Embed presentation
Downloaded 48 times




















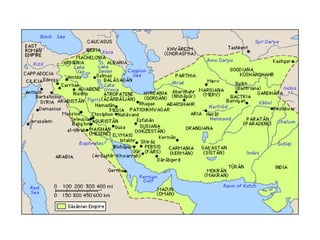






























The Sasanian Empire lasted from 224-651 AD in Persia and was the last native Persian empire before the Arab conquest. It was founded by Ardashir I after the collapse of the Parthian Empire and Zoroastrianism was established as the state religion. Major Sasanian rulers included Shapur I, Shapur II, and Khosrau I who expanded the empire through military campaigns. The empire declined in the 7th century due to overextension and wars with the Byzantine Empire, leading to its final defeat and collapse when Arab Muslims conquered Persia in the 630s-640s.




















































