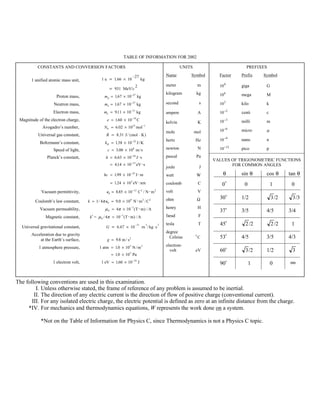
This document provides tables of constants, conversion factors, units, prefixes, values of trigonometric functions for common angles, and equations for Newtonian mechanics, electricity, and magnetism that are relevant for the 2002 AP Physics B exam. The tables include fundamental physical constants such as the speed of light, Planck's constant, electron mass, and more. Units covered include meters, kilograms, seconds, amperes, kelvins, and others. Prefixes from giga to pico are also listed.