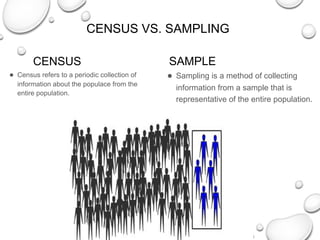
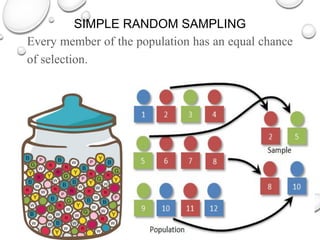
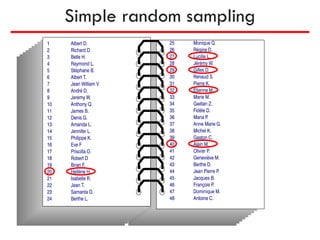
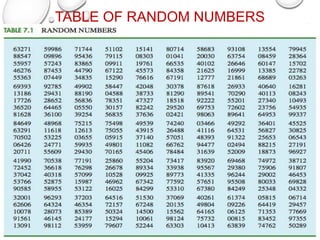
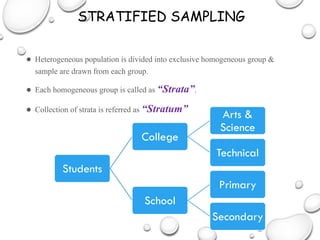
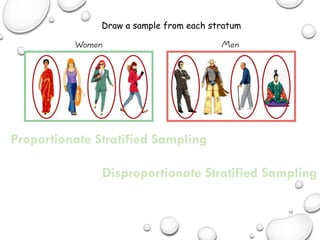
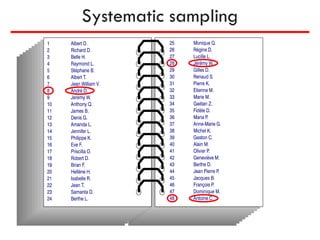
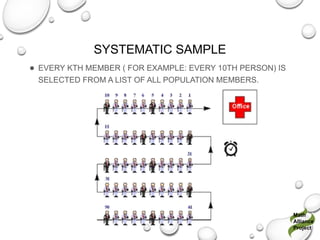
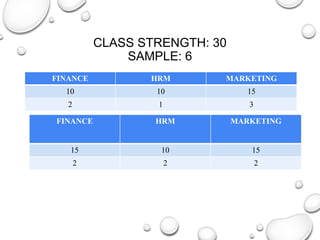
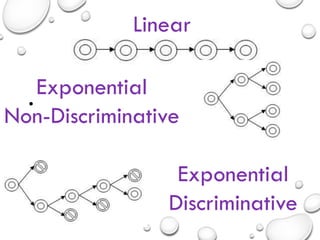
The document discusses the differences between census and sampling, highlighting key aspects such as reliability, time consumption, cost, and convenience. It details various sampling methods, including probability and non-probability techniques, as well as specific approaches such as stratified, systematic, and cluster sampling. Additionally, it provides definitions for important terms related to population and sampling design, underscoring their relevance in research methodology.