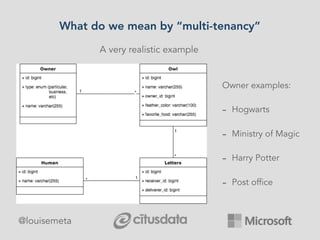
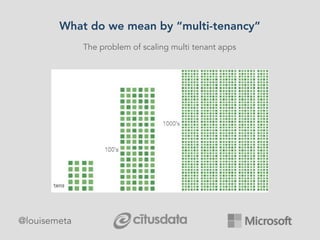
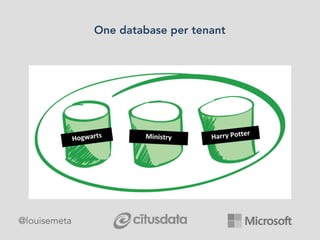
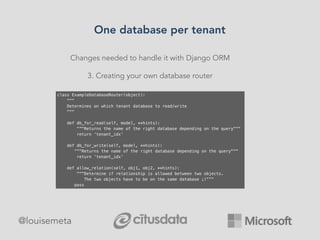
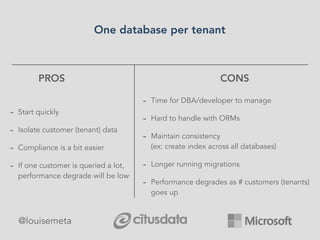
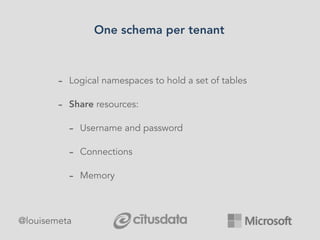
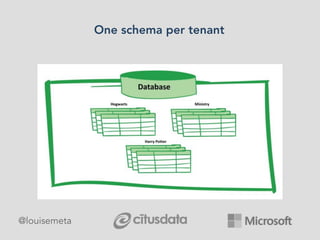
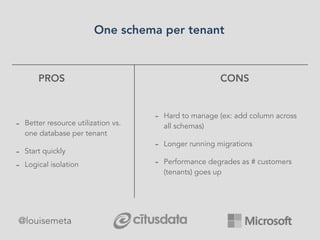
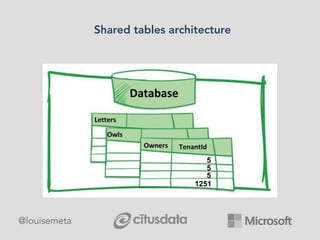
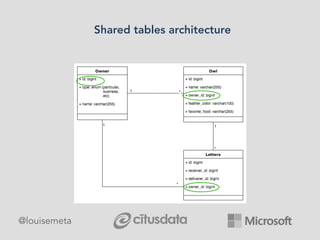
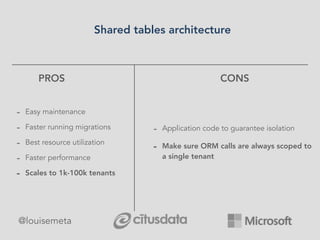
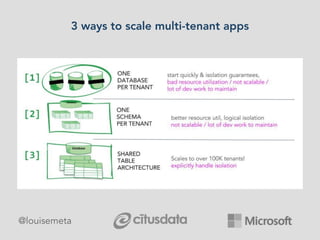
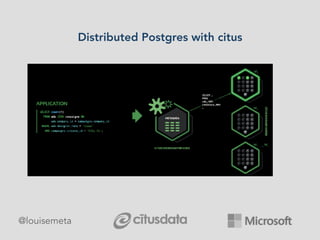
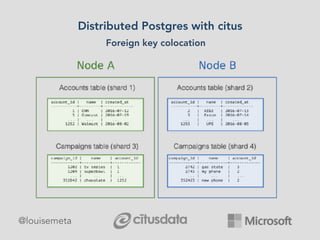
The document explores scaling multi-tenant applications using Django ORM and PostgreSQL, defining multi-tenancy and offering three solutions: one database per tenant, one schema per tenant, and shared tables architecture. It emphasizes the benefits and drawbacks of each approach, particularly focusing on the implementation of shared tables with Django-Multitenant for efficient tenant isolation. Additionally, it highlights the advantages of using PostgreSQL and the Citus extension for distributed architecture to enhance scalability.