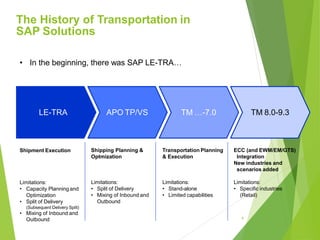
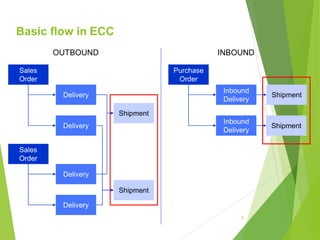
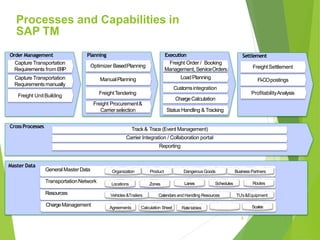
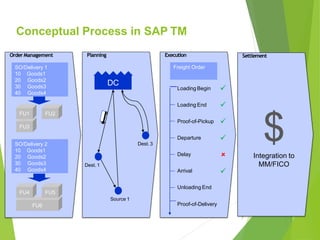
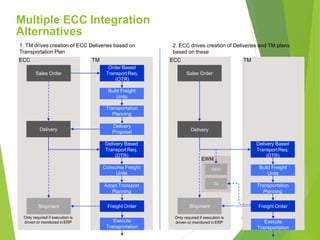
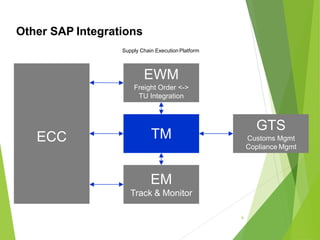
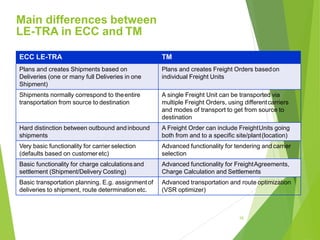
This document provides an introduction to SAP TM for Shippers. It discusses the history and evolution of transportation management in SAP solutions. It describes the basic inbound and outbound flows in ECC and the key processes and capabilities in SAP TM for planning, execution, and settlement. It presents the conceptual process flow in TM and discusses the different integration alternatives with ECC. It also outlines some of the other SAP integrations with TM and highlights the main differences between LE-TRA and SAP TM. Finally, it covers some key considerations around integration, master data, transportation requirements, freight units, and takeaways about SAP TM.