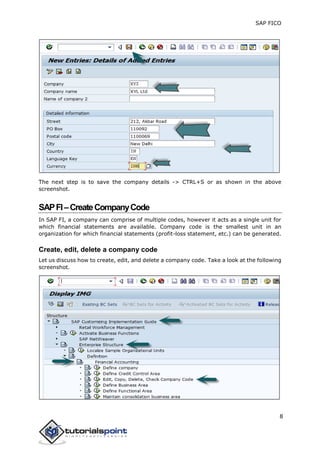
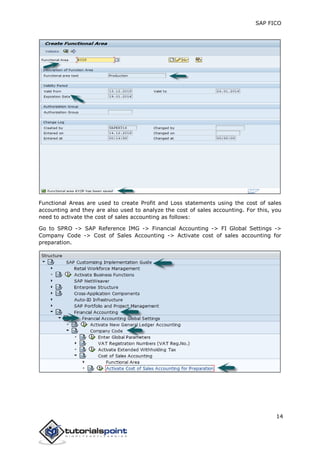
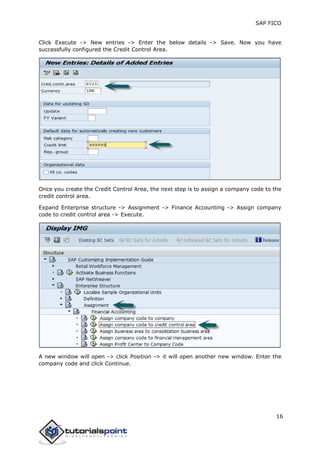
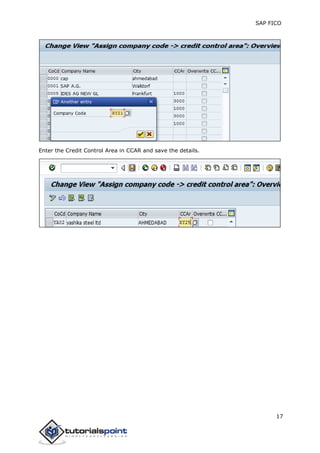
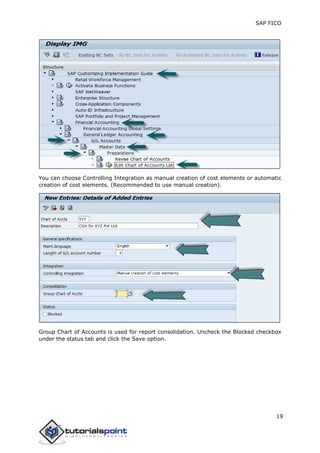
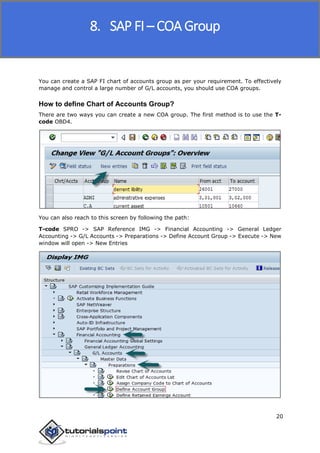
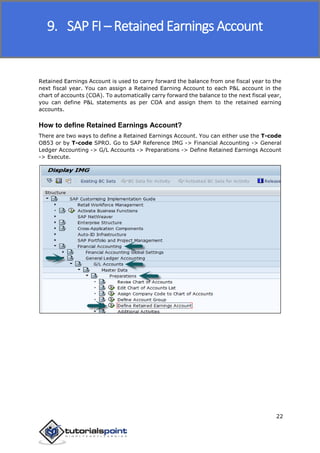
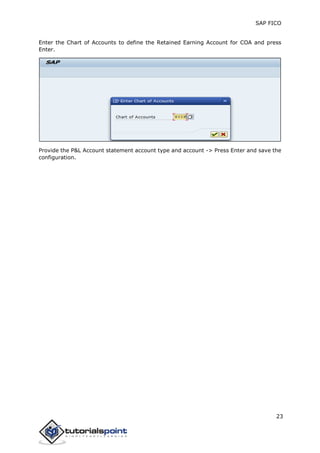
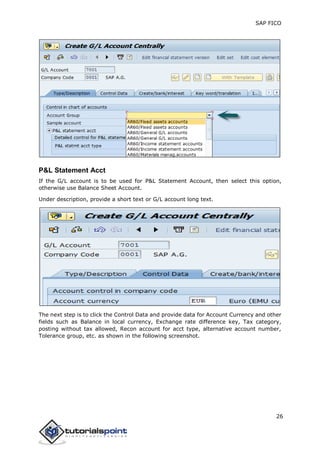
