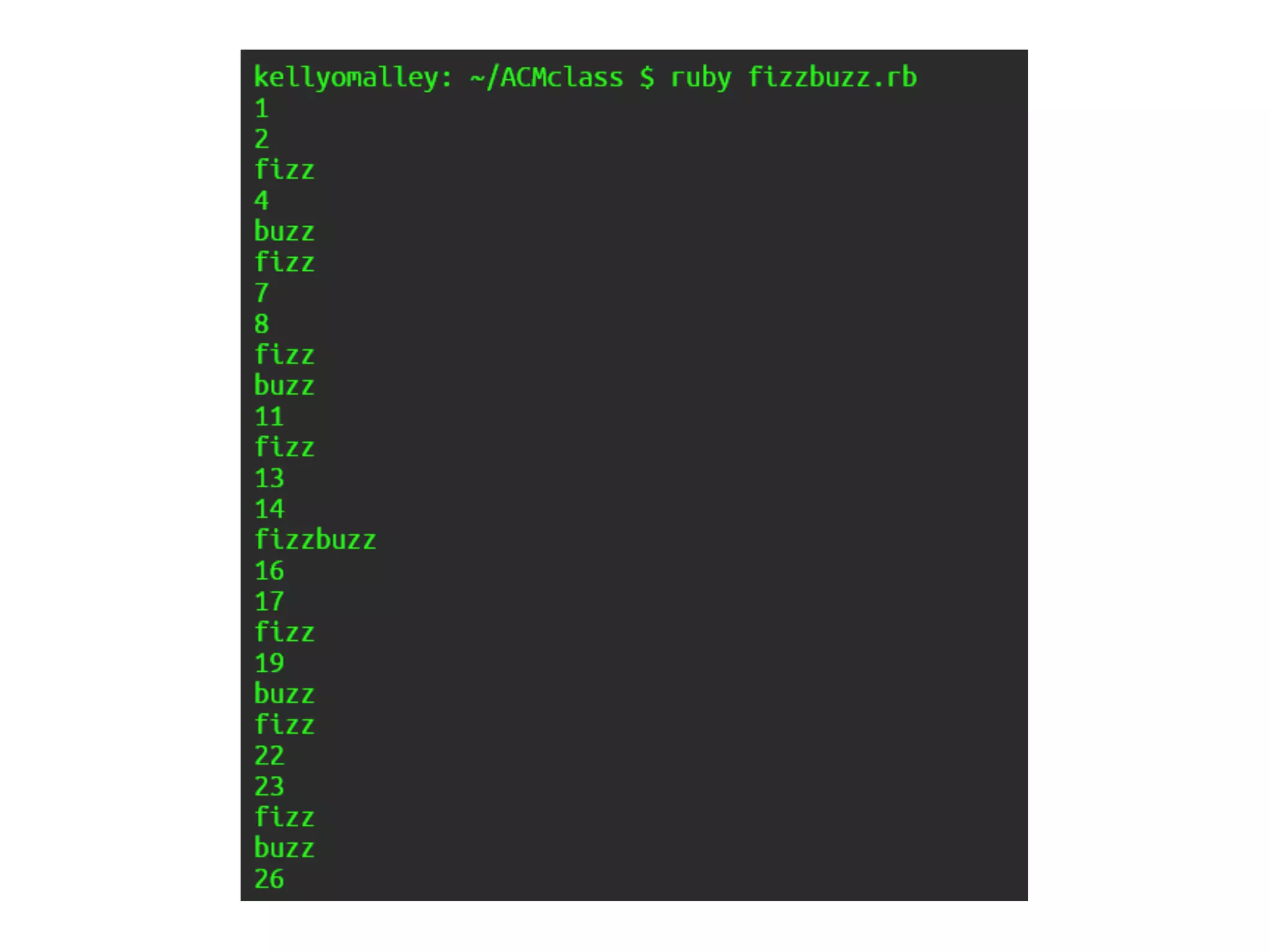
