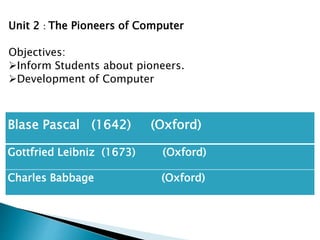
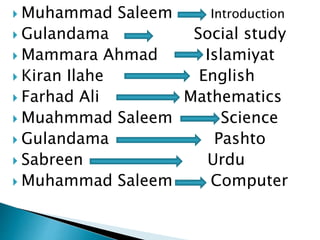
This document outlines the curriculum for grade 4. It includes the following subjects: Social Studies, Islamiyat, English, Mathematics, and Science.
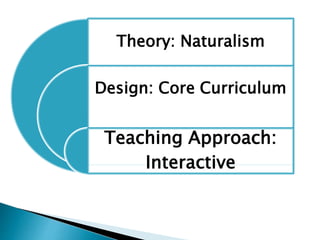
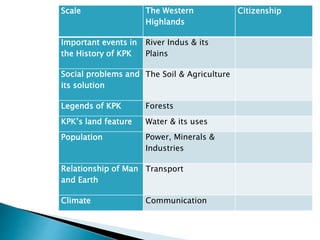
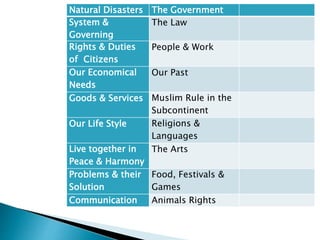
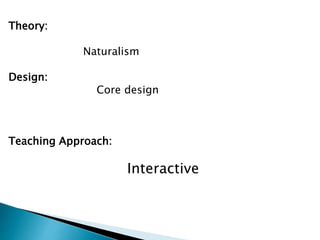
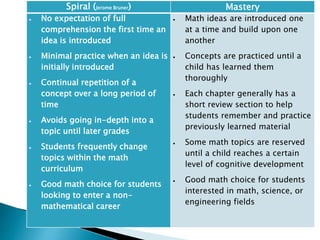
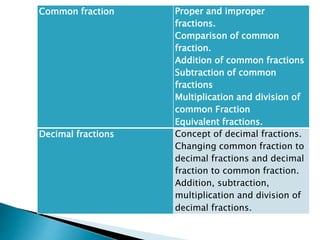
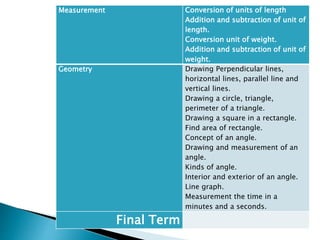
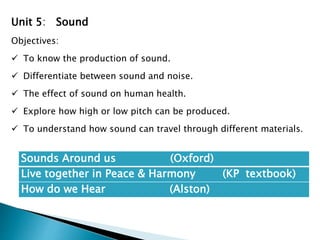
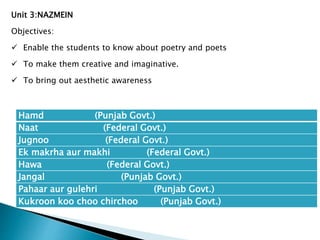
The curriculum follows a naturalistic approach and core design. Subjects include assessments, units, objectives, and assigned textbooks. For example, in Social Studies the units cover history, geography, citizenship, economy, and culture/society. Mathematics units include numbers, fractions, measurement, geometry, and final term assessments. Science units focus on life cycles, the solar system, states of matter, and sound.
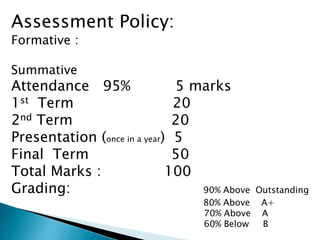
The curriculum aims to develop students' skills through an interactive teaching approach across subjects. It assesses students with formative and summative evaluations, including presentations,