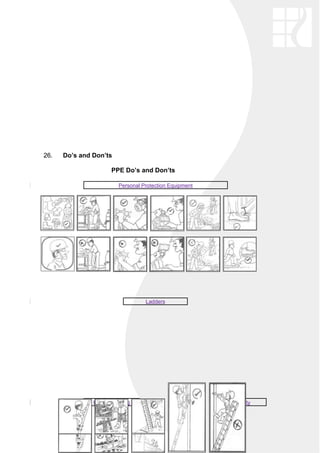
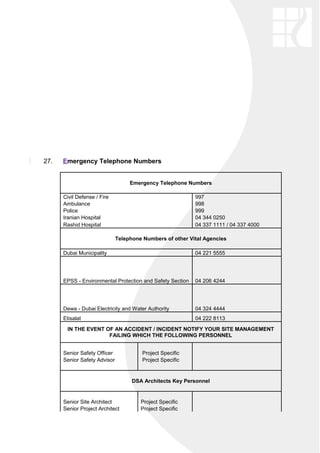
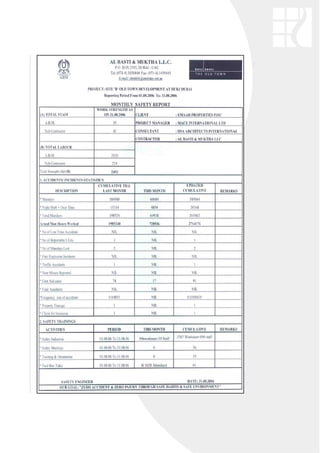
The document outlines an occupational health and safety policy for DSA Architects International. It commits to ensuring a safe workplace that complies with legislative requirements. It encourages employees to report any unsafe practices or conditions. The policy will be implemented by embracing risk management principles, adopting a consultative approach, and disseminating health and safety information. The accompanying health and safety manual provides guidance on various safety topics like electricity, confined spaces, lifting equipment, and more to prevent accidents and ensure efficiency. Compliance is the responsibility of all site workers.