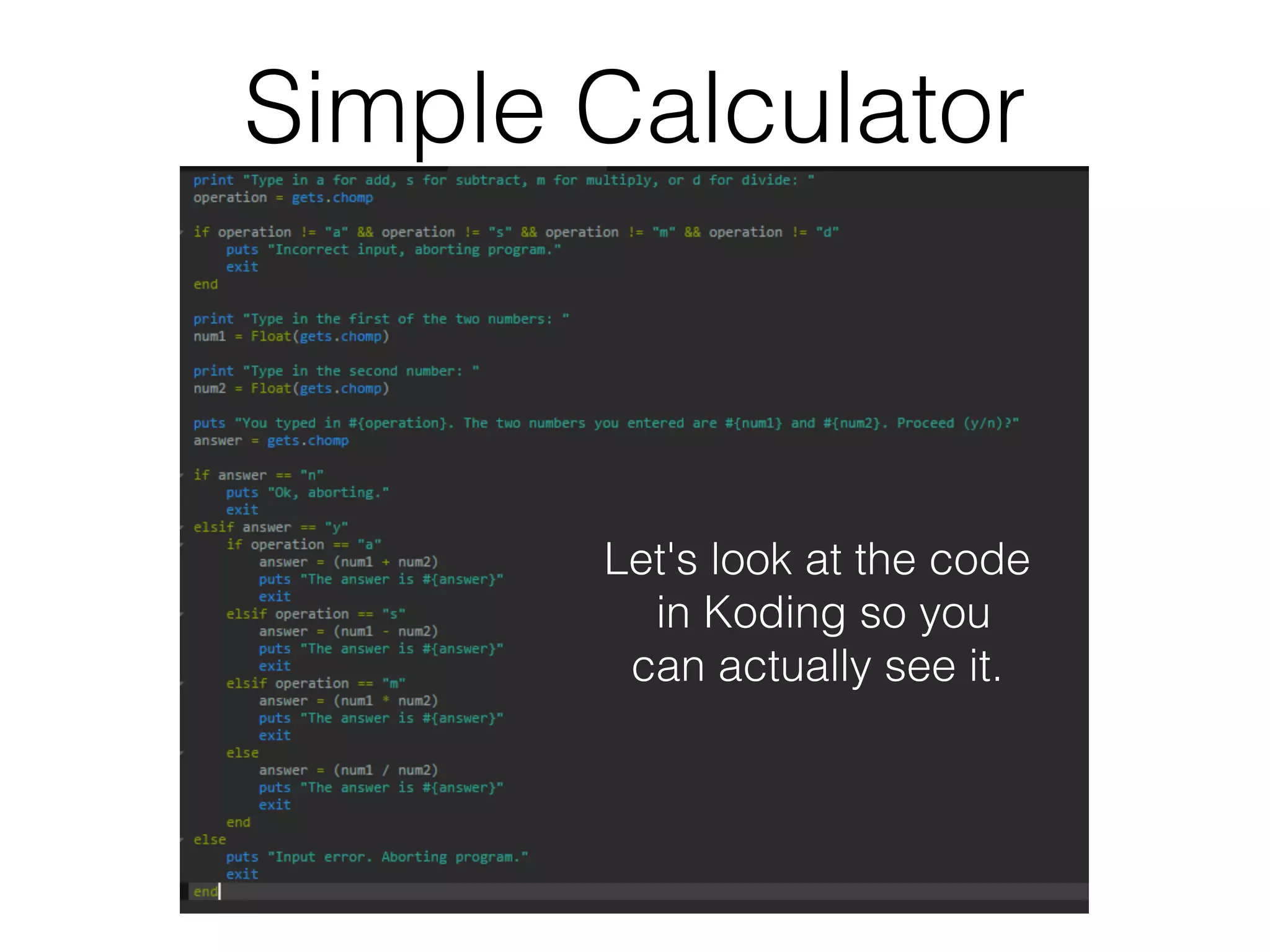
