1. The document discusses strategies for improving health literacy and activation in communities. It focuses on empowering individuals to better manage their own health and recovery.
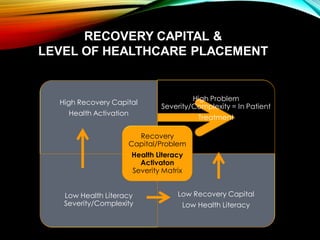
2. A major barrier is that people often feel passive and overwhelmed by their health, lacking understanding of how to manage it. The strategies aim to build knowledge, skills, and confidence.
3. Activating recovery requires trust between community organizations and those they serve. When people trust the resources available, success in managing health and recovery is more likely.