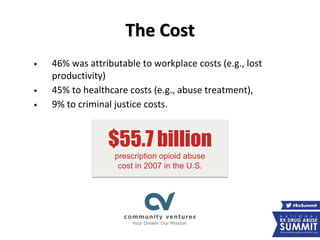
The document discusses the economic impact of addiction and tools for financial capability in recovery. It notes that prescription drug abuse costs the US $55.7 billion annually, with costs including healthcare, lost productivity, and criminal justice. Addiction ruins lives by causing economic instability, debt, fines, and drained savings. The document advocates for including financial literacy and coaching in recovery plans to help rebuild financial lives, provide accountability, and allow for better long-term financial decisions through goal-setting and milestones. It provides examples of financial programs and online tools that can be resources.