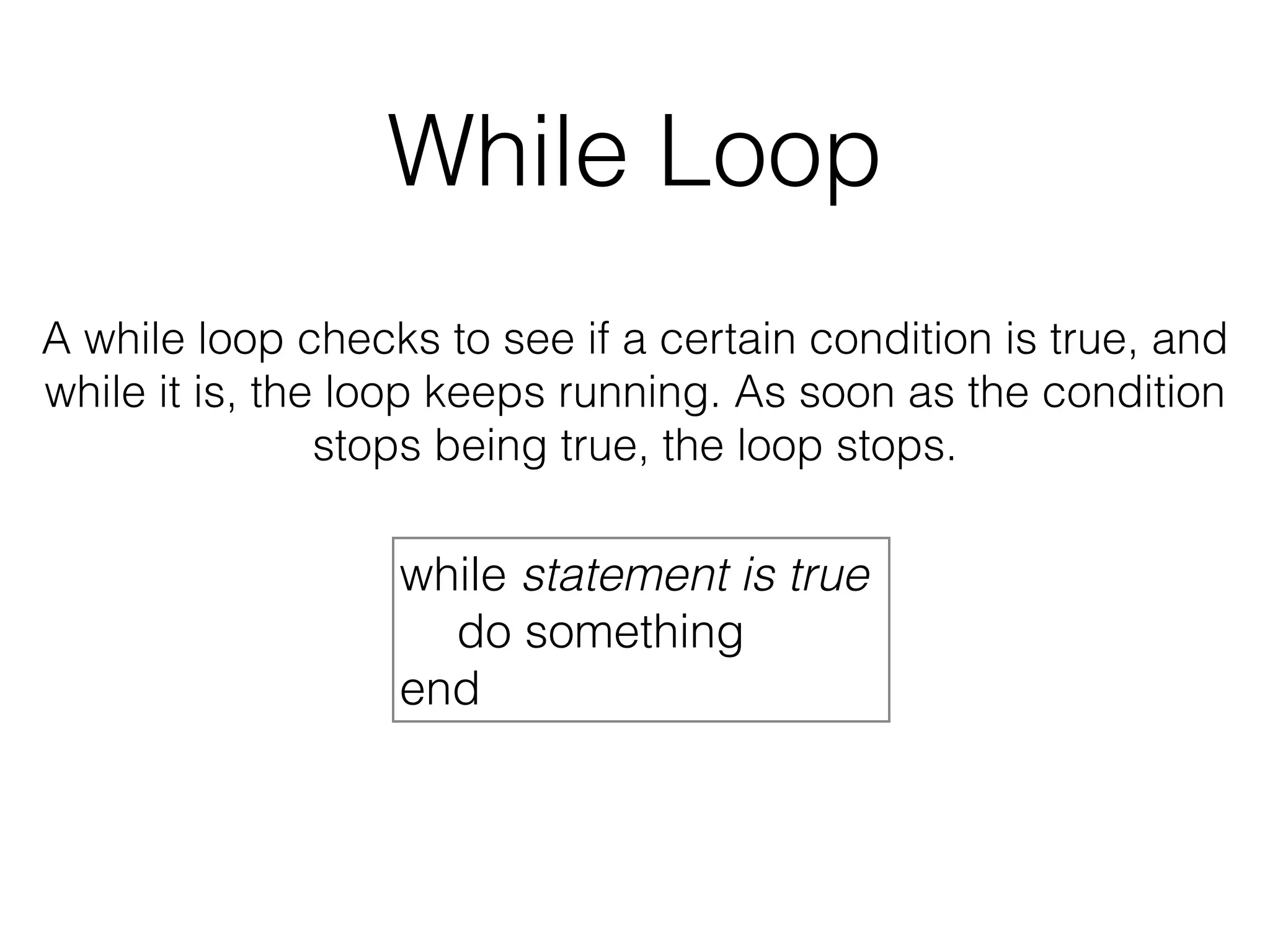
