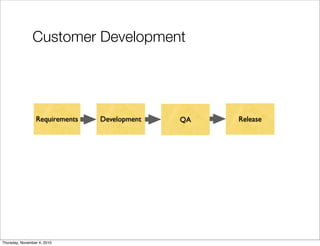
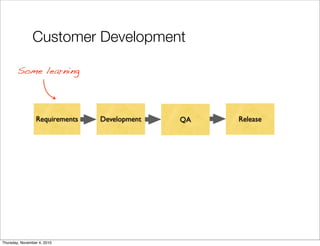
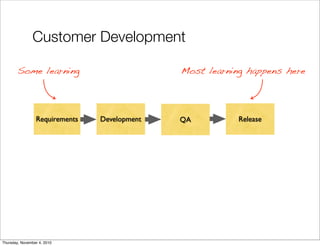
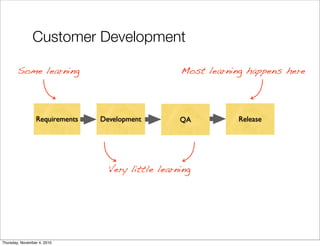
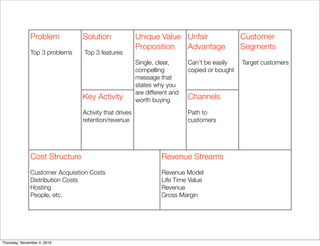
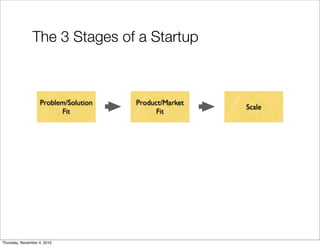
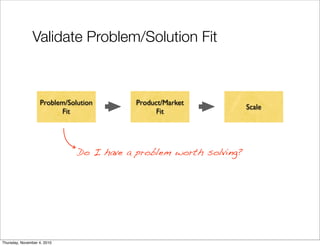
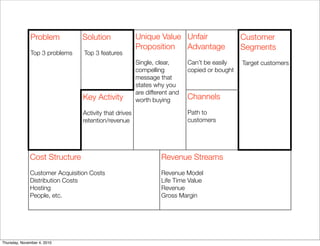
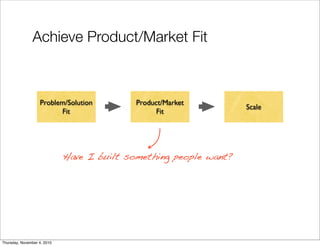
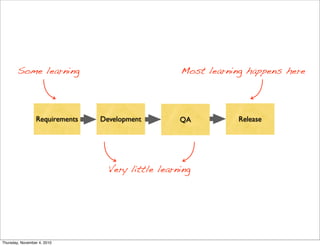
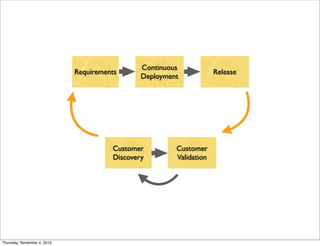
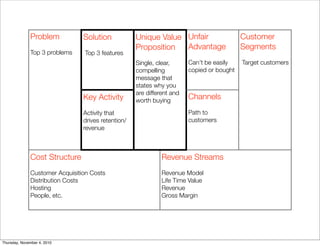
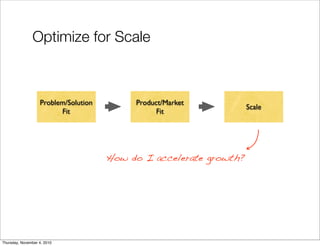
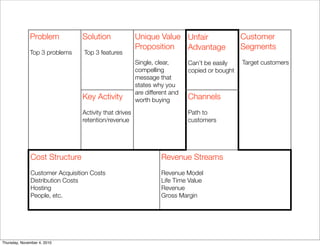
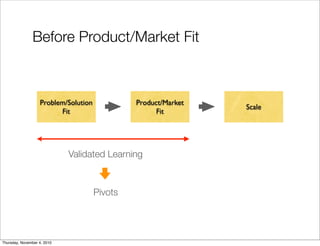
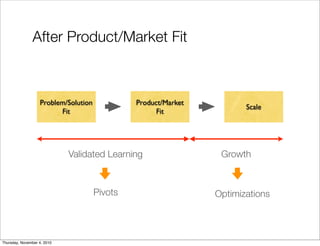
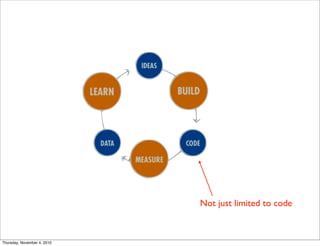
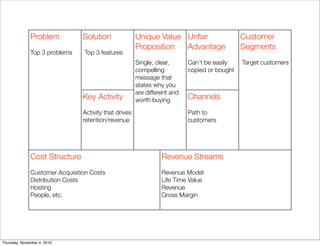
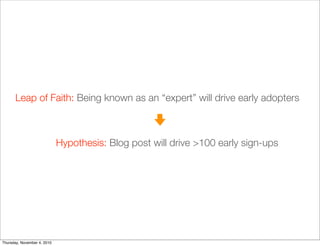
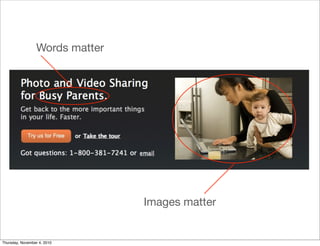
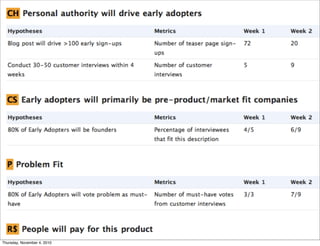
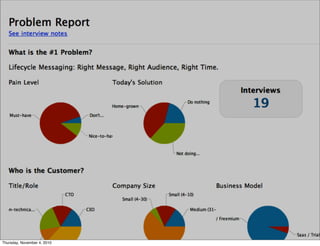
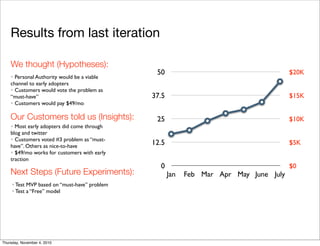
The document discusses the concept of "Running Lean", which is a systematic process for iterating a startup's web application from the initial "Plan A" to a plan that works. It involves using techniques from Customer Development, Lean Startup, and Bootstrapping. The key aspects are validating problems and solutions with customers, achieving product/market fit through iterative releases, and optimizing for scale once fit is achieved. Progress is measured through validated learning loops involving hypotheses, experiments, qualitative/quantitative validation, dashboards, and communication of learnings. The overall goal is to iterate quickly from the initial plan to one that works through a continuous process of customer feedback and validation.