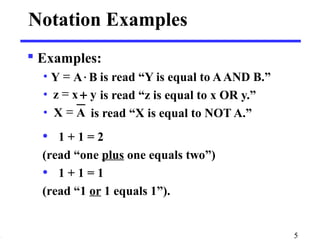
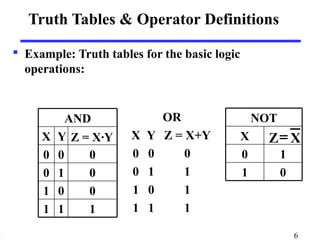
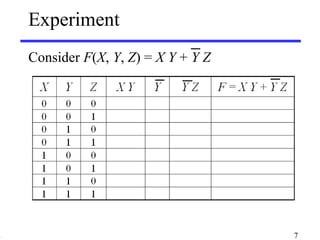
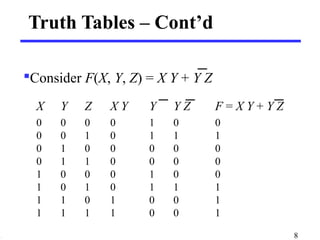
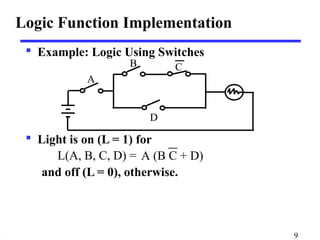
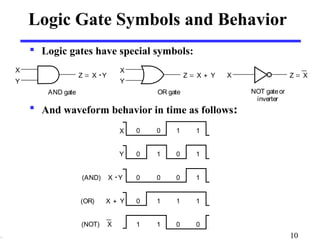
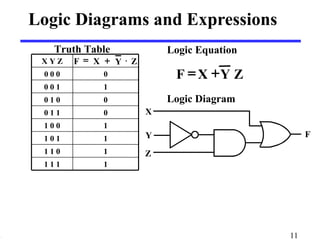
This document discusses logic circuits and how logic expressions are represented using logic gates. It covers basic logical operators like AND, OR, and NOT. Truth tables are used to define the behavior of each logic gate and how they combine input values. Logic functions can be implemented using switches and gates. Diagrams and equations are used to represent complex logic expressions.