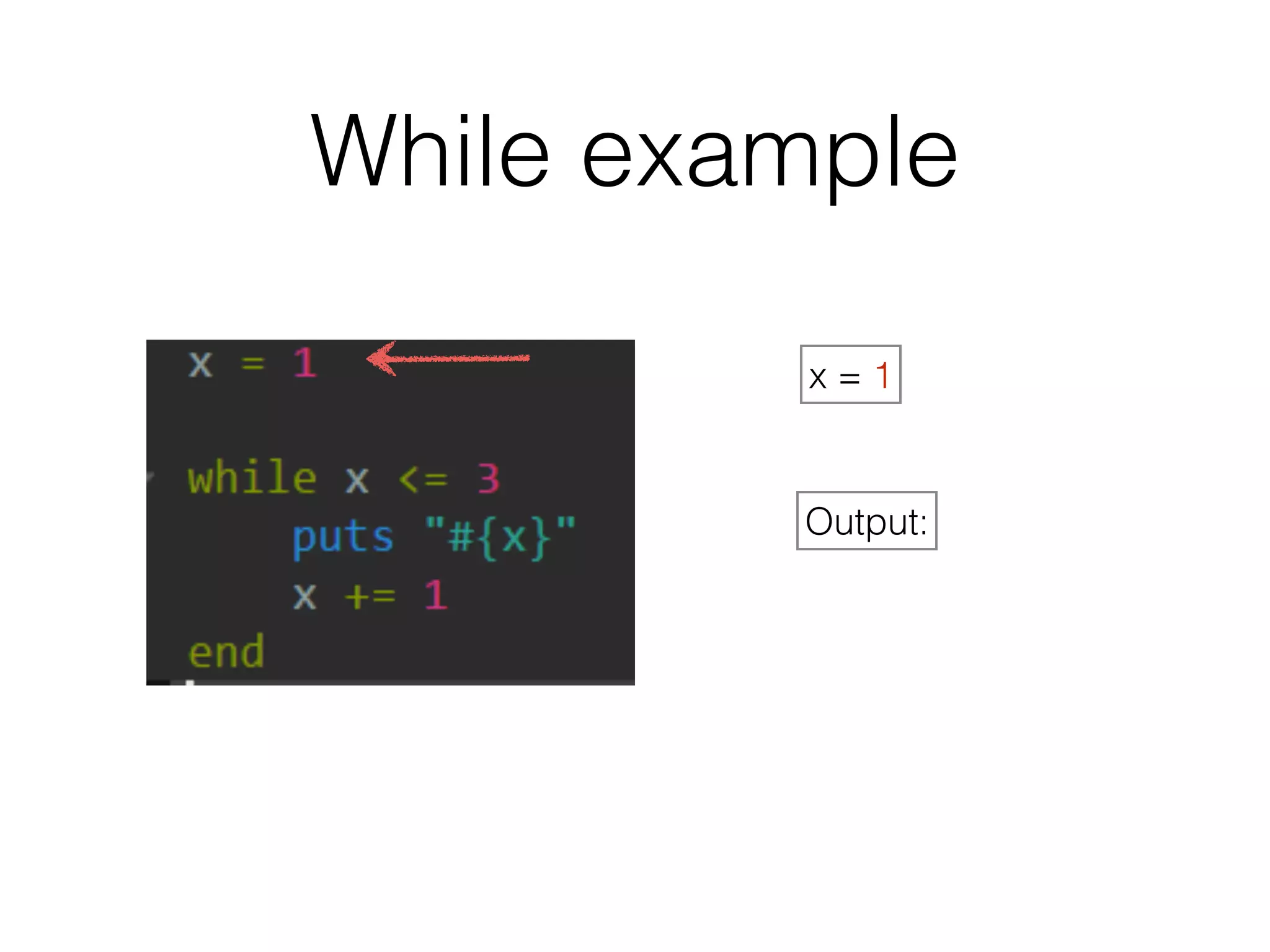