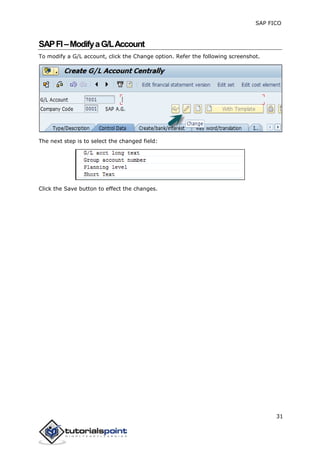
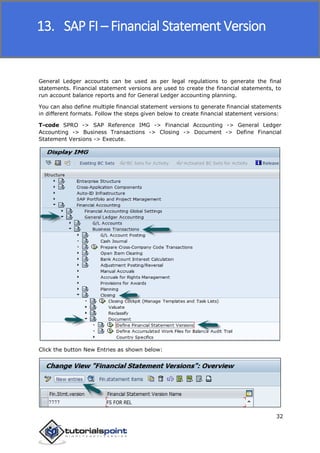
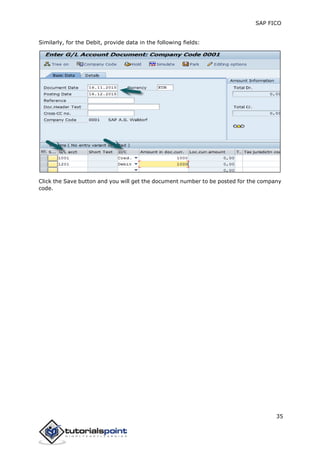
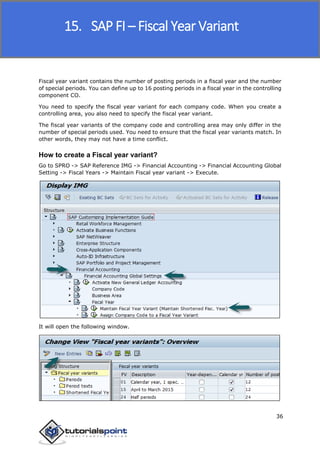
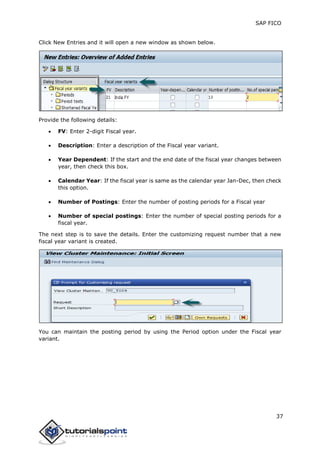
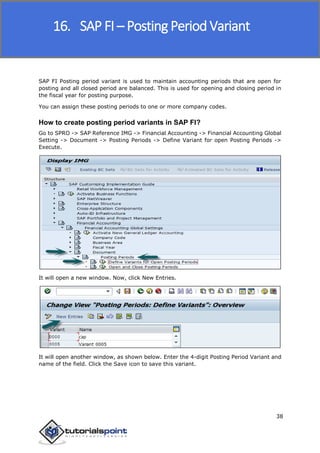
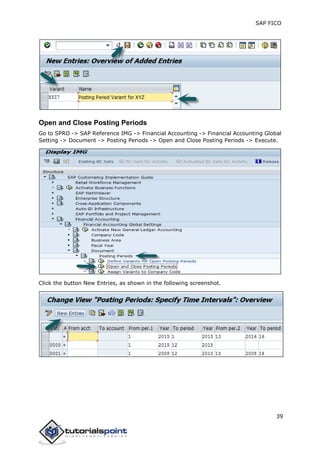
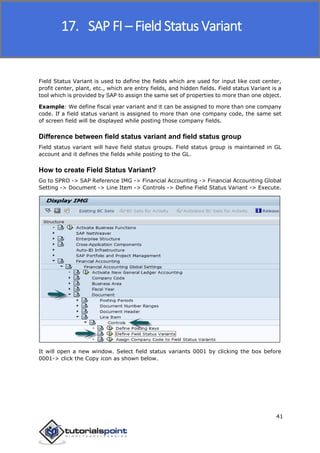
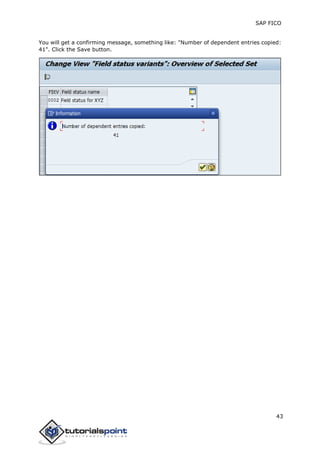
