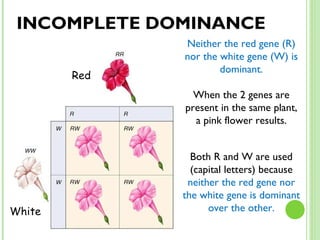
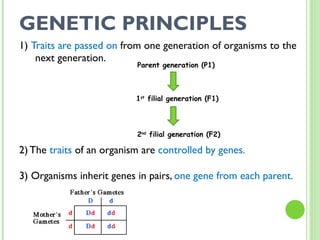
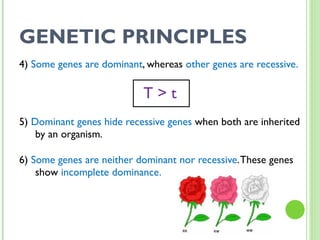
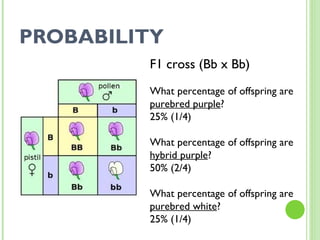
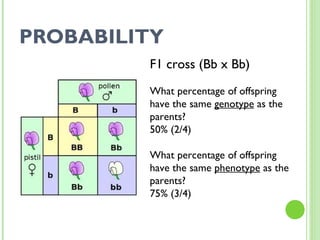
This document provides an introduction and review of genetics concepts for students. It includes definitions of key genetics vocabulary. It discusses Mendel's experiments with pea plants and the principles he developed including dominant and recessive traits, inheritance of traits from parents, and using Punnett squares to determine probability of offspring traits. It provides examples of problems involving incomplete dominance and probability. It assigns homework to complete practice problems and review class notes, and notifies students there is no homework over spring break.