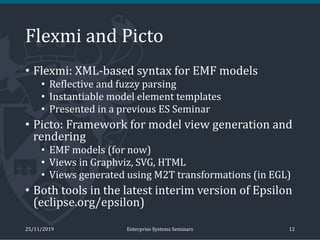
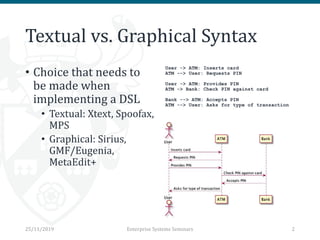
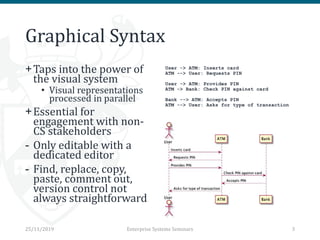
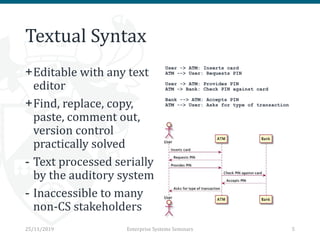
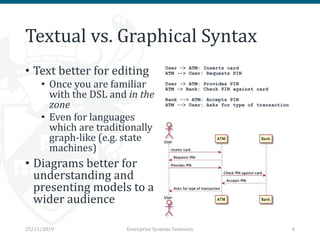
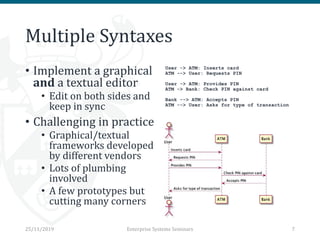
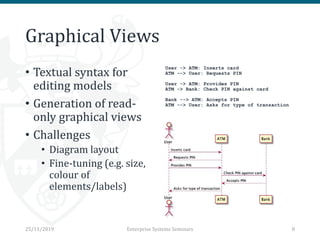
The document discusses the implementation and trade-offs between textual and graphical syntax in the context of domain-specific languages (DSLs), highlighting their respective advantages for editing and understanding models. It mentions tools like Flexmi and Picto for model visualization and transformation, along with future developments for better integration and user experience. The challenges of maintaining synchronization between graphical and textual frameworks are also noted.

![Fine-Tuning
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("Hello world");
}
25/11/2019 Enterprise Systems Seminars 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/picto-es-seminar-191126104708/85/Picto-Model-Visualisation-via-M2T-Transformation-10-320.jpg)
![Fine-Tuning
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("Helloworld");
}
25/11/2019 Enterprise Systems Seminars 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/picto-es-seminar-191126104708/85/Picto-Model-Visualisation-via-M2T-Transformation-11-320.jpg)