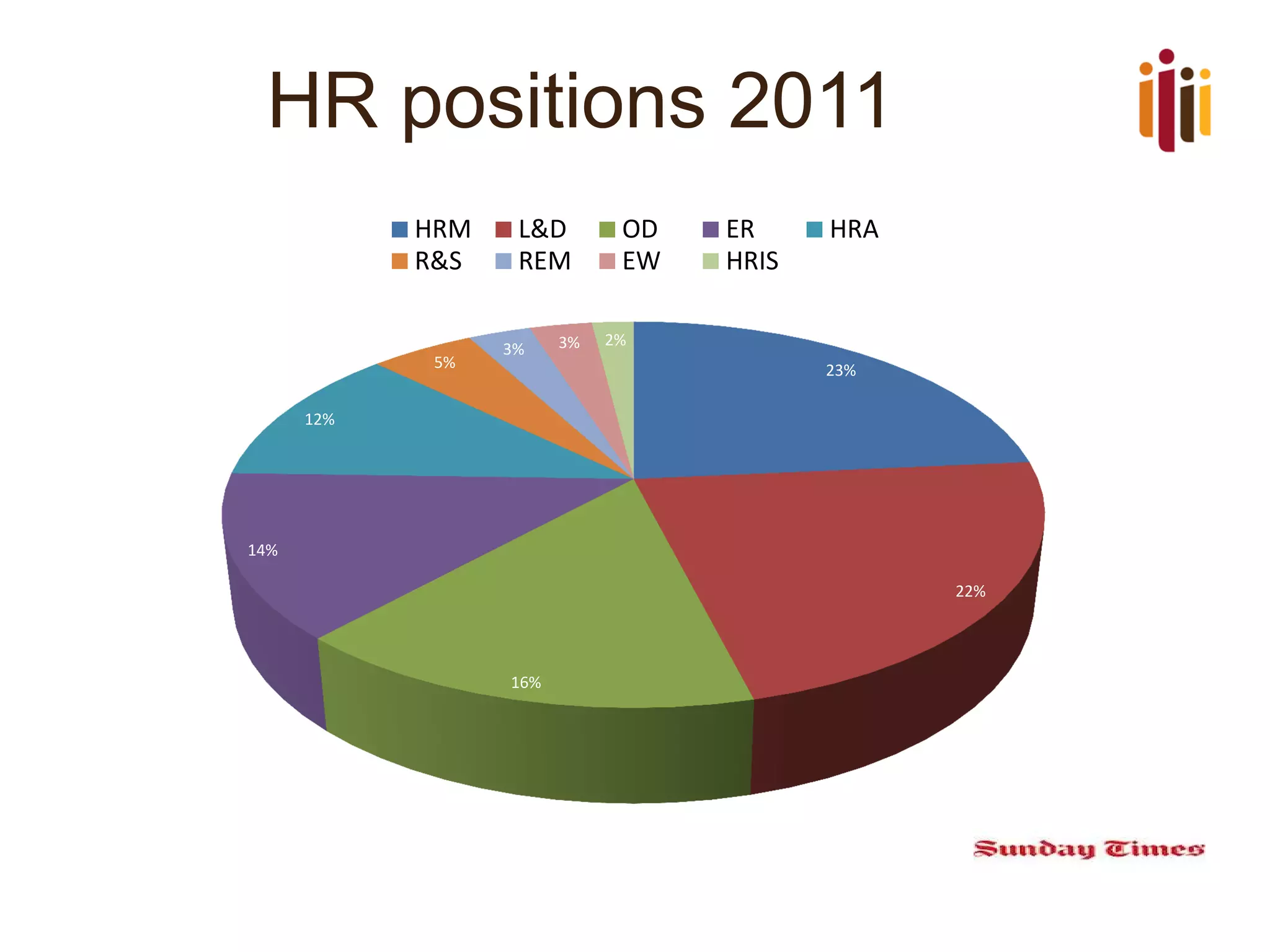
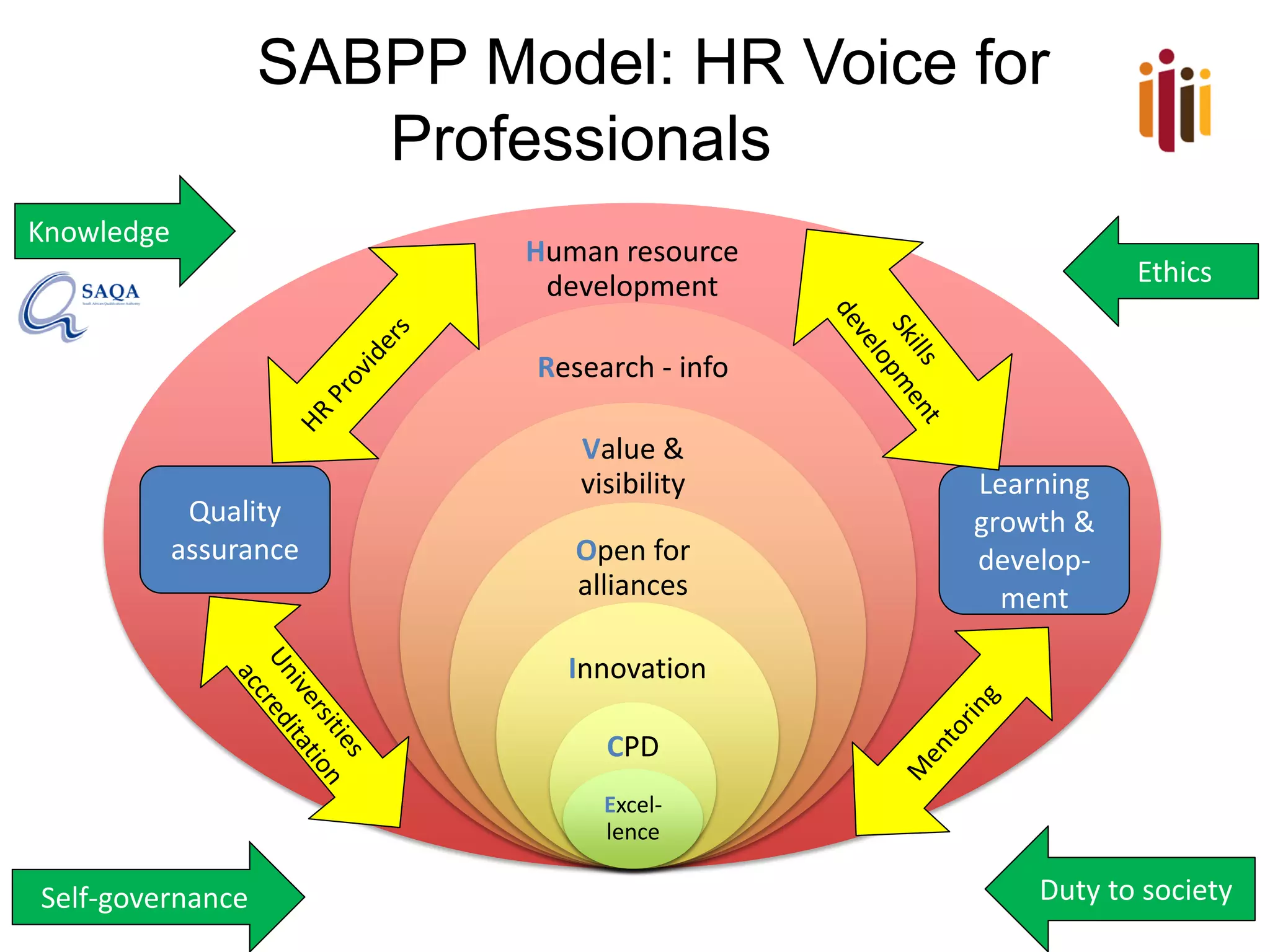
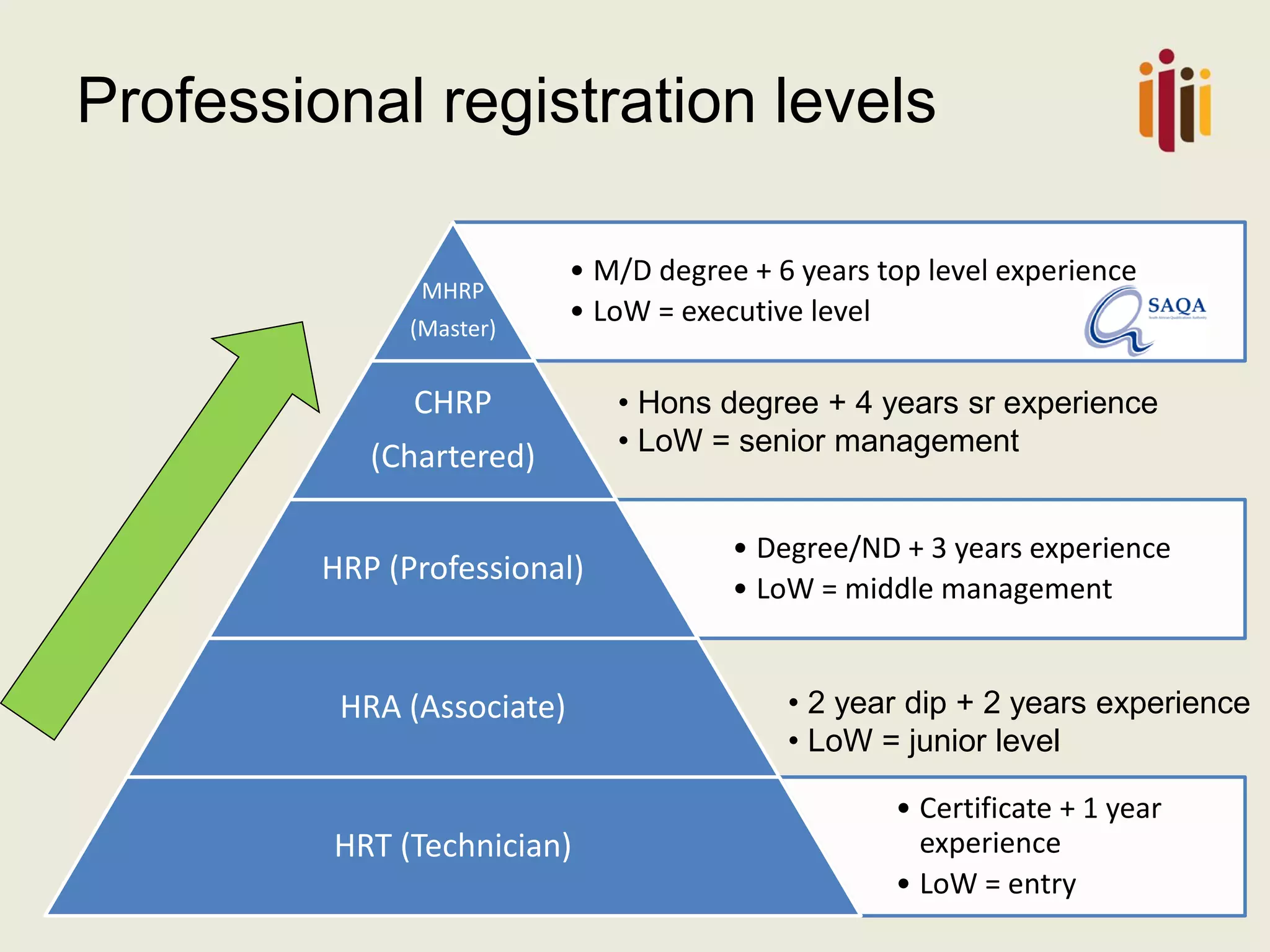