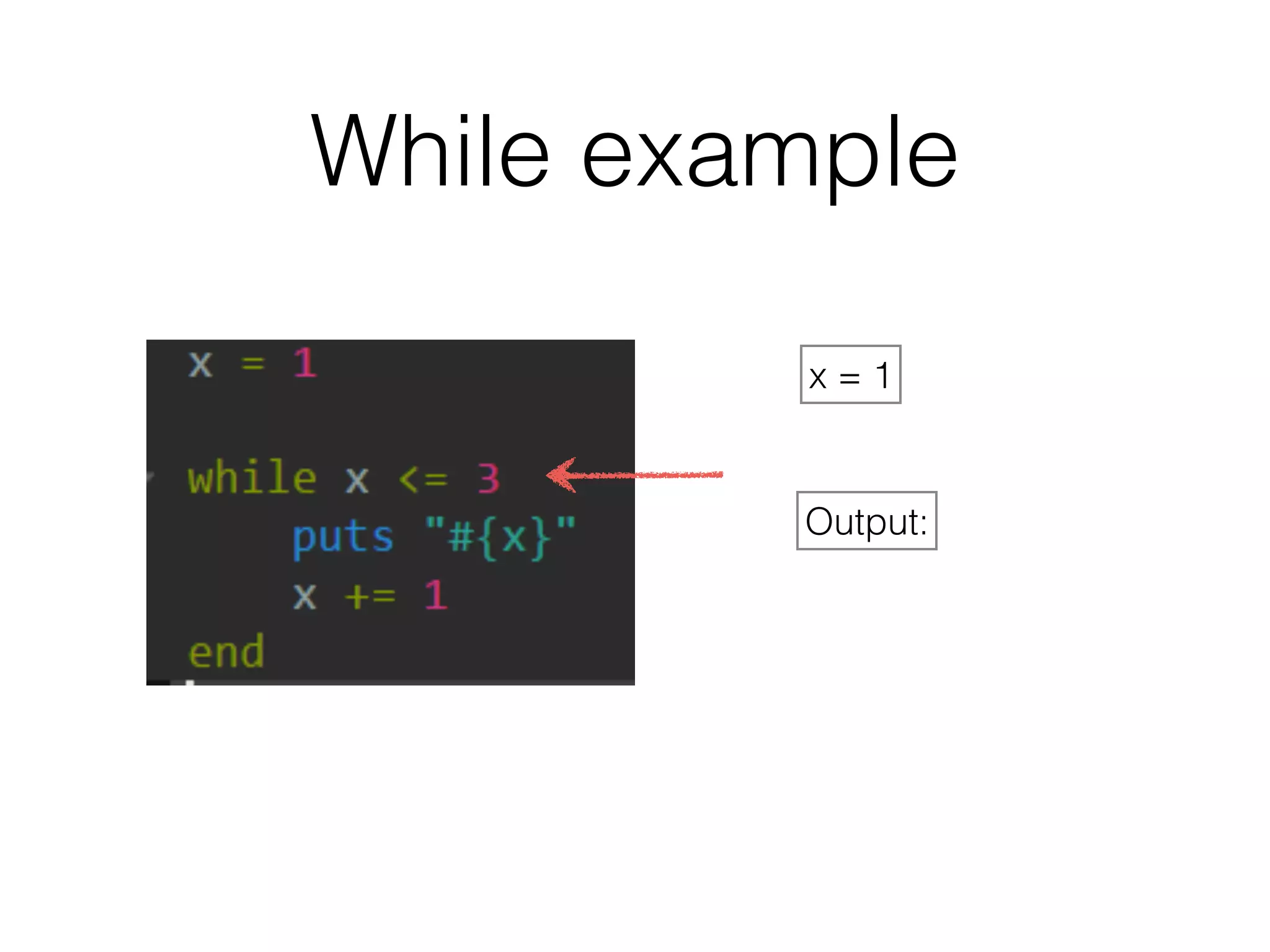
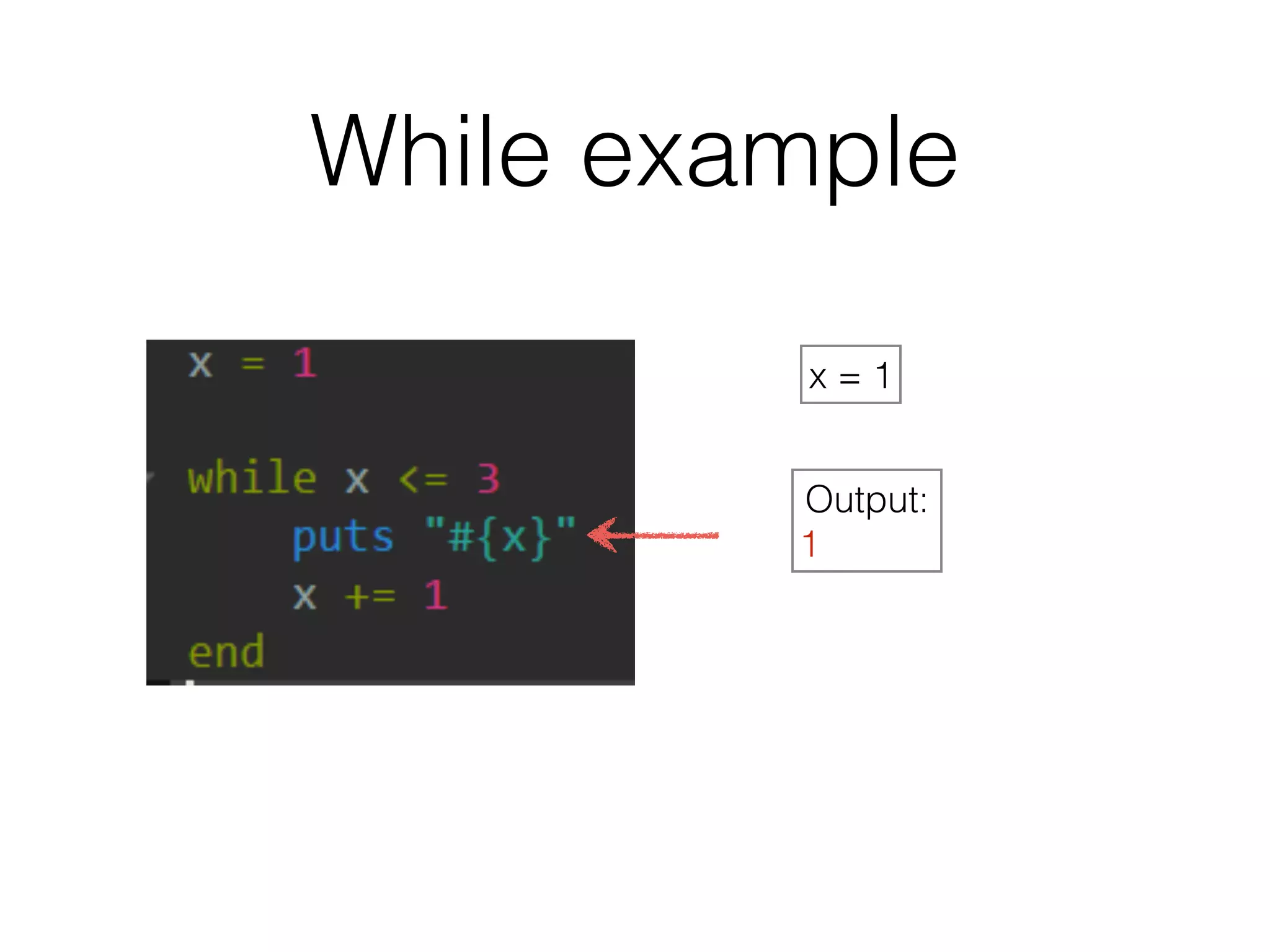
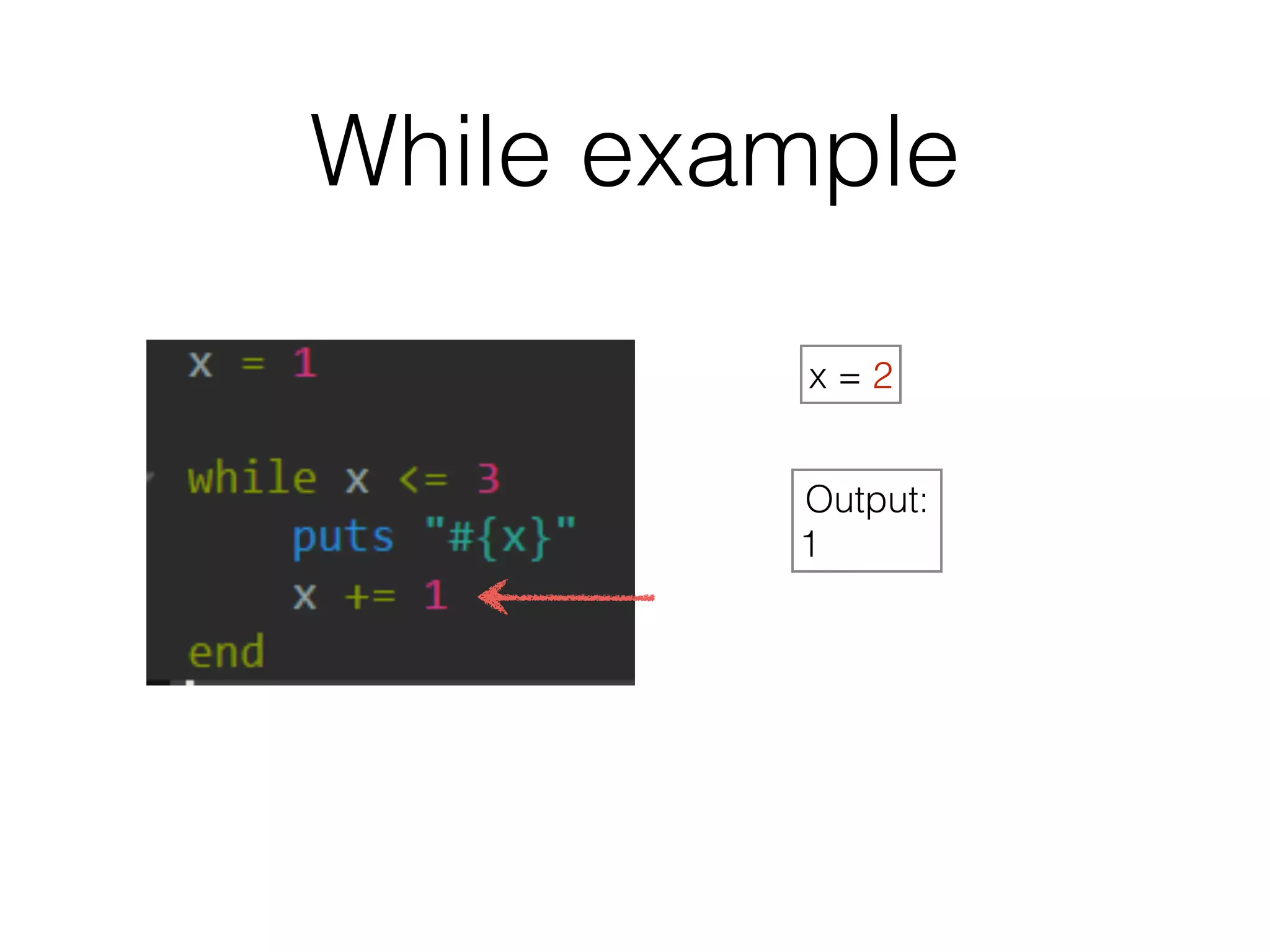
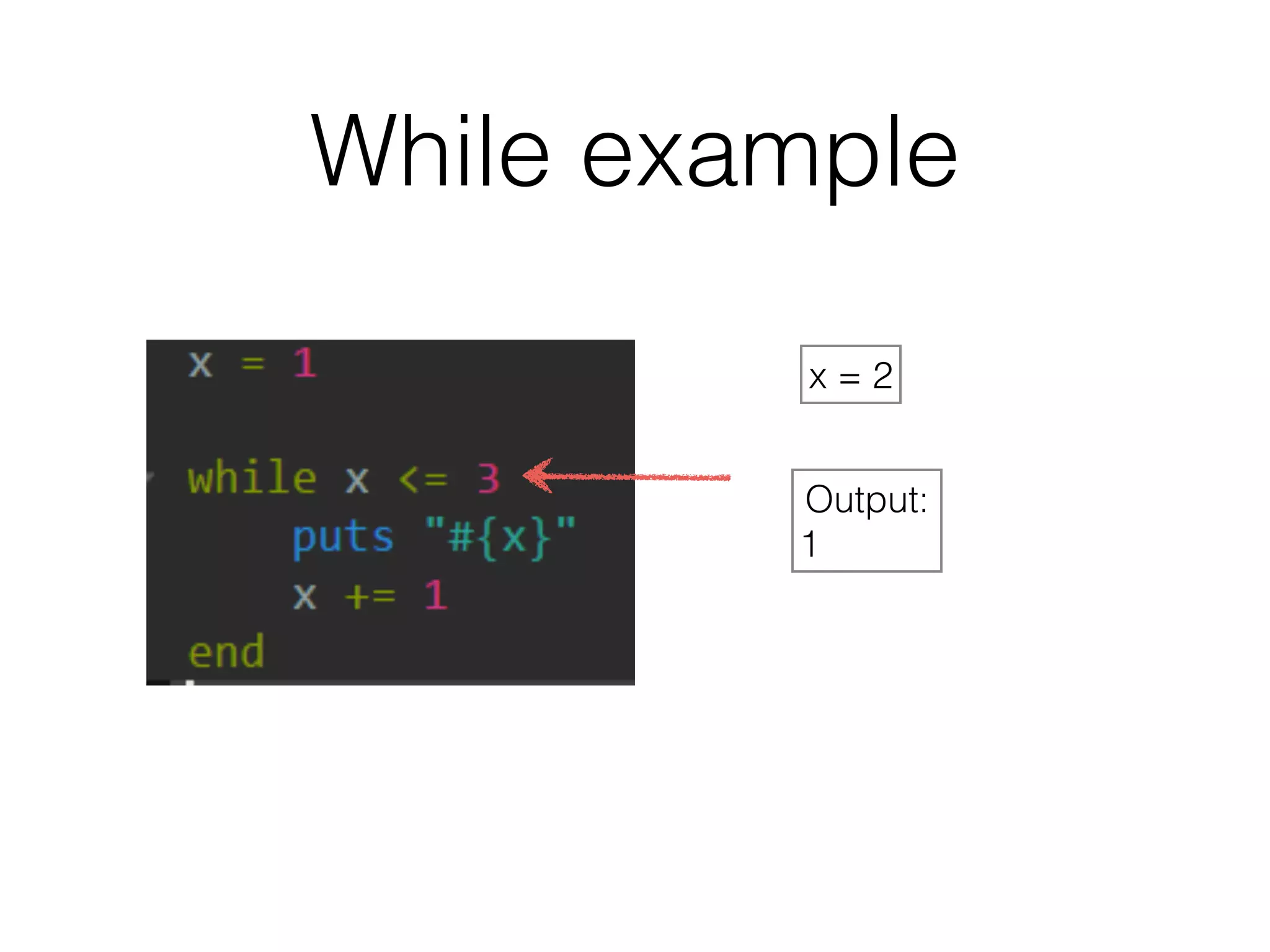
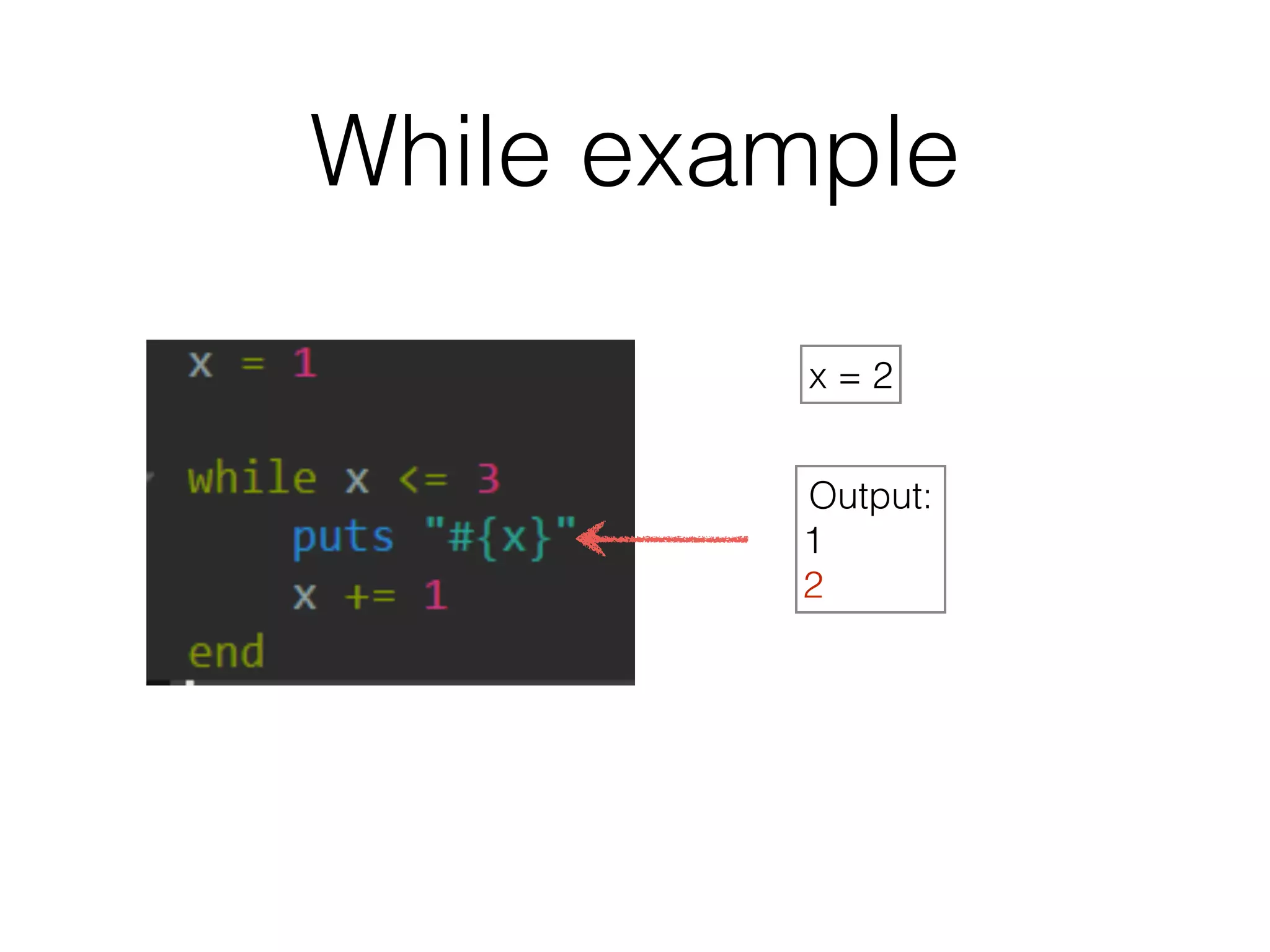