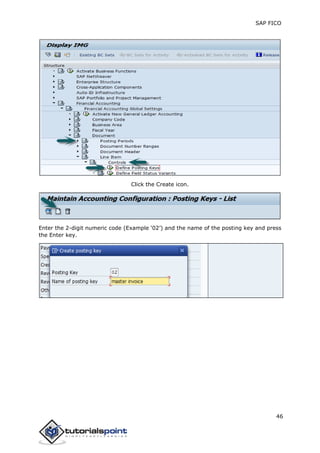
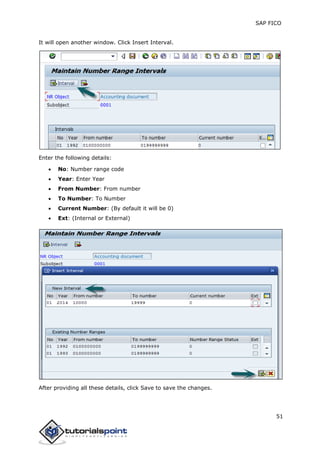
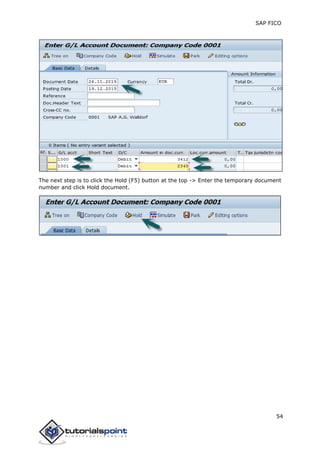
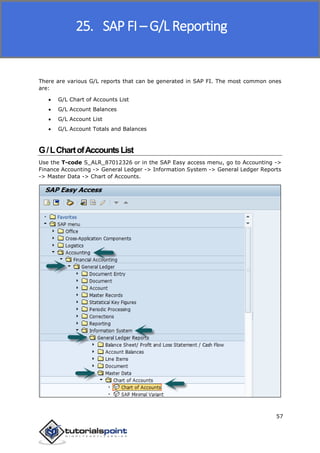
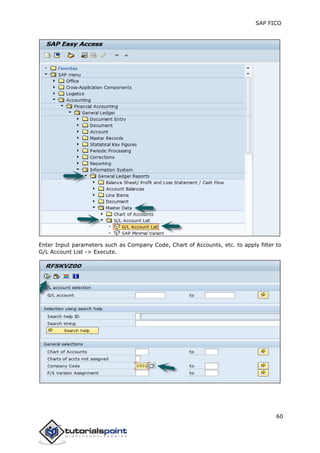
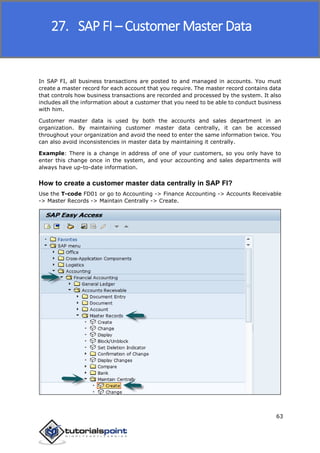
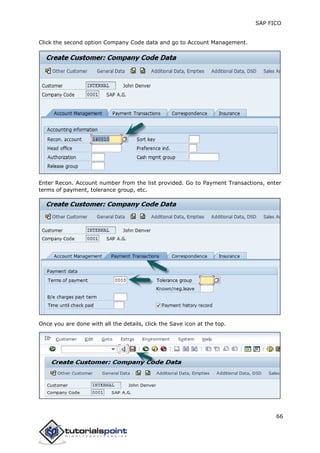
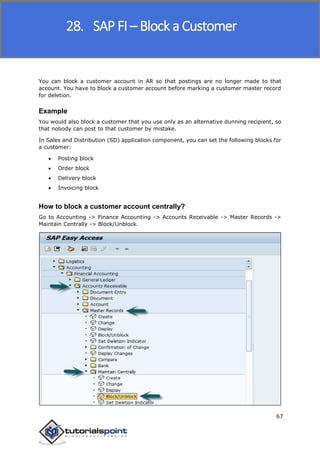
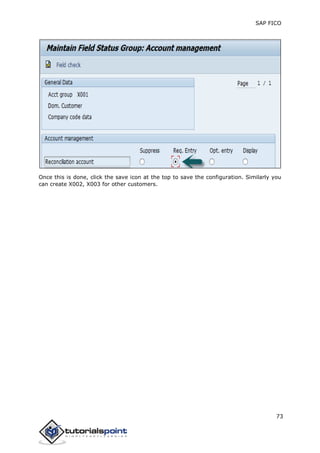
