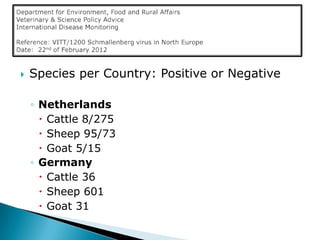
Schmallenberg virus is a new emerging livestock disease detected in several European countries. It causes late abortions and birth defects in newborn sheep, goats and cattle. In adult cattle it can cause mild fever, reduced milk yield, and diarrhea. The virus is transmitted by midges and first emerged in Germany and the Netherlands in 2011. Farmers are advised to report any suspicious cases.