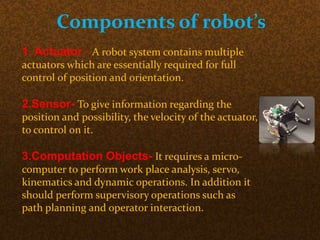
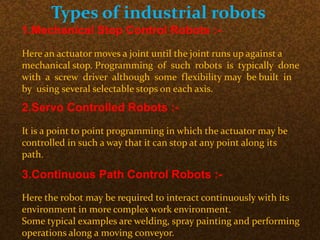
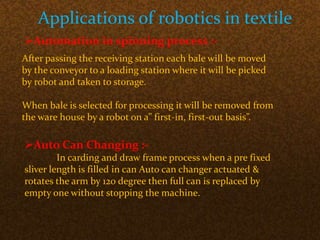
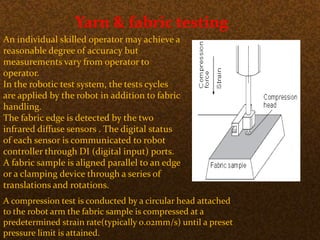
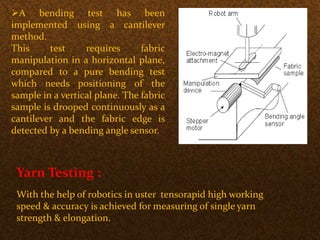
The document discusses the application of robotics in the textile industry, highlighting various types of robots and their specific uses such as in spinning, garment manufacturing, and fabric testing. It emphasizes the benefits of automation, including increased productivity, improved product quality, and cost reduction, while also addressing the disadvantages such as high costs and potential job displacement. The conclusion suggests further development and integration of robotics in textiles will depend on economic factors within the sector.