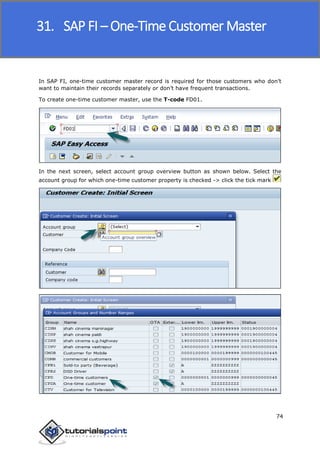
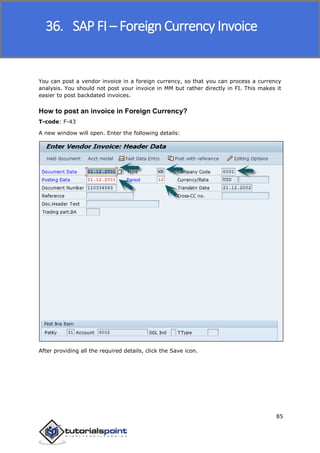
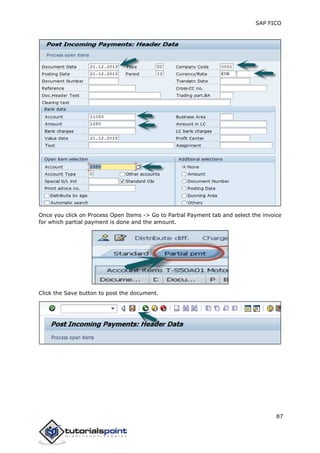
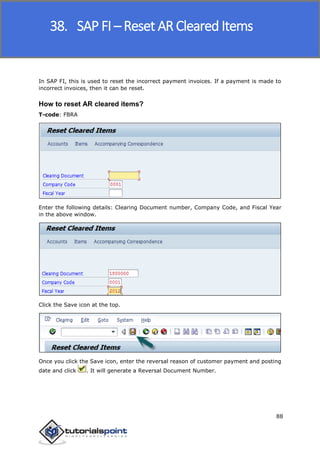
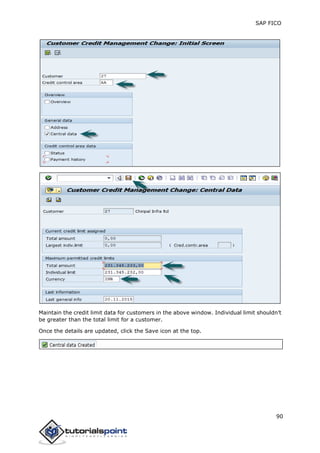
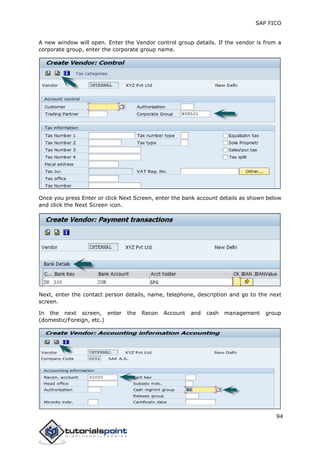
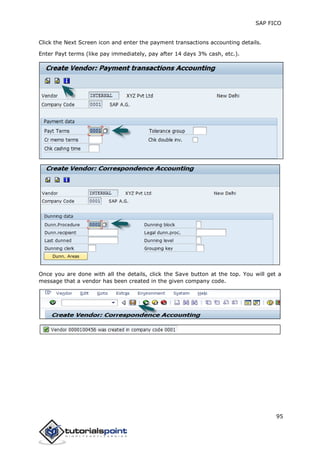
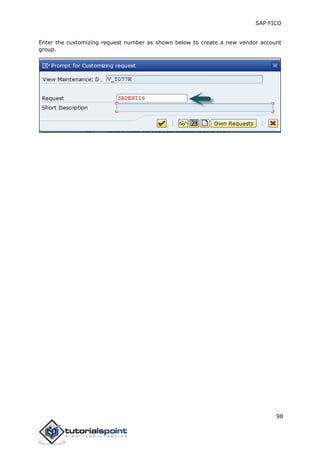
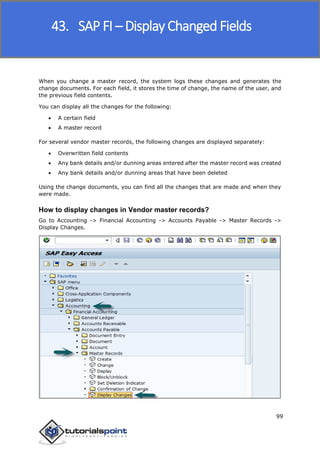
