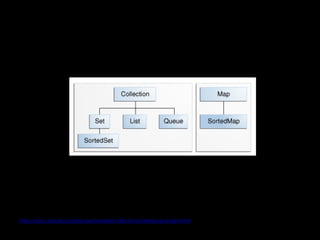
This document provides an introduction to the Java programming language. It discusses Java concepts like object-oriented programming, the Java Virtual Machine, primitive data types, variables, control flow, classes and objects, inheritance, interfaces, exceptions, collections, multithreading, design patterns, and more. It also includes code examples and references to Oracle's Java documentation for further reading.
















![Arrays
int[] grades;
grades = new int[15];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c02-javaprimer-121102141329-phpapp01/85/Mobile-Software-Engineering-Crash-Course-C02-Java-Primer-20-320.jpg)









![void main(string[] args)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c02-javaprimer-121102141329-phpapp01/85/Mobile-Software-Engineering-Crash-Course-C02-Java-Primer-30-320.jpg)
![Instance vs Class methods
void shootBall(Point point)
static void main(string[] args)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c02-javaprimer-121102141329-phpapp01/85/Mobile-Software-Engineering-Crash-Course-C02-Java-Primer-31-320.jpg)