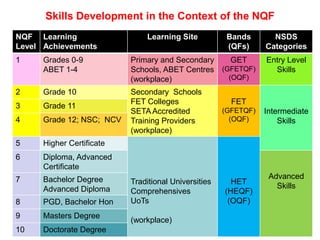
UoTs can play an important role in developing high-level skills in South Africa. Policies call for improving skills to support economic growth and address skills shortages. UoTs are well-positioned to develop skills through responsive career-focused programs, cooperative education with industry, and applied research. UoTs can offer certificates, diplomas, and degrees to broaden access and support applied knowledge production. Strategic partnerships with industry, FET colleges, and governments further skills development through curriculum collaboration, research, and work-based learning opportunities. UoTs face challenges in balancing qualifications, developing articulation pathways, promoting interdisciplinarity, and focusing on attributes like innovation and entrepreneurship.