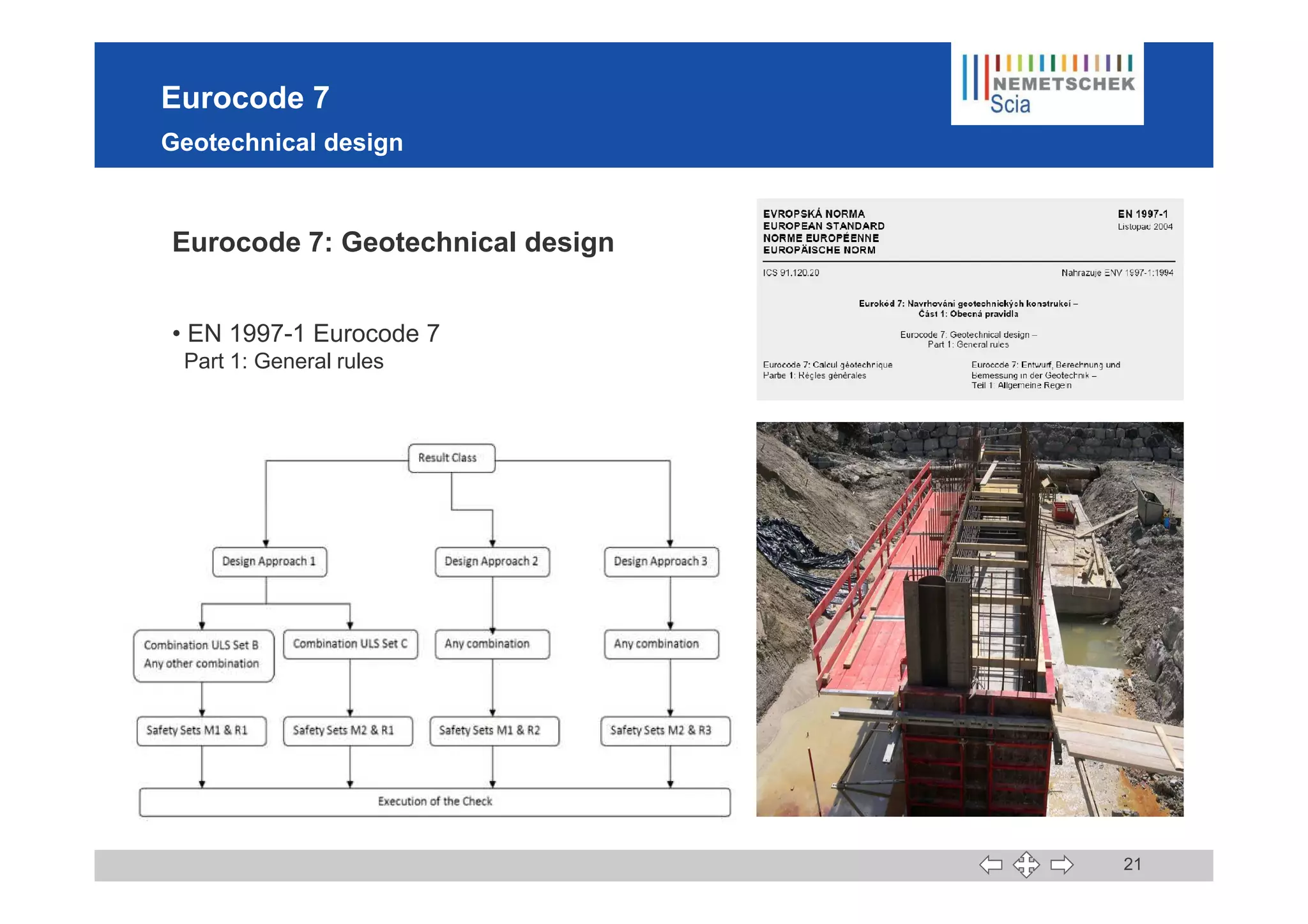
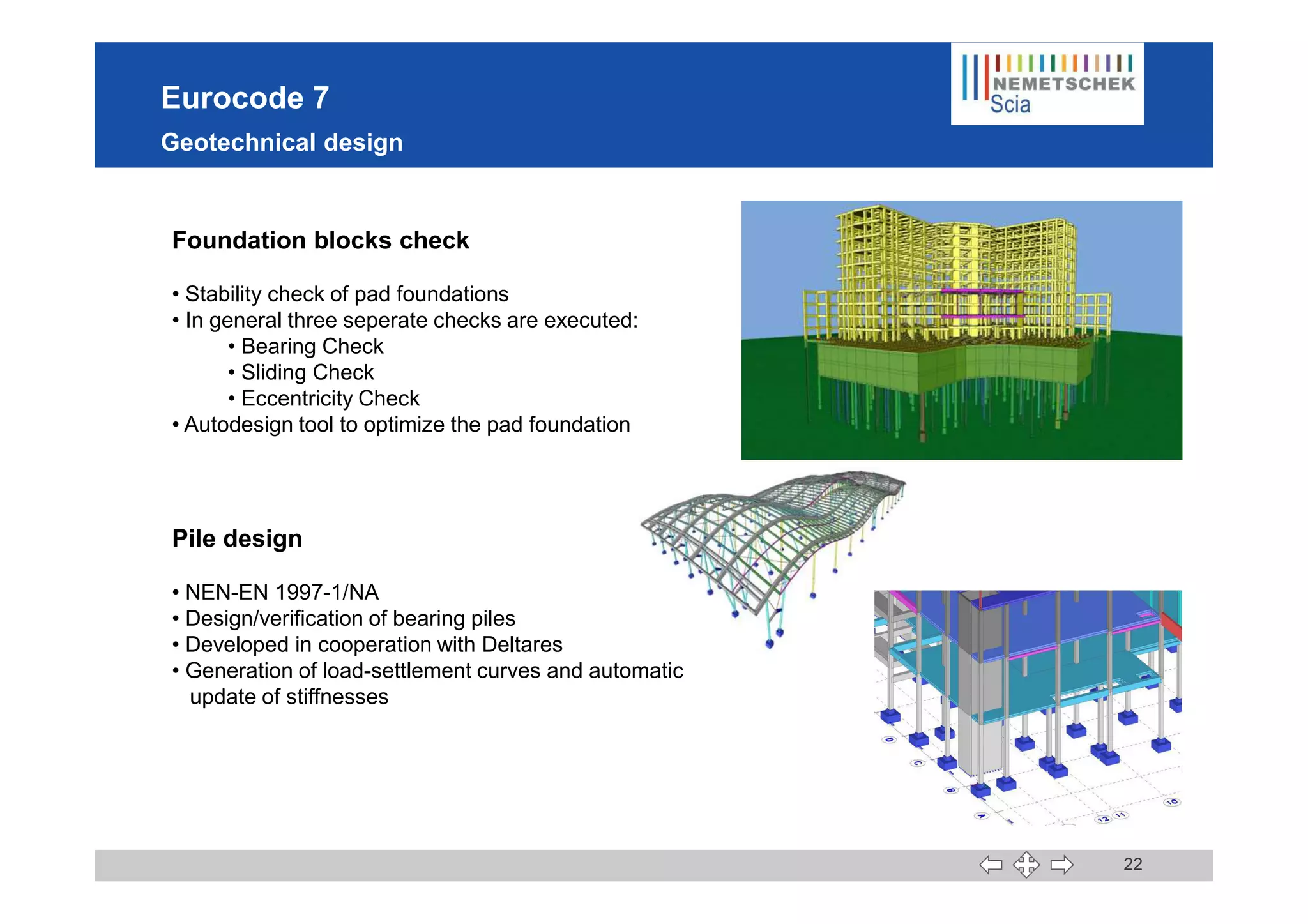
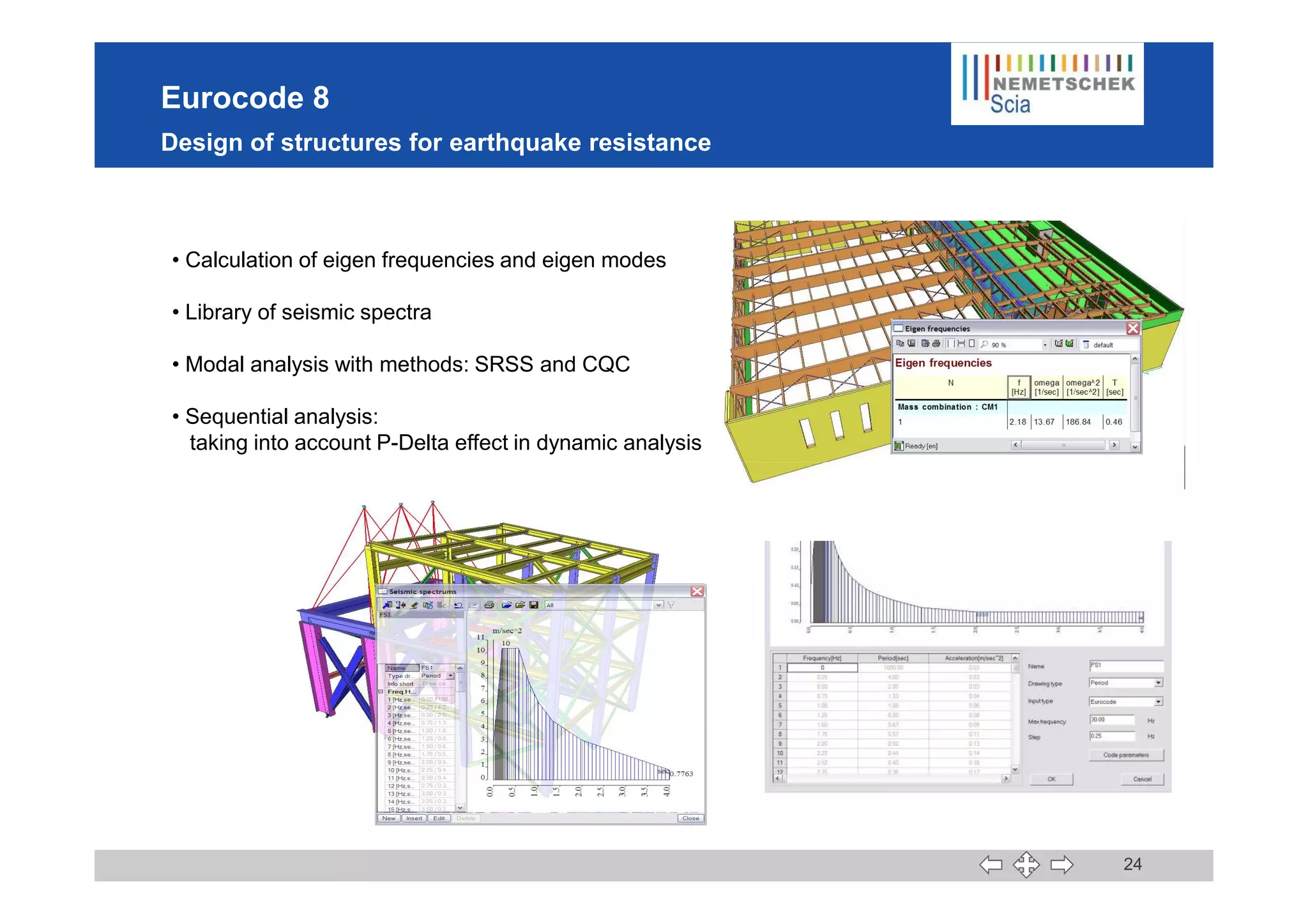
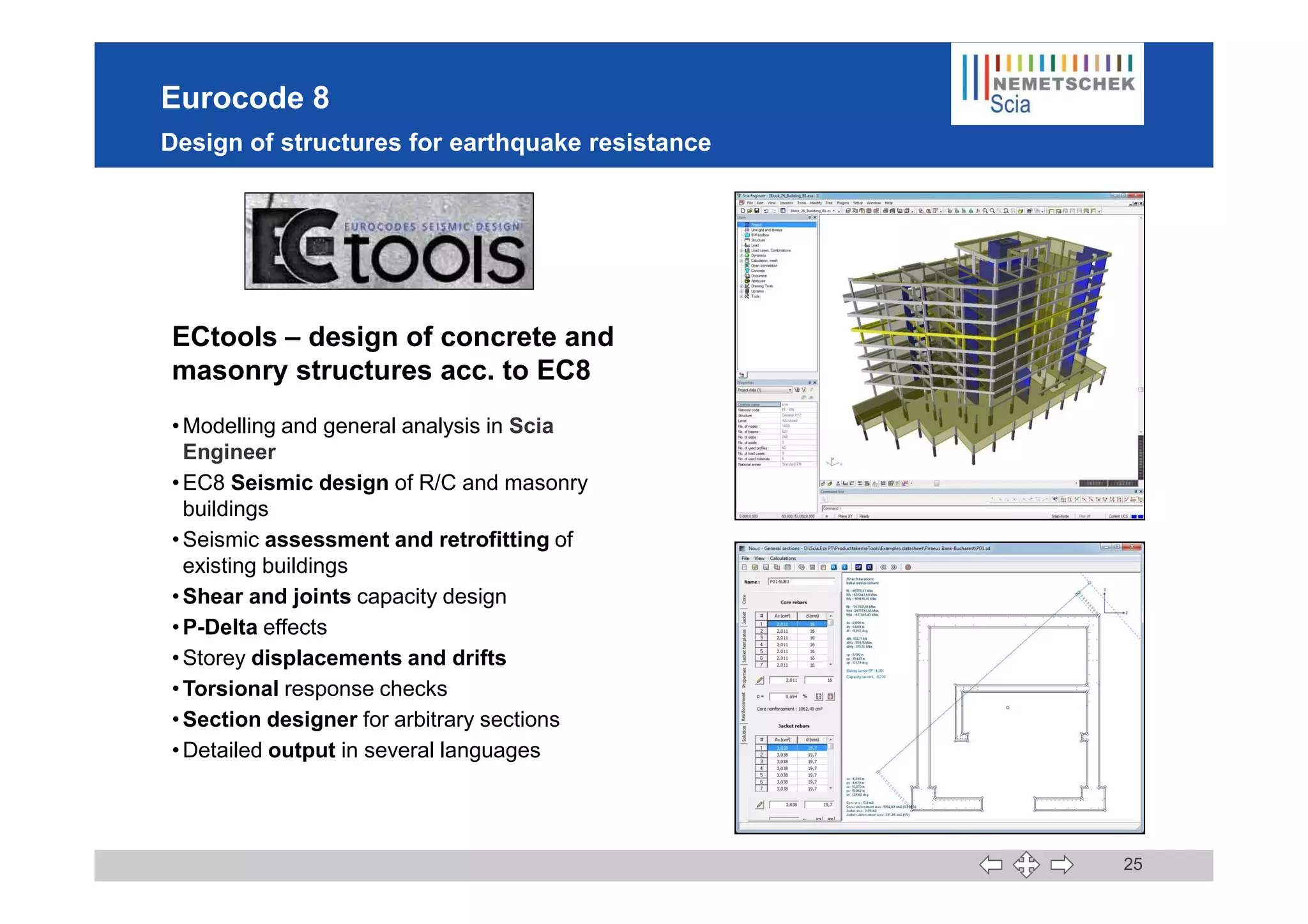
This document discusses the implementation of Eurocodes in the structural analysis software Scia Engineer. It summarizes that Scia Engineer allows for design in accordance with Eurocodes in 1D, 2D, 3D, and 4D. It has extensive experience implementing Eurocodes and participates in various Eurocode workgroups. Scia Engineer is certified for implementation of EC2 and EC3 and was found to be a best performer in commercial Eurocode software by the European Commission.