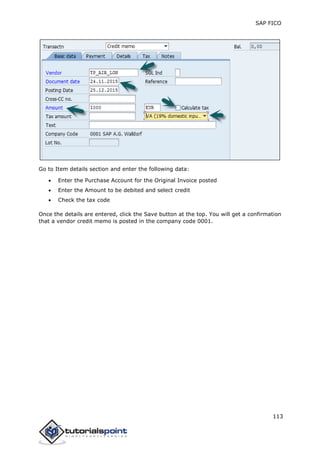
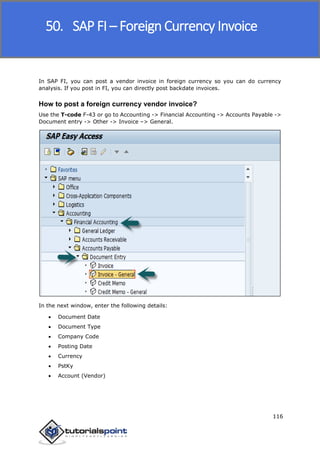
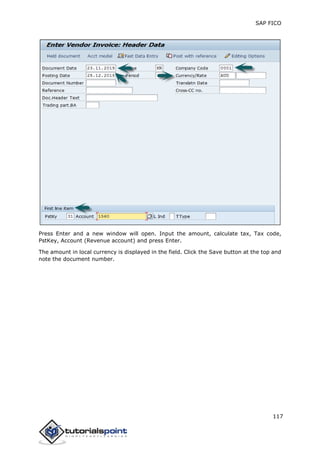
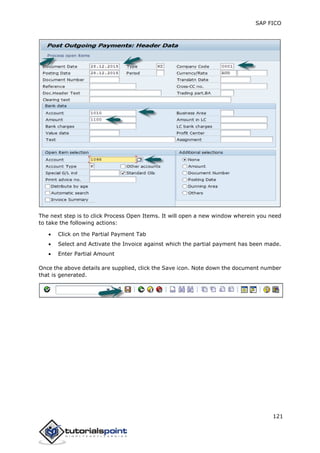
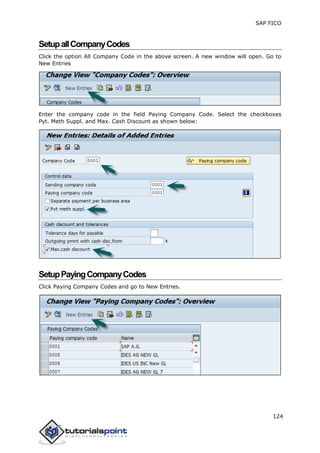
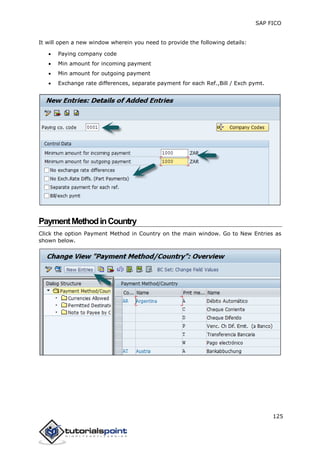
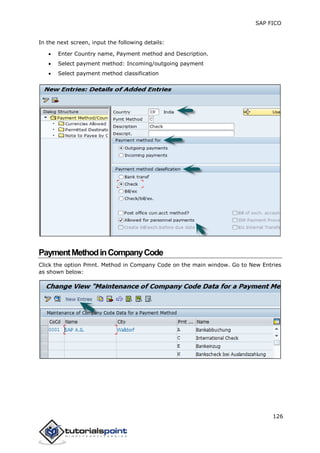
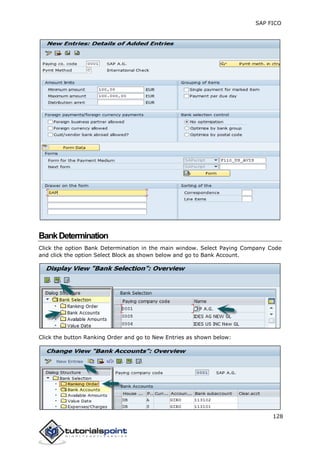
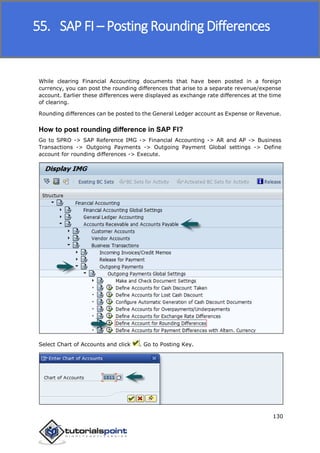
