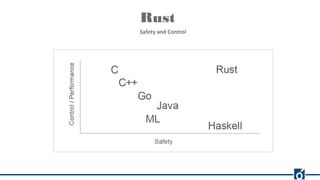
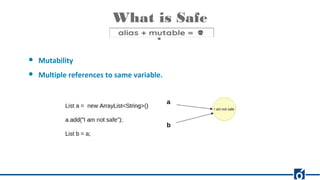
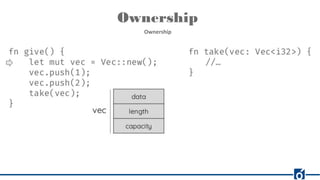
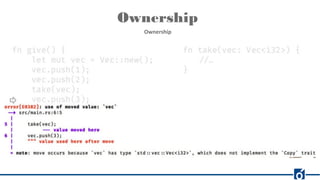
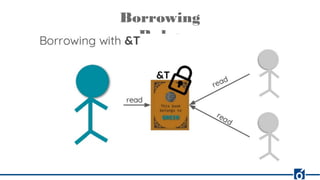
Rust is a systems programming language that emphasizes safety and performance, particularly through its ownership model and type system. It allows for efficient and reliable software development without the need for garbage collection, offering compile-time checks to ensure memory safety. Rust's rich tooling, including package management through Cargo and code formatting with rustfmt, facilitates a productive development environment.