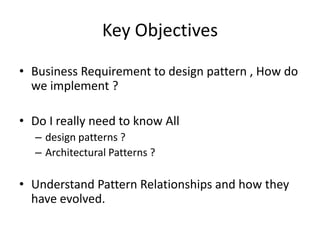
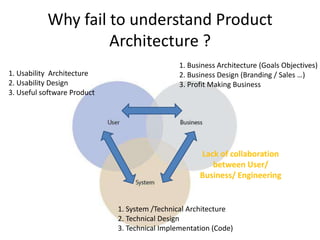
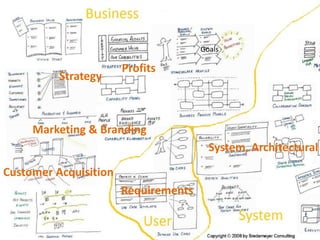
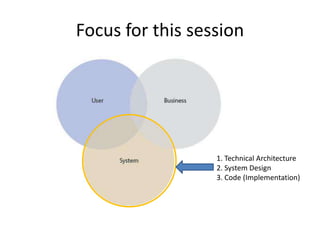
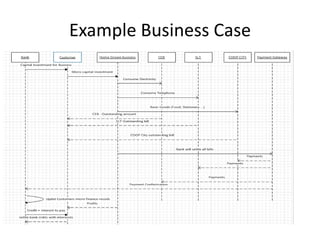
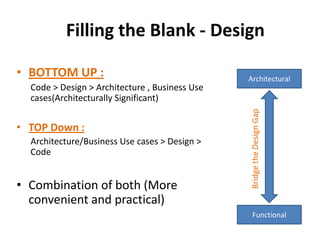
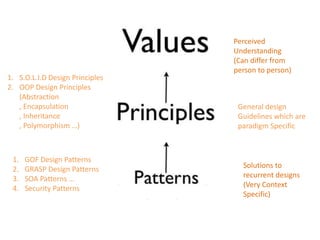
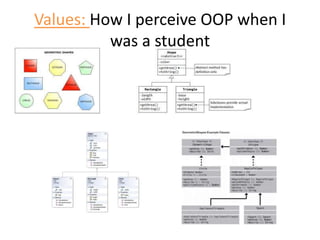
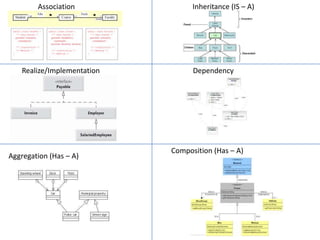
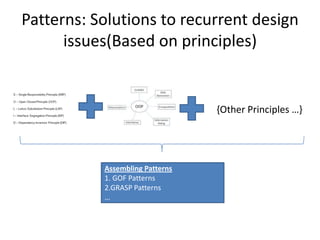
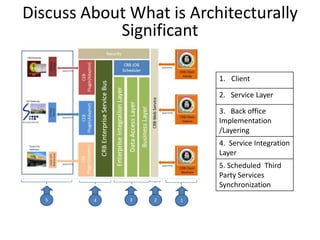
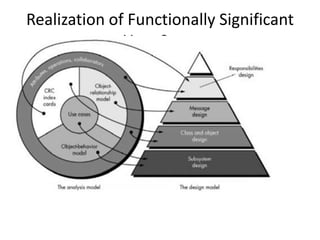
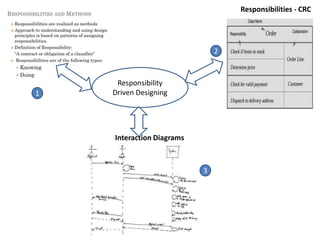
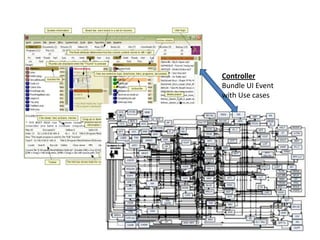
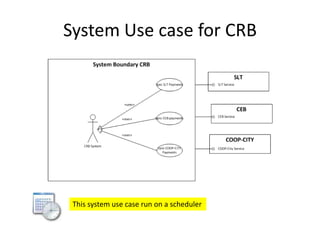
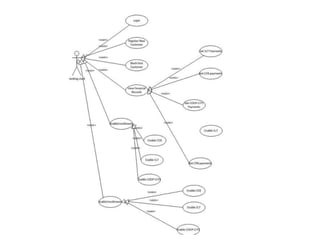
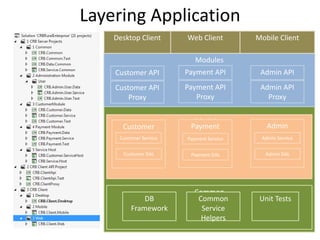
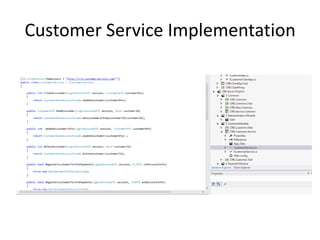
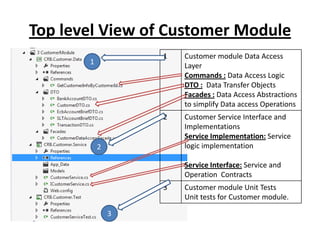
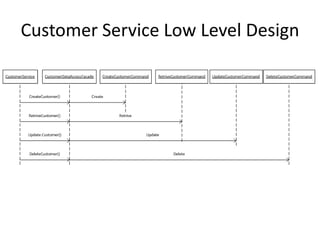
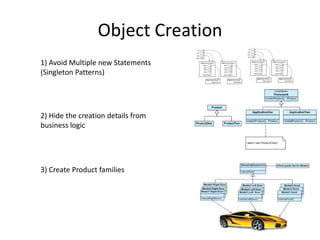
The document discusses software architecture and design patterns. It begins by describing the author's confusion with their code and lists objectives like understanding how to implement patterns and architectural relationships. It then defines concepts like object-oriented programming, design patterns, and software architecture. The remainder discusses filling gaps between architecture and design, perceived understanding versus guidelines, and examples of applying minimal viable products, layering, and design patterns like GOF patterns to a banking system.