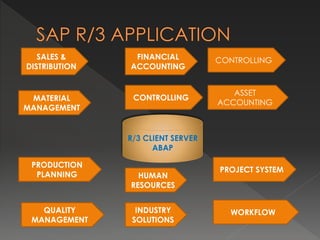
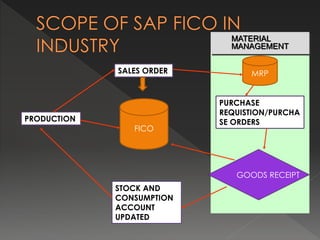
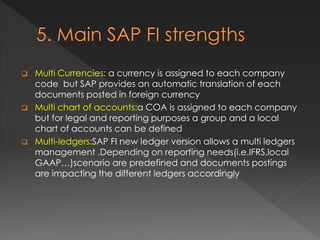
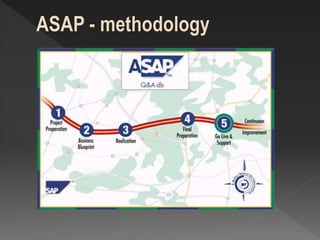
SAP is a large enterprise software company that provides an integrated business software package called SAP R/3 to help integrate key areas of a business like finance, sales, manufacturing, and human resources. SAP FI is SAP's financial management module that allows companies to manage accounting, payables, receivables, and other financial processes in a centralized, integrated manner. It uses real-time processing, multi-currency and language support, and is designed for global enterprises. Implementing SAP involves preparing the business needs, documenting current processes, configuring the system, testing, training users, and going live supported by the implementation team.