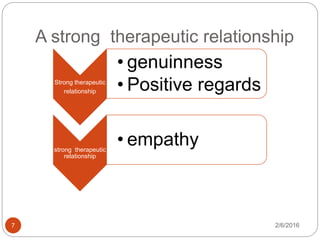
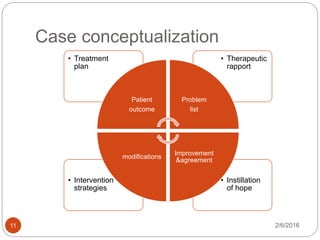
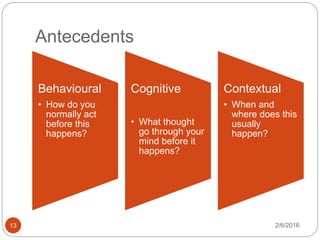
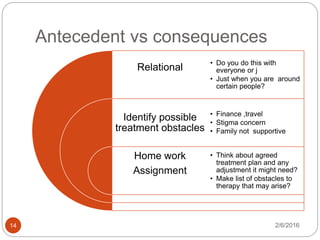
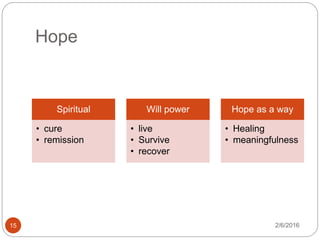
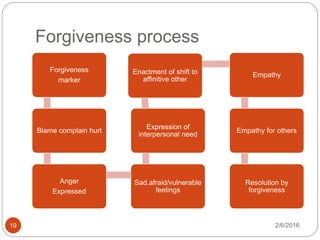
This document outlines the key components of cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and acceptance therapy. It discusses that CBT aims to help patients identify and change negative and dysfunctional thoughts and behaviors to improve emotions. Acceptance therapy teaches patients to accept situations they cannot change through practice. A strong therapeutic relationship involving genuineness, empathy, and positive regard is important. The document also discusses case conceptualization, instilling hope in patients, addressing antecedents and consequences of behaviors, and typical CBT session structure.