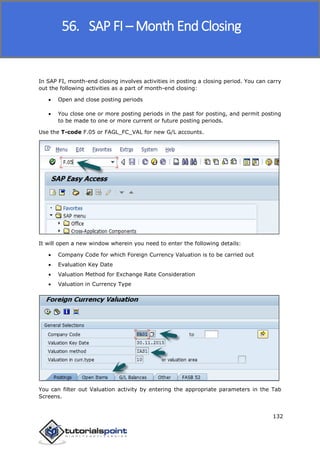
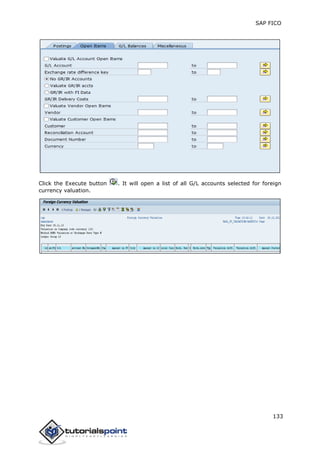
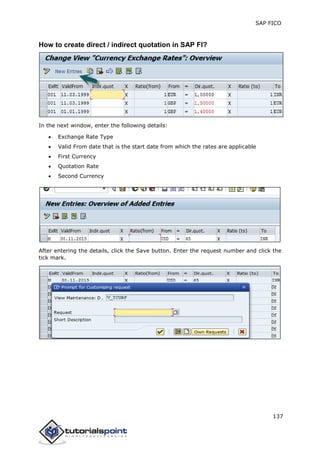
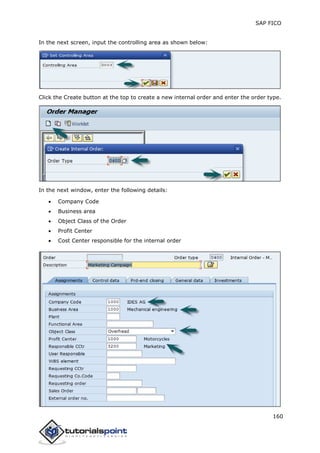
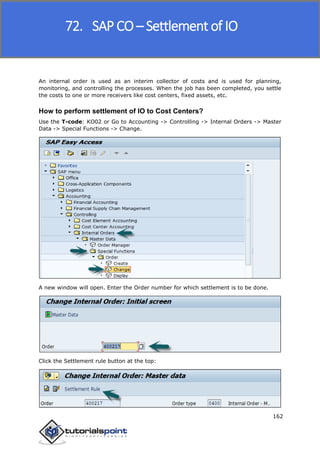
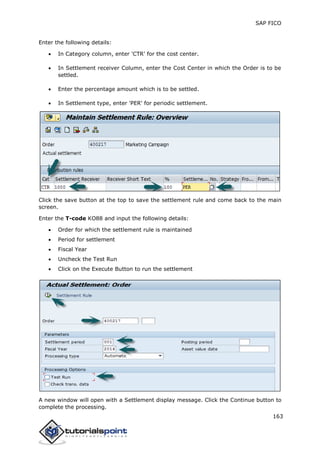
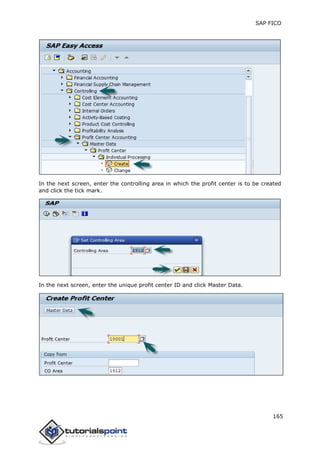
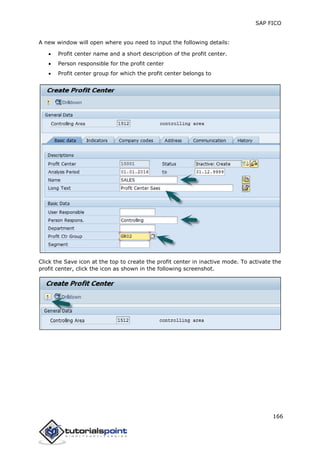
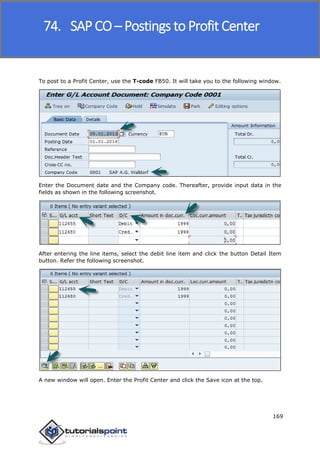
