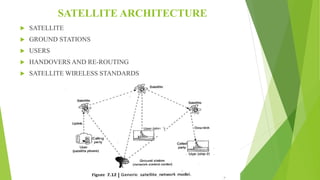
The document provides an overview of satellite networks, detailing the types of orbits: Low Earth Orbit (LEO), Medium Earth Orbit (MEO), and Geosynchronous Earth Orbit (GEO). It covers the characteristics and applications of each orbit type, including their advantages and disadvantages, as well as features of satellite communication such as coverage and security. Additionally, it addresses various applications of satellite networks, such as weather forecasting and navigation.