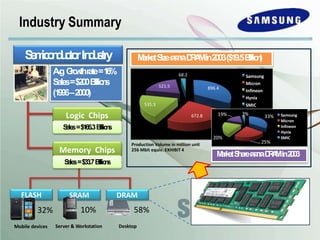
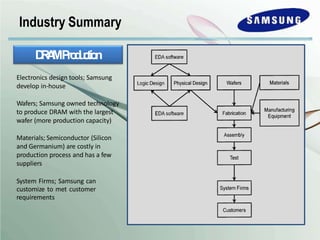
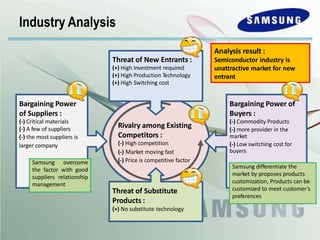
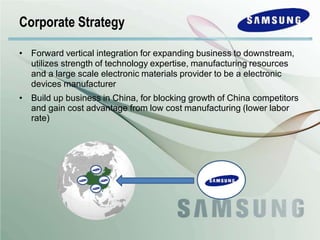
The document outlines Samsung's historical growth and strategic positioning within the semiconductor industry, noting a 16% average growth rate from 1960-2000. It discusses the company's response to the 2001-2002 semiconductor crisis, emphasizing their survival through branding and competitive strategies. Additionally, it analyzes the challenges and opportunities faced by Samsung, including market dynamics, technological advancements, and strategic initiatives for future growth.