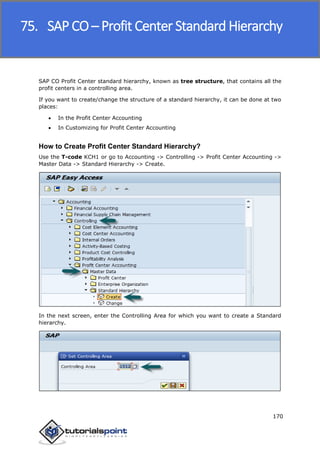
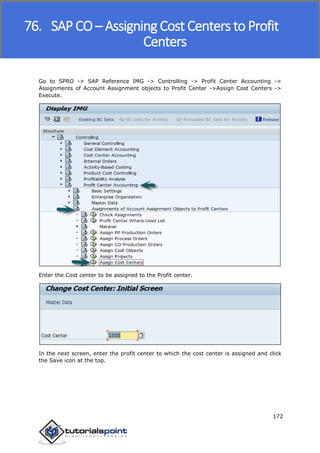
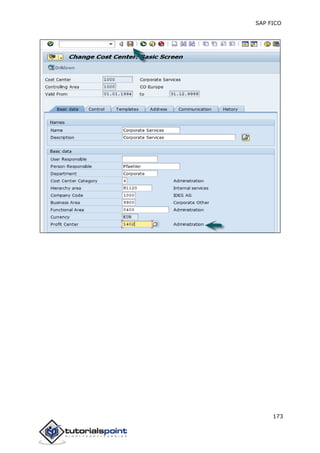
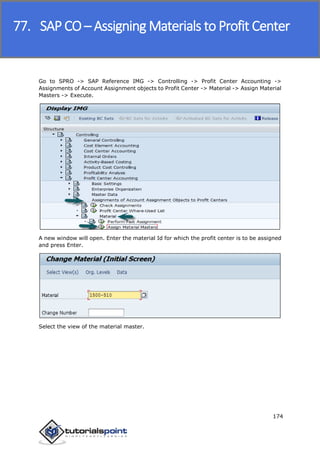
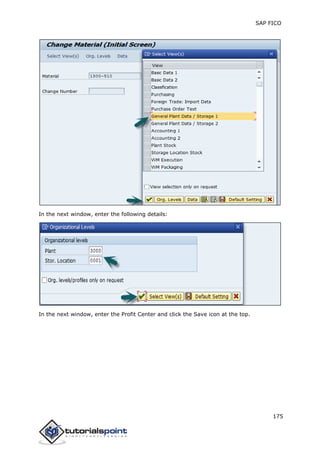
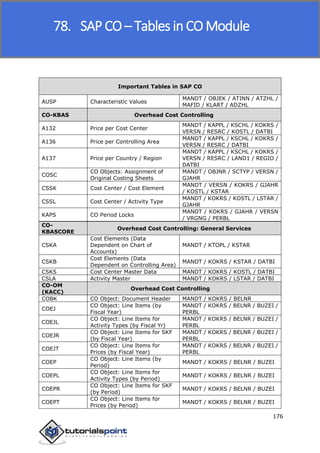
SAP FI is a module used for financial accounting and analysis. It allows users to store financial data, integrate with other SAP modules like SD, MM, and analyze an organization's financial conditions. SAP FI comprises submodules including general ledger, accounts receivable, accounts payable, asset accounting, and bank accounting. It enables management of financial accounting data within an international framework of multiple companies, currencies, and languages.