This document outlines the key components of a sampling design for assessing water quality, including:
1) Defining the objective and focusing sampling locations downstream of any discharge points.
2) Identifying the target population of water bodies of interest.
3) Determining the sampling strategy by selecting locations, frequency, collection methods, and implementing quality assurance practices.
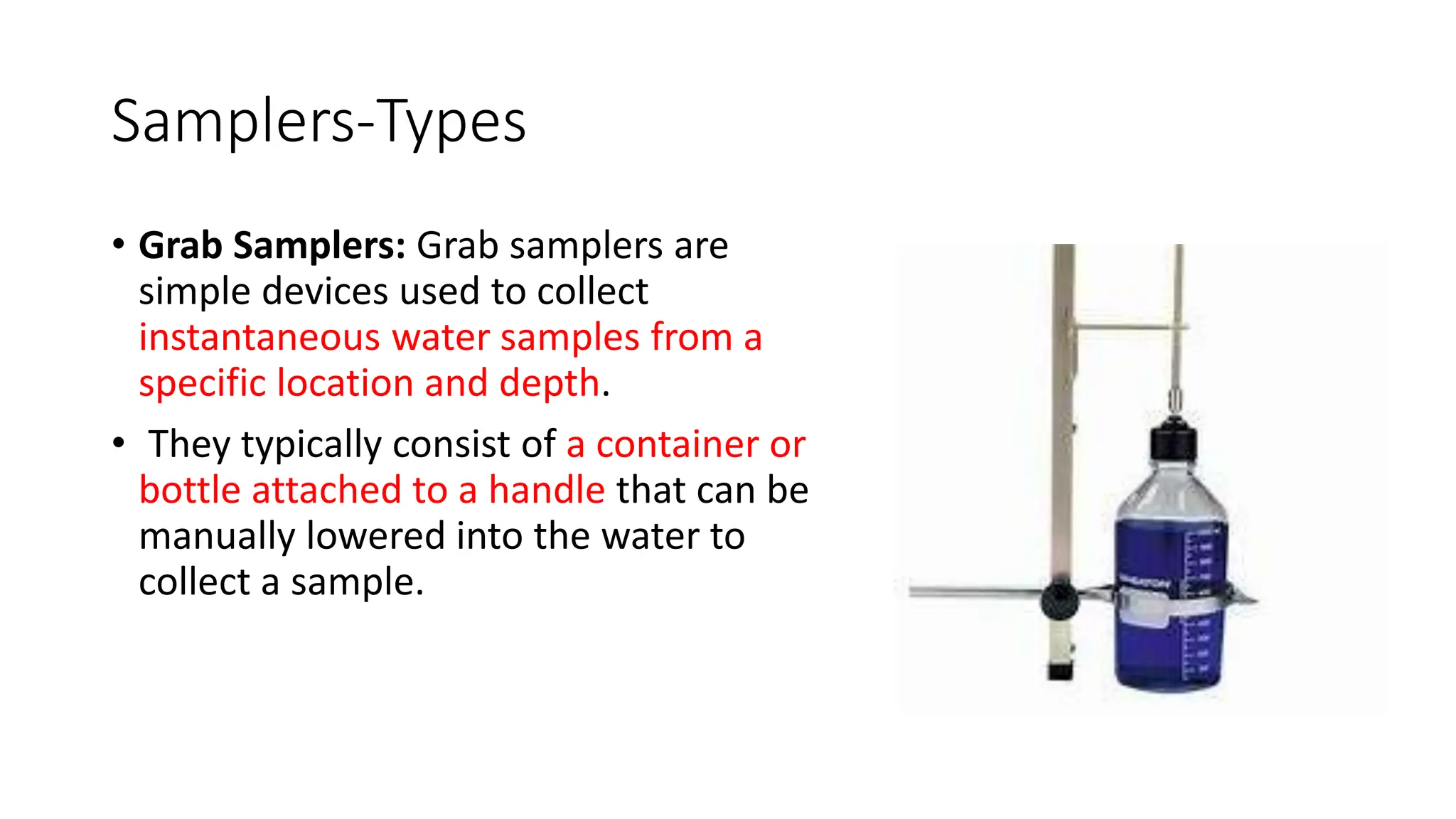
4) Describing different types of samplers like grab samplers, pole samplers, integrated samplers, and automatic samplers to efficiently collect representative water samples.