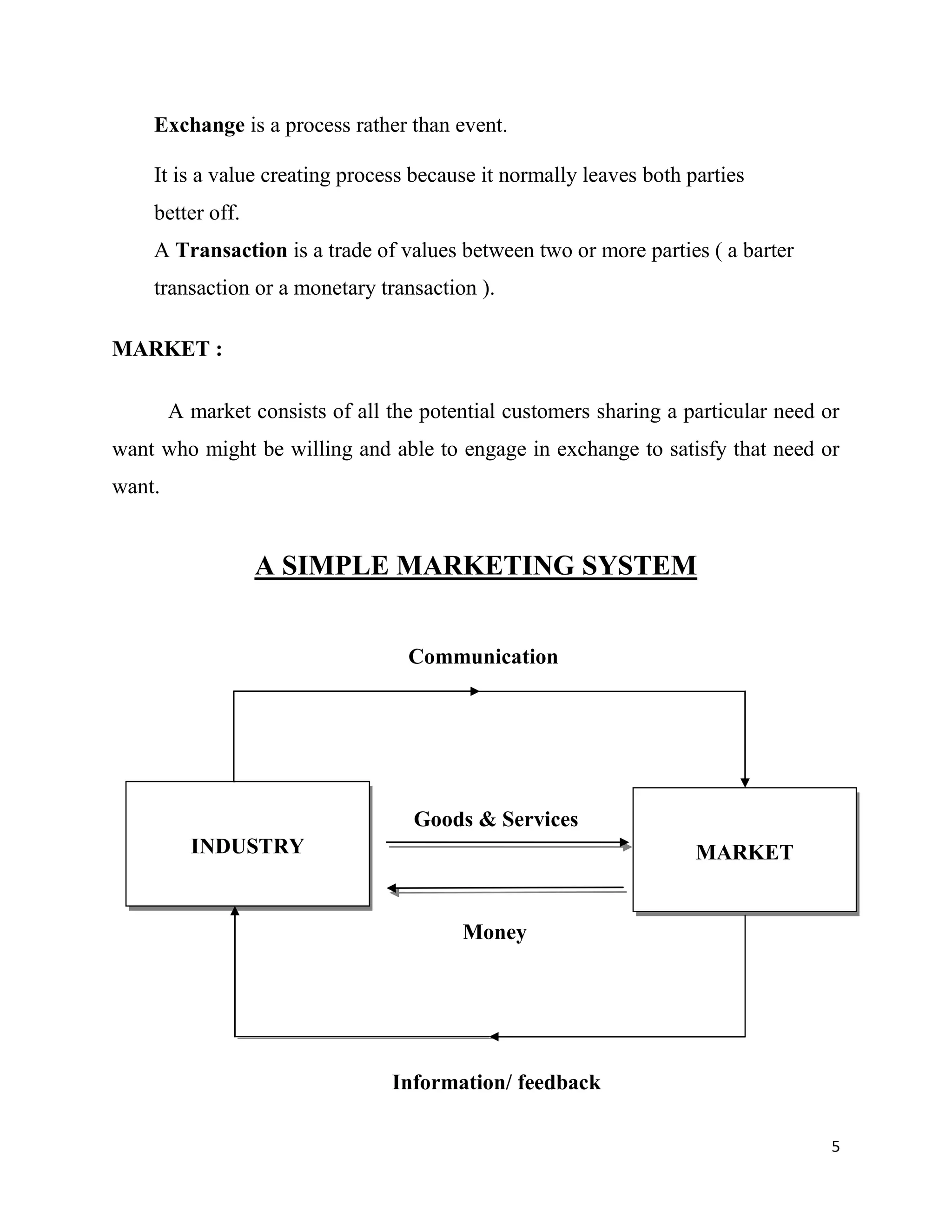
The document is a basic guide to sales and marketing, highlighting key concepts such as marketing definitions, the marketing management process, and the distinctions between marketing and sales. It describes the 4 P's of marketing, five marketing concepts, and the importance of understanding customer needs and satisfaction. The guide emphasizes the differences between marketing, which targets a broader audience, and sales, which focuses on individual transactions.