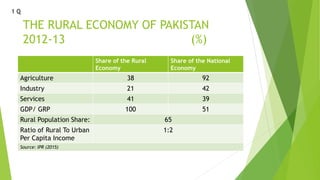
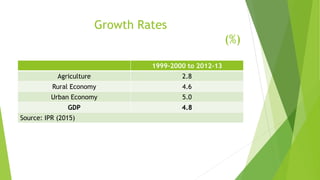
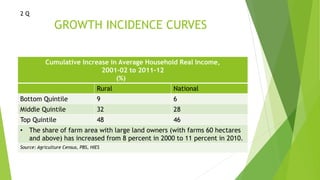
The document discusses the role of agriculture and government in rural development in Pakistan, citing key statistics on the rural economy and growth rates from 1999-2013. It outlines public investment in agriculture and rural development, the impact of the 18th amendment, and proposed policies and programs for improvement. A vision for the next 20 years is presented, emphasizing population growth, agricultural productivity, and improved access to services.