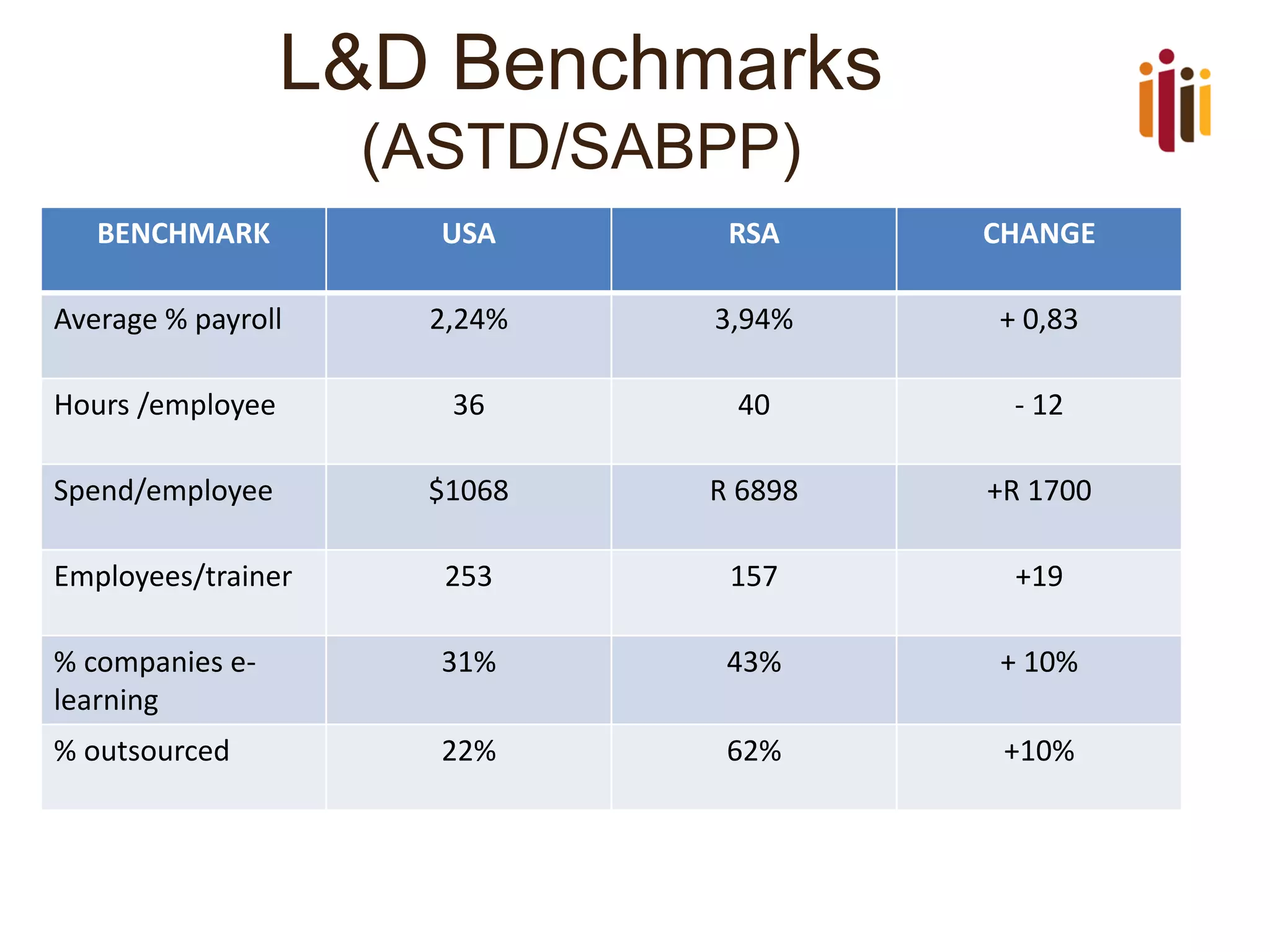
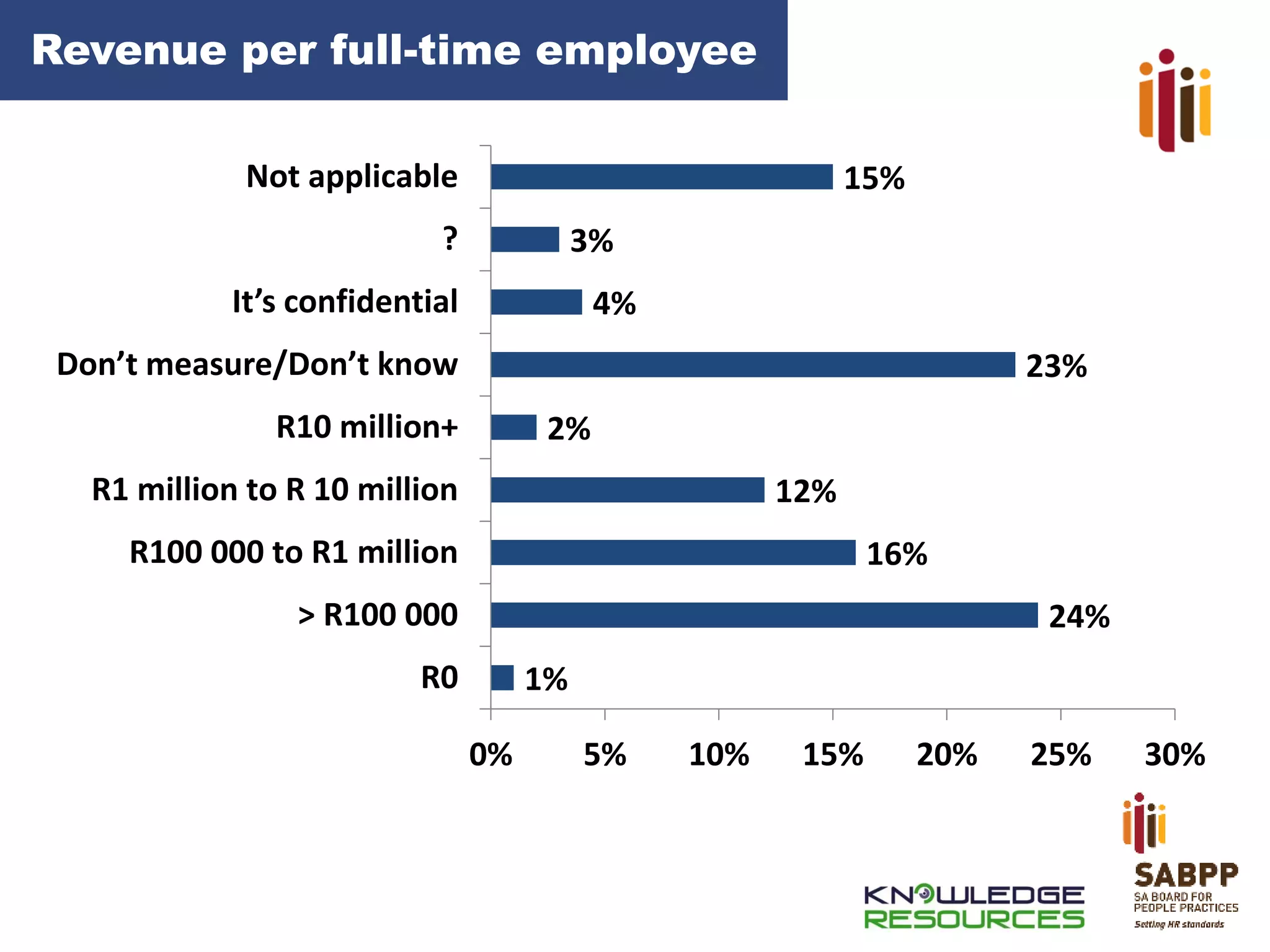
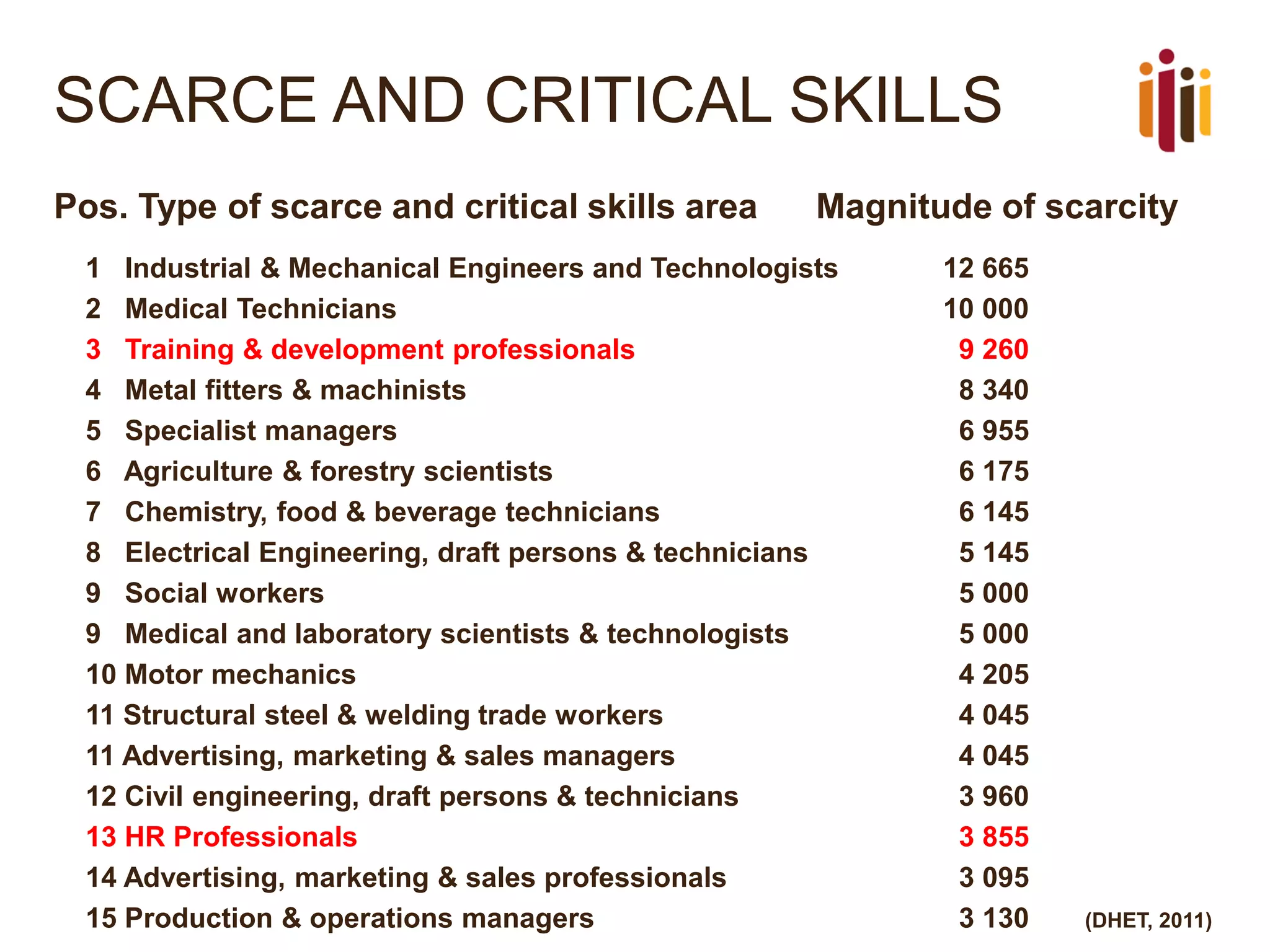
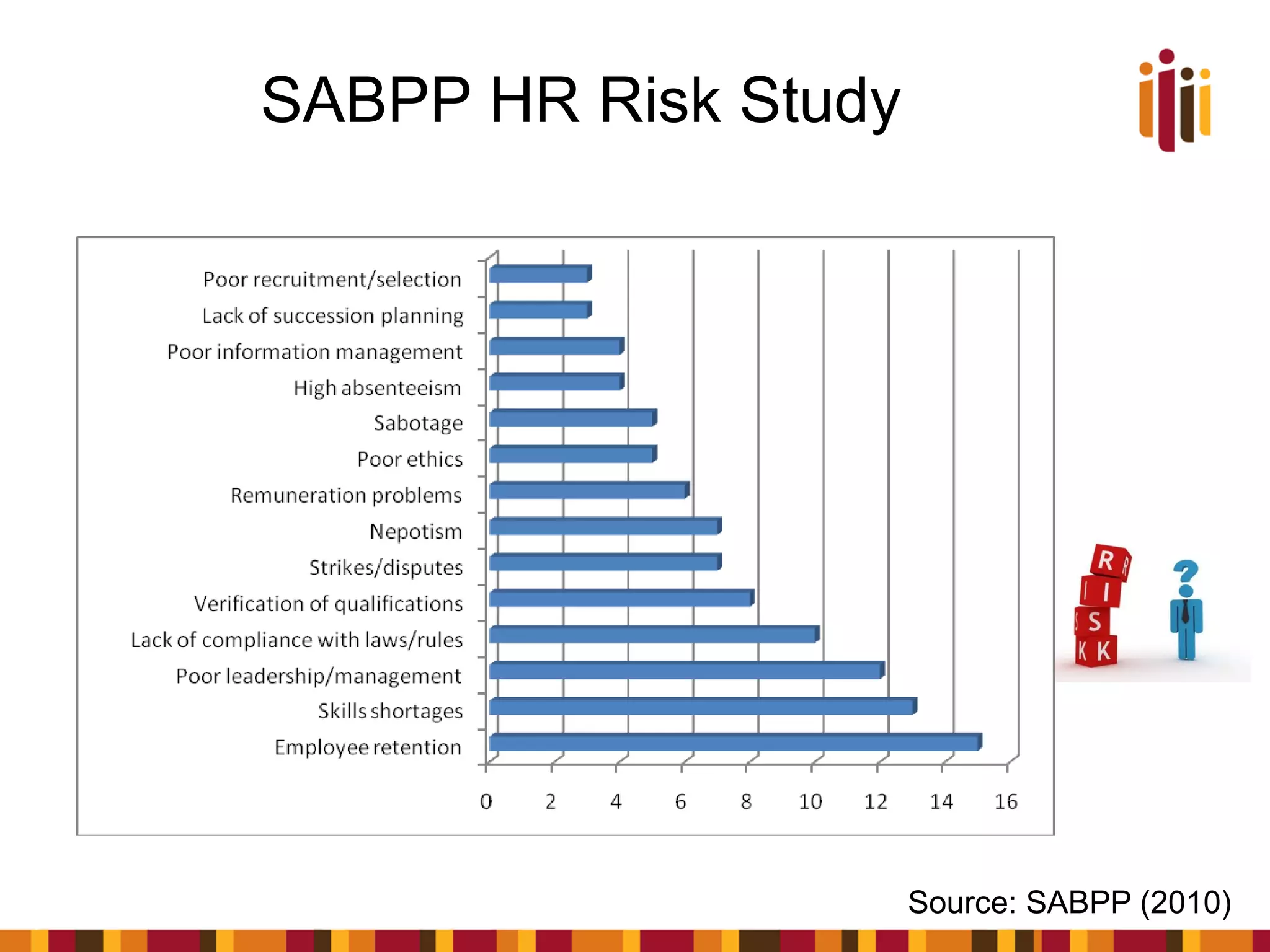
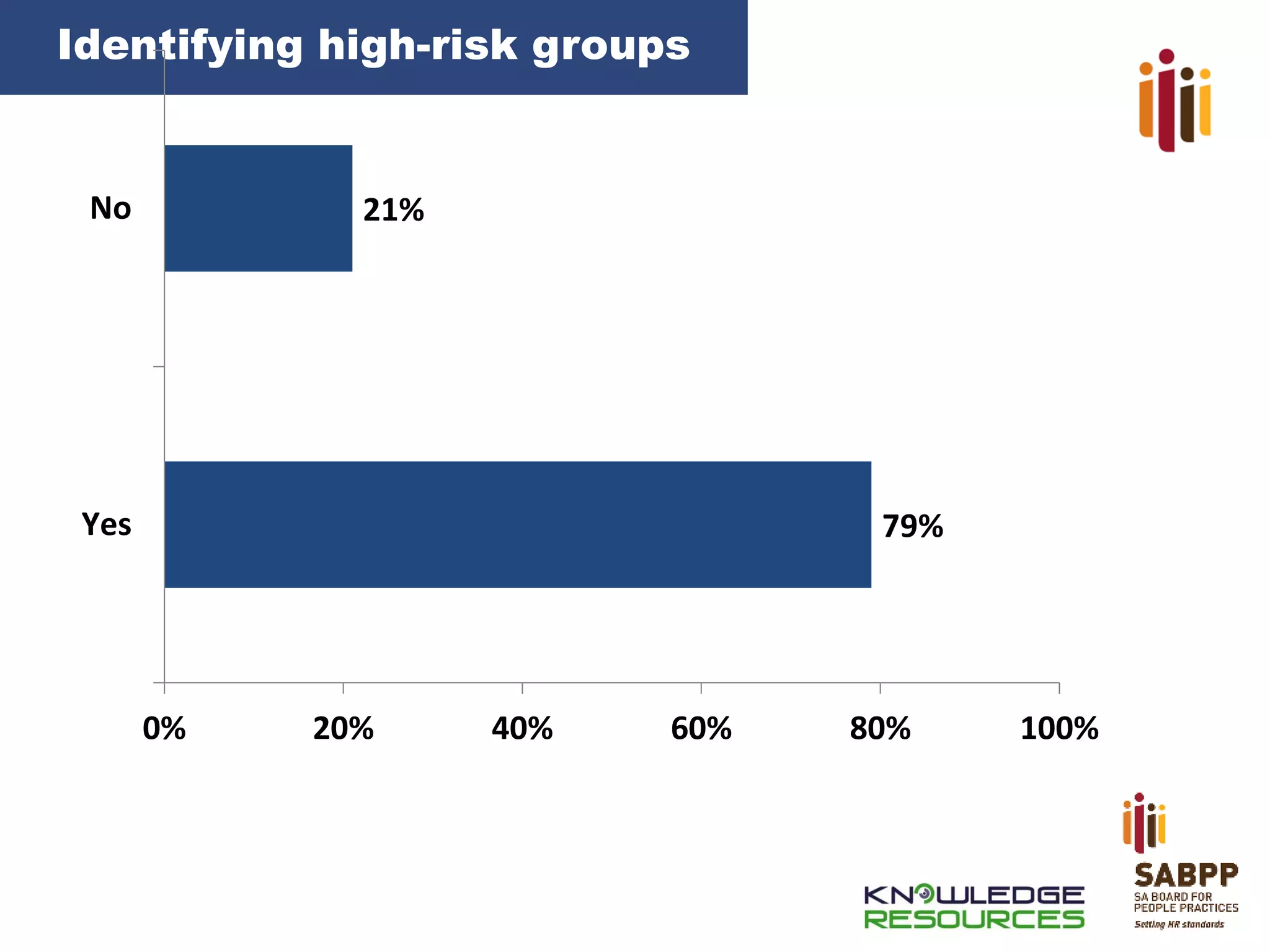
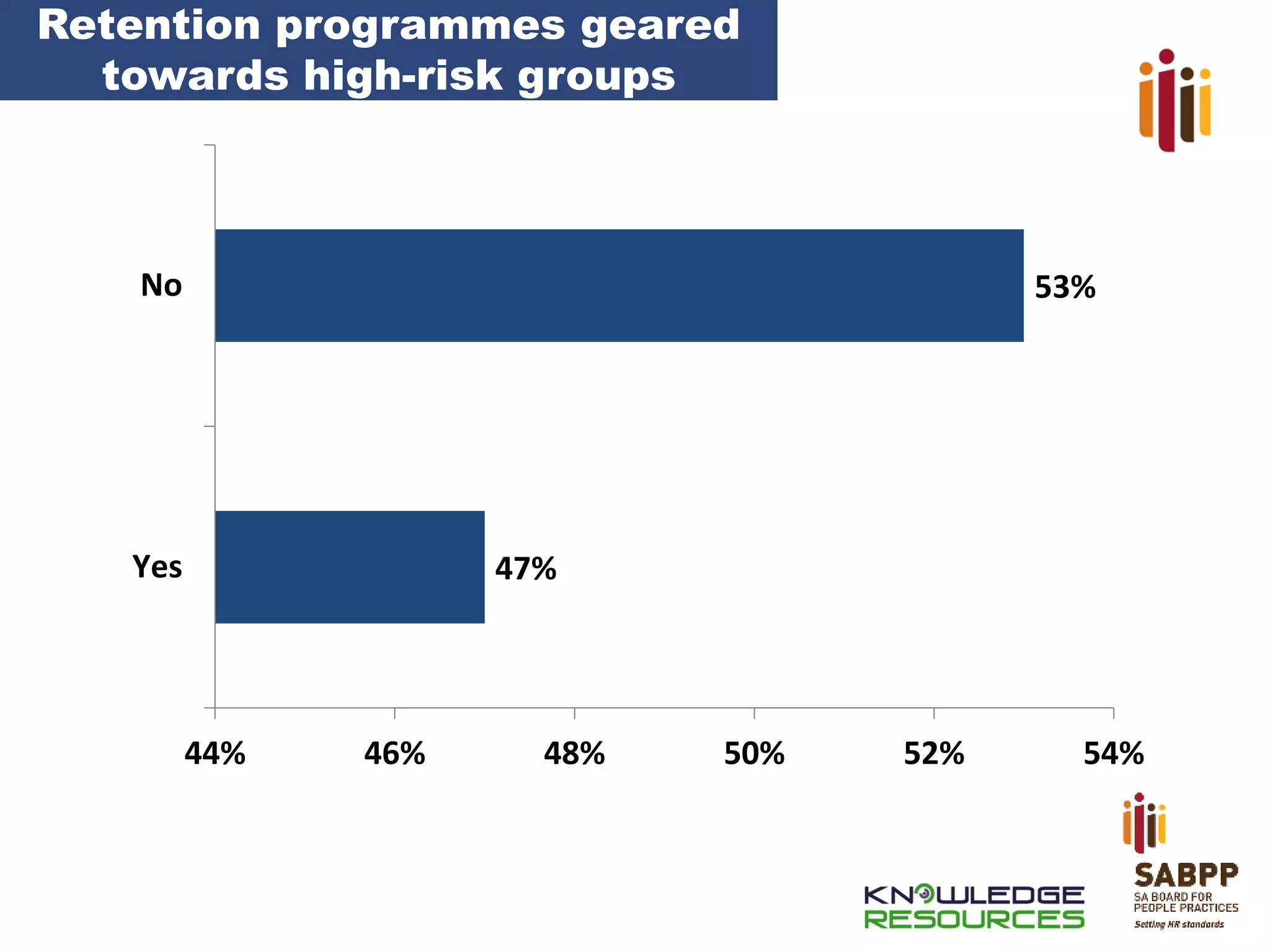
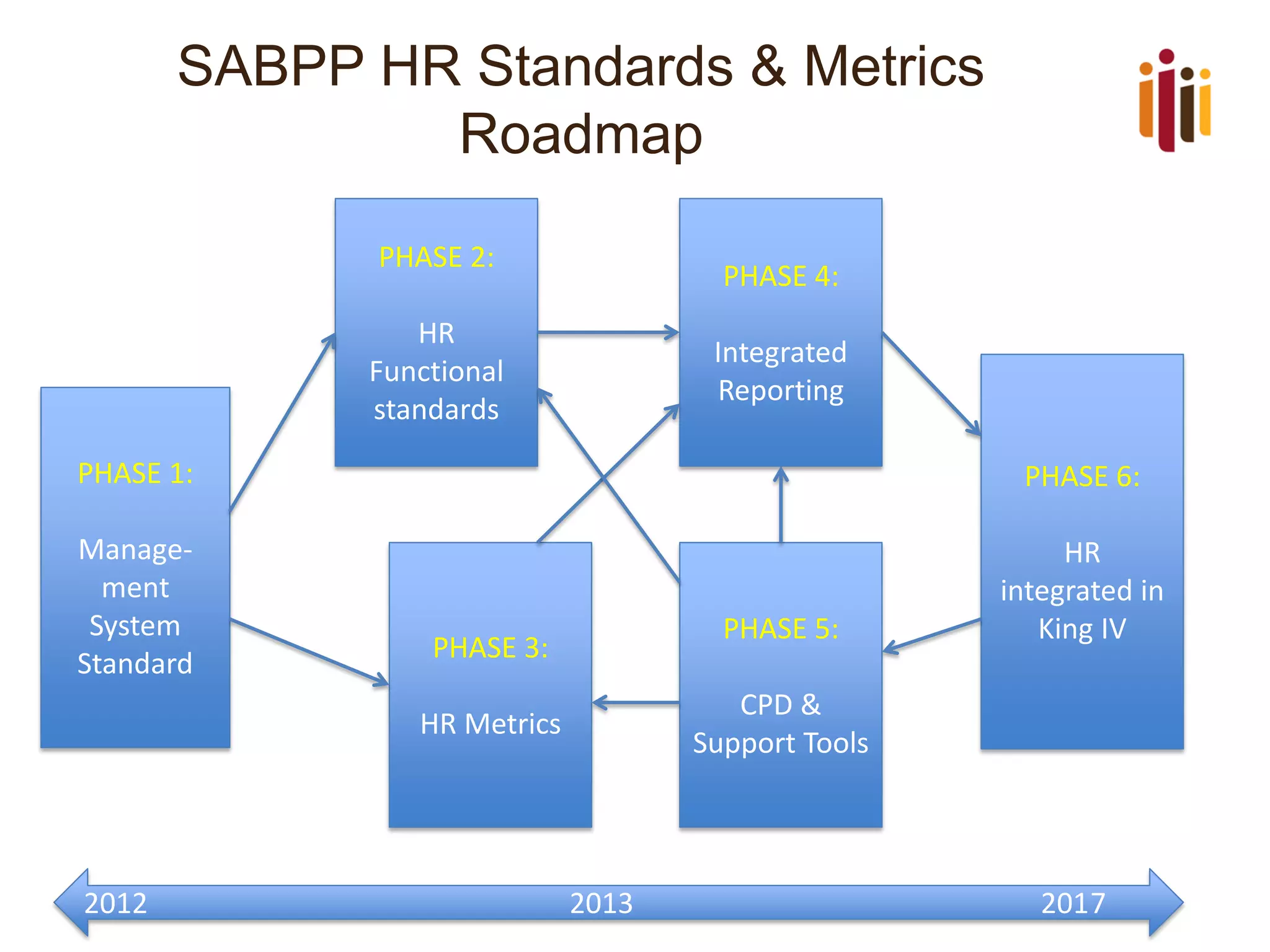
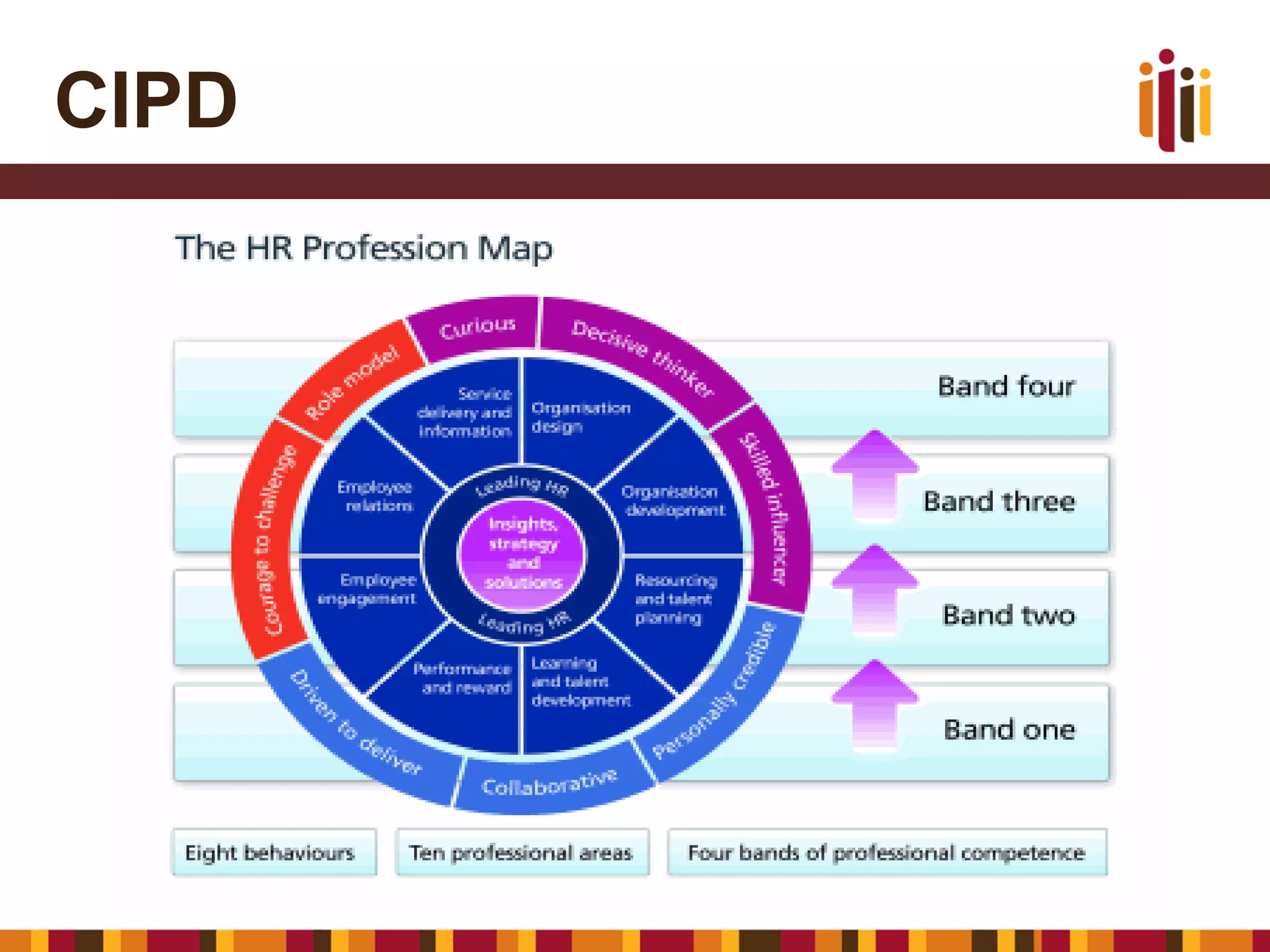
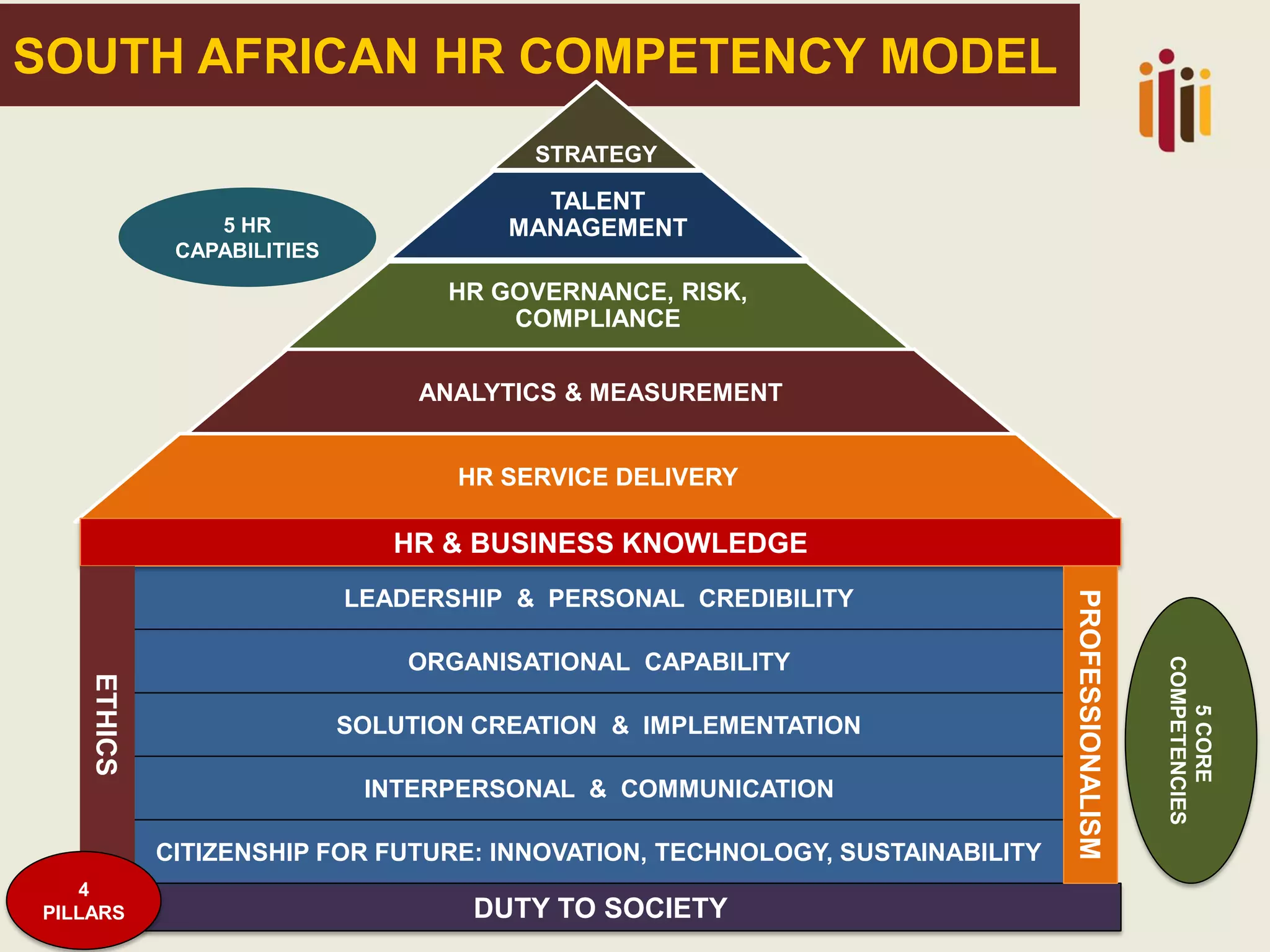
The document provides an overview of advancing the HR profession in South Africa. It discusses trends in HR, benchmarks for HR functions, and proposes an HR competency model. Specifically, it notes that HR is increasingly seen as a strategic partner, and highlights priorities like talent management, leadership development, and skills development. Workforce analytics and metrics are still limited in many organizations. An HR competency model is presented as a way to enhance professionalism in the field.