This document provides an introduction and overview of the Ruby programming language. It discusses installing Ruby on Windows and Mac systems, data types including numbers, strings, and arrays. It also covers variables, arrays, iterators, methods including built-in and user-defined methods, and flow control including if/else conditional statements and while loops. The document encourages comments and feedback.




![Variables, Arrays, and Iterators
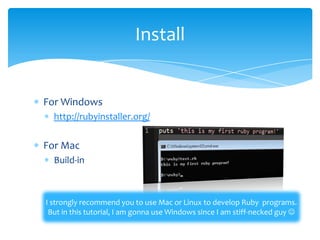
Arrays
[ele1, ele2, ele3]
Some array methods
.pop
.push
.join(‘join string’)
.last
.length](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rubyintroduction-part1-121118111542-phpapp02/85/Ruby-introduction-part1-7-320.jpg)
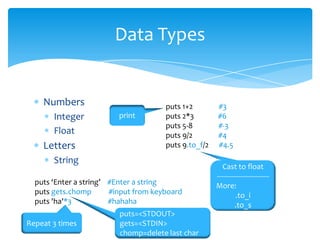
![Variables, Arrays, and Iterators
There is a special array method : each
iterator
An array with 3 elements
color= [‘R', 'G', 'R']
color.each do | c | | c | = variable in this
puts “color=” + c do…end block
end
Output=
color=R
color=G
color=B](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rubyintroduction-part1-121118111542-phpapp02/85/Ruby-introduction-part1-8-320.jpg)