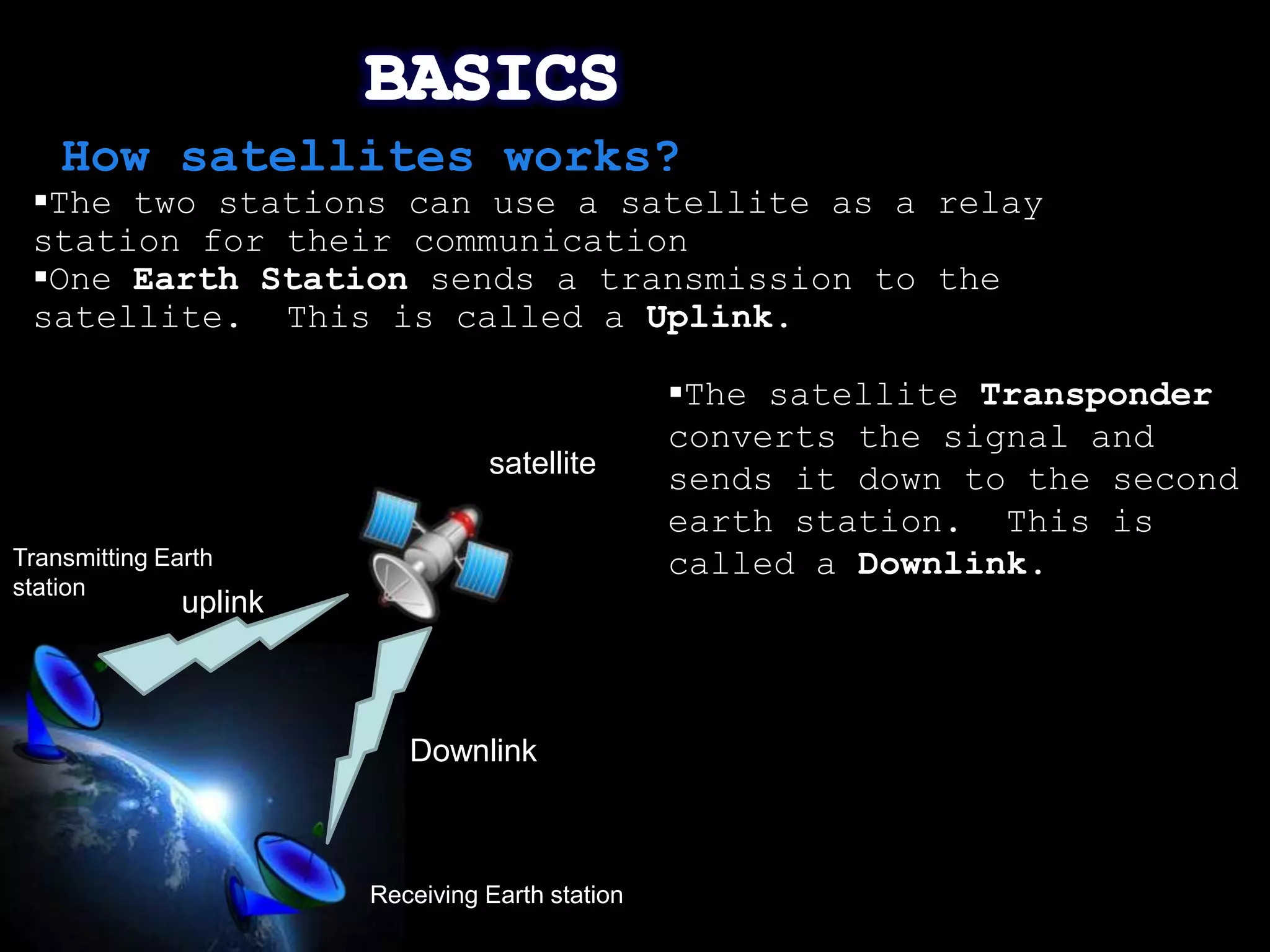
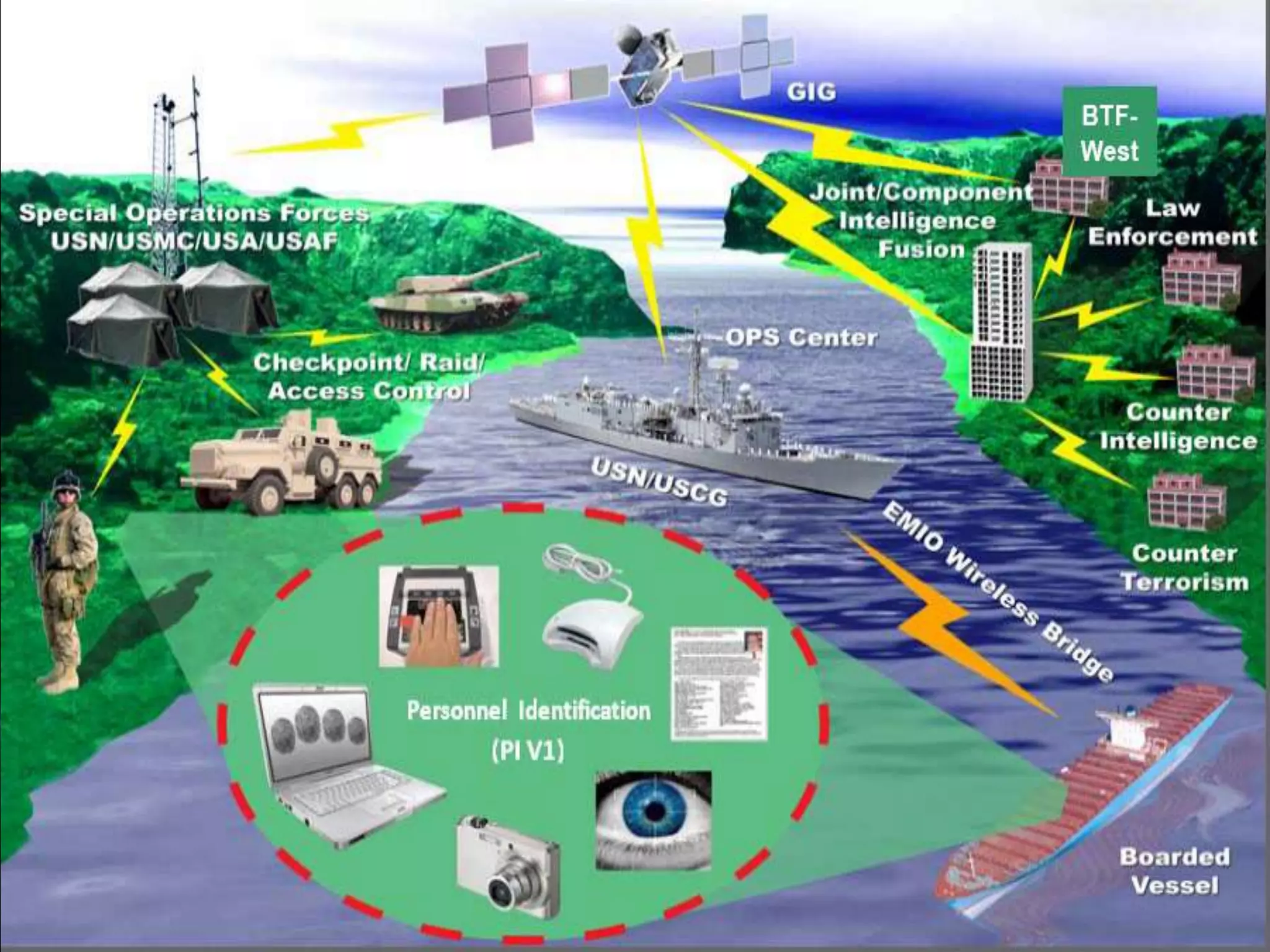
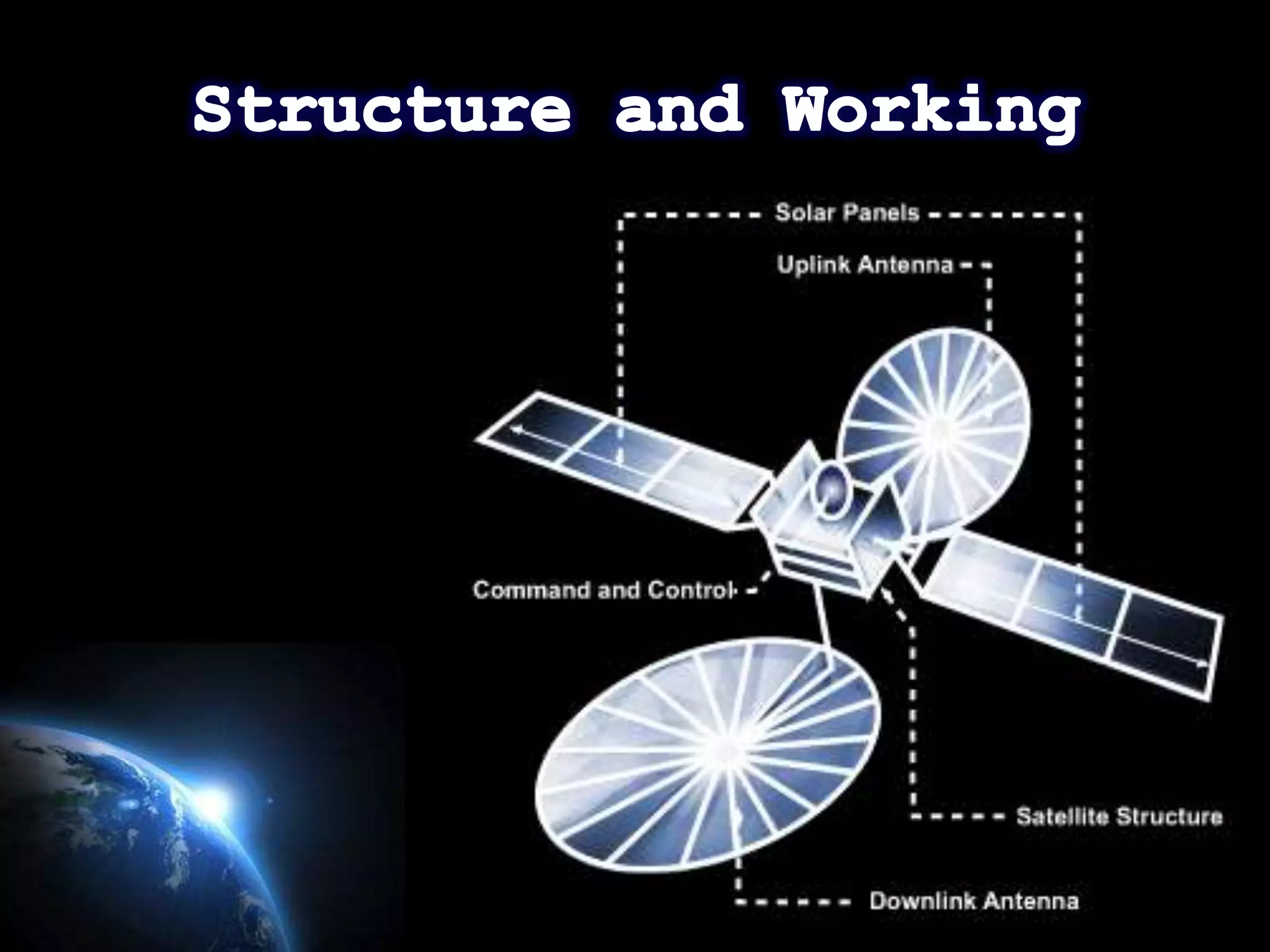
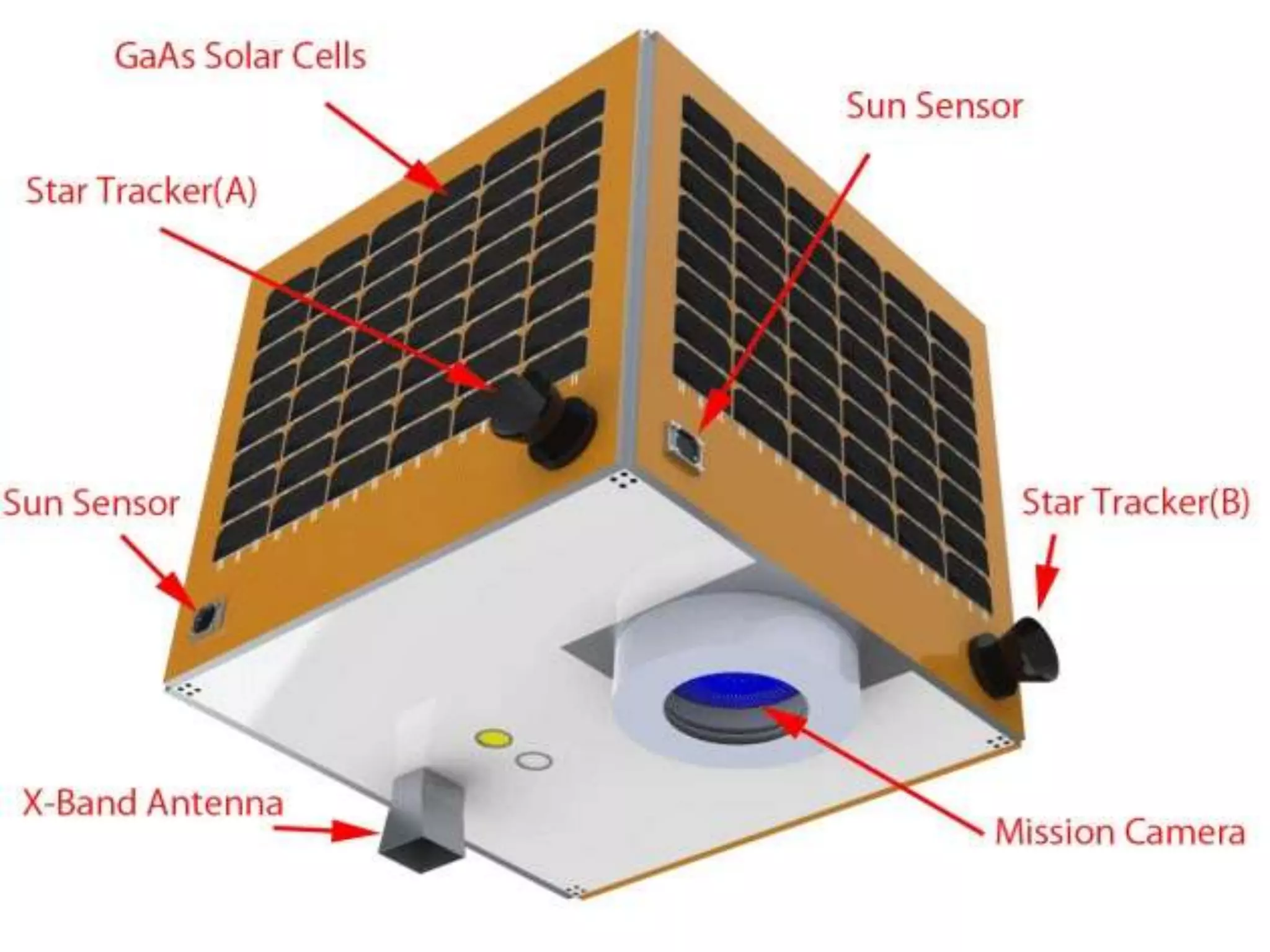
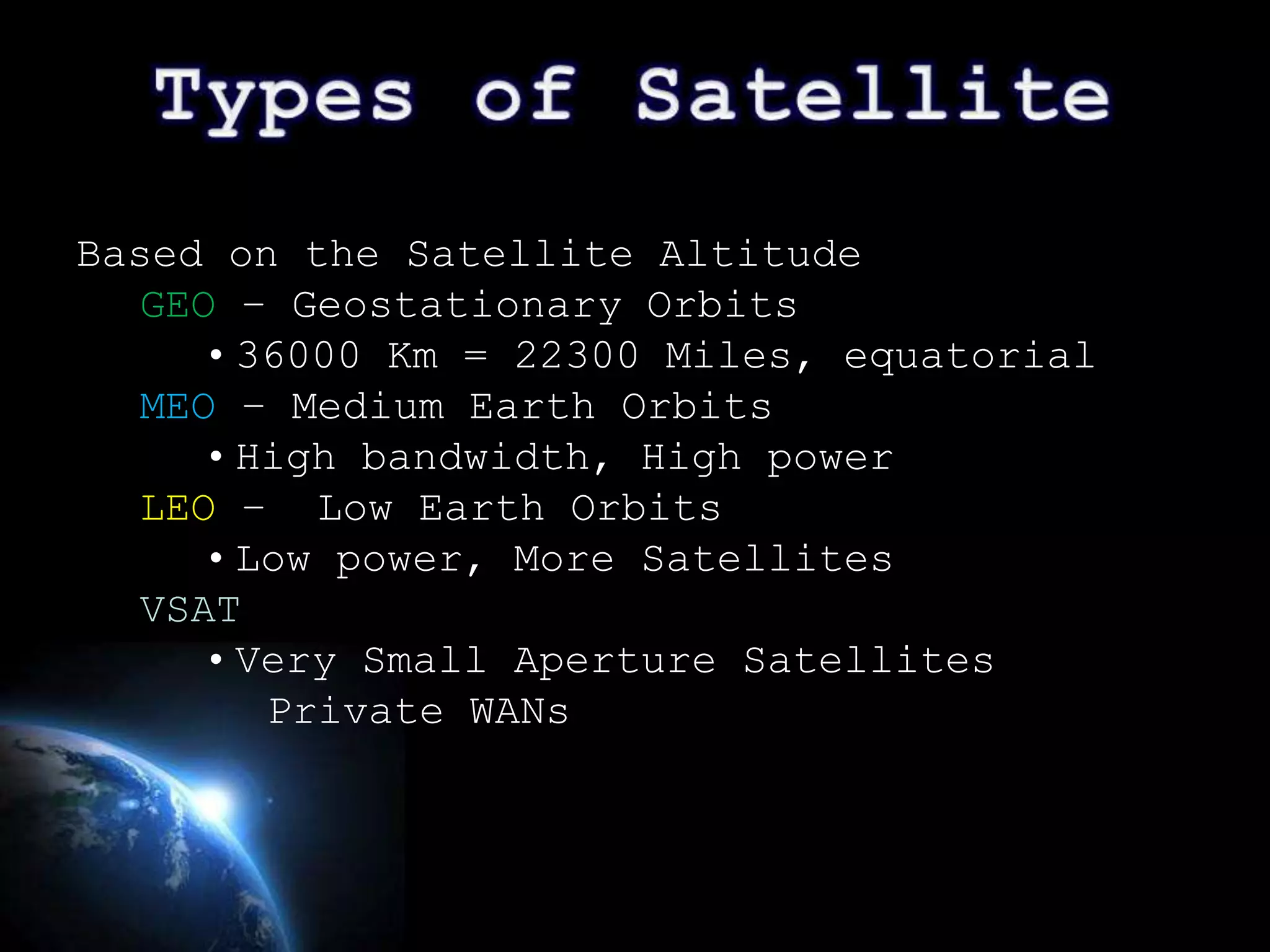
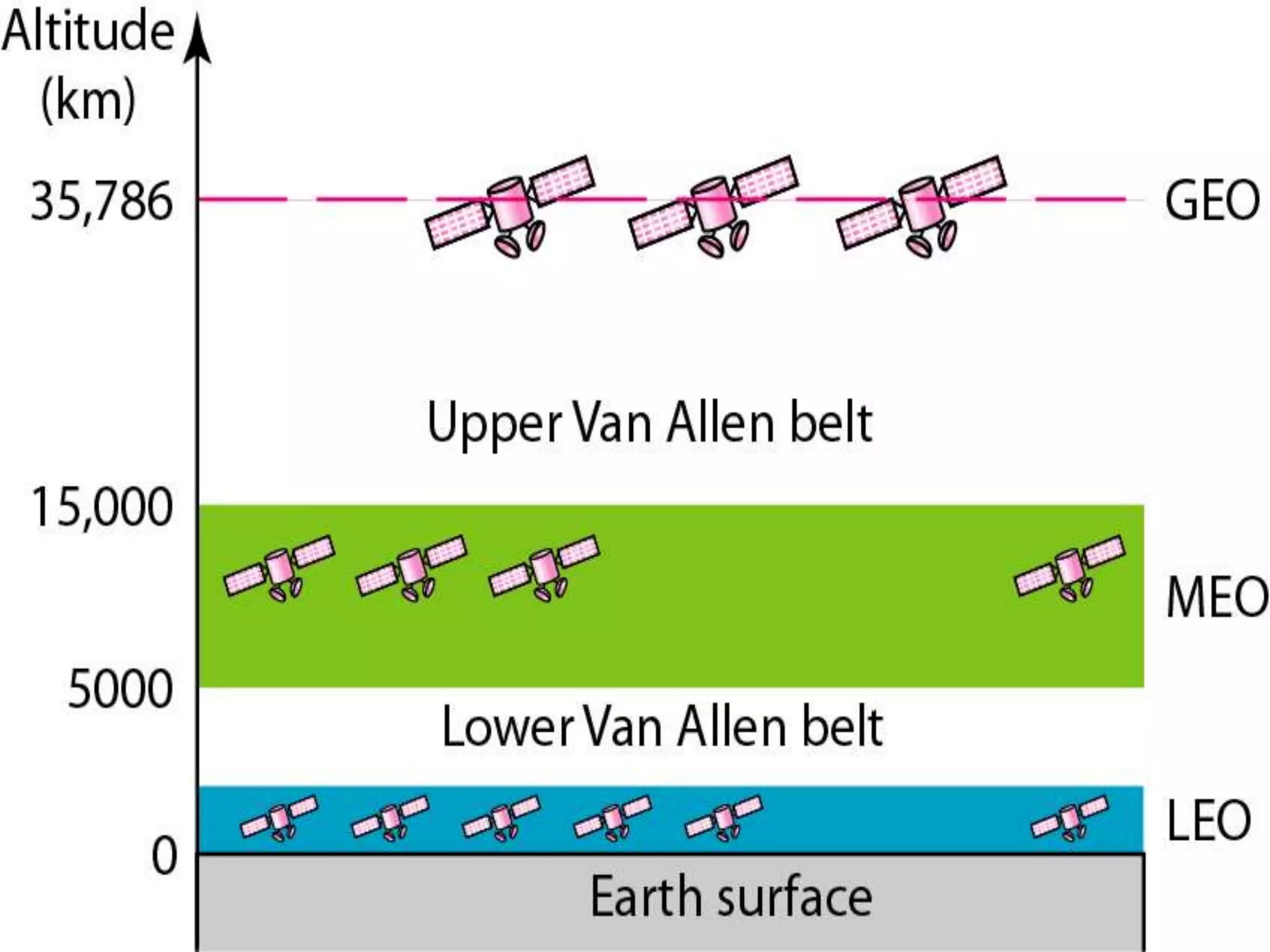
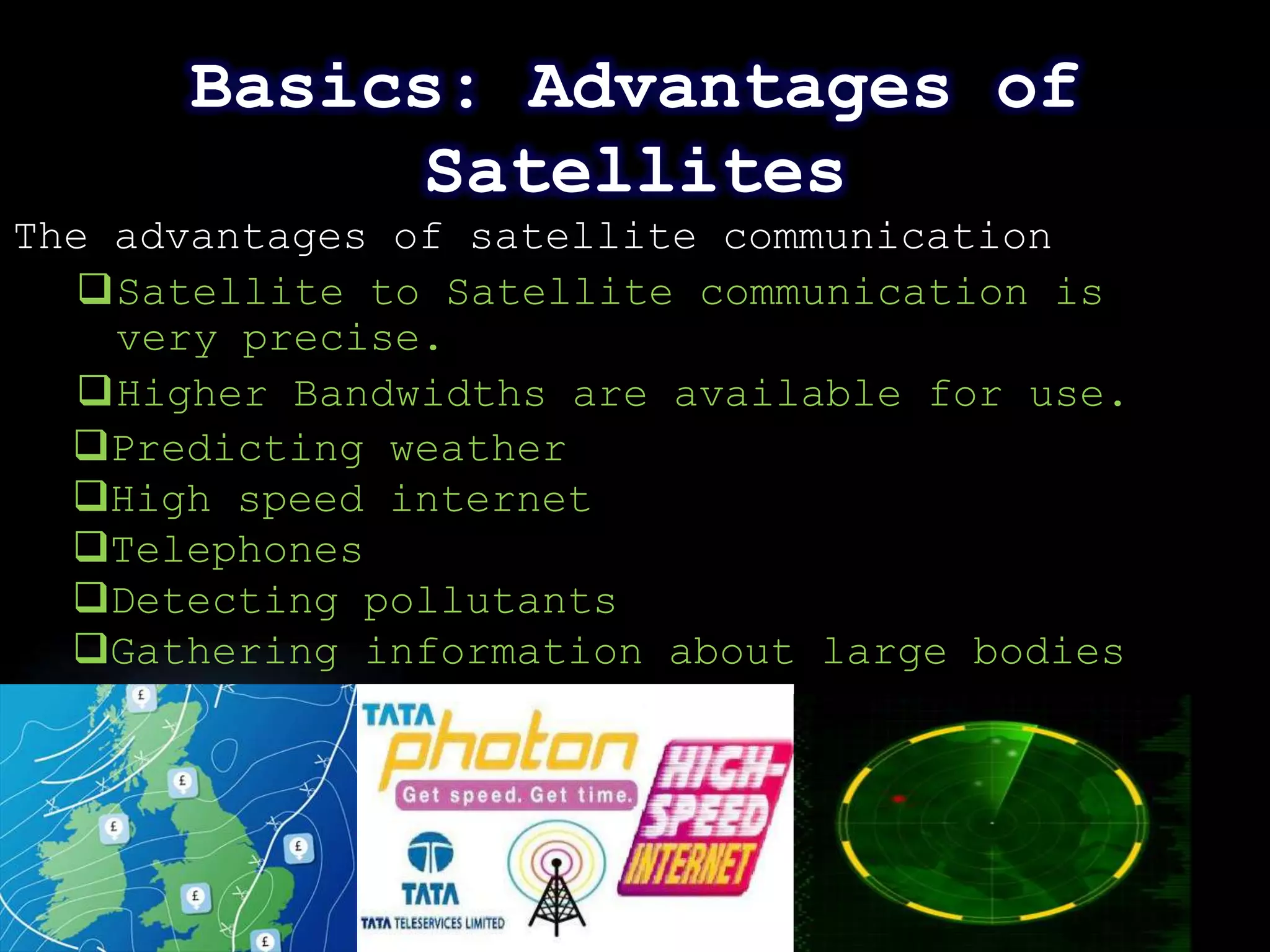
This document provides an overview of the history of satellite communication. It discusses early satellites like Sputnik 1, the first artificial satellite launched by the Soviet Union, and Telstar 1, the first to transmit transatlantic television signals. It also mentions Intelsat and the introduction of geosynchronous orbit. The document then discusses the basics of how satellite communication works and the advantages it provides like global coverage and high bandwidth. Some disadvantages like cost and signal delay are also noted. Contact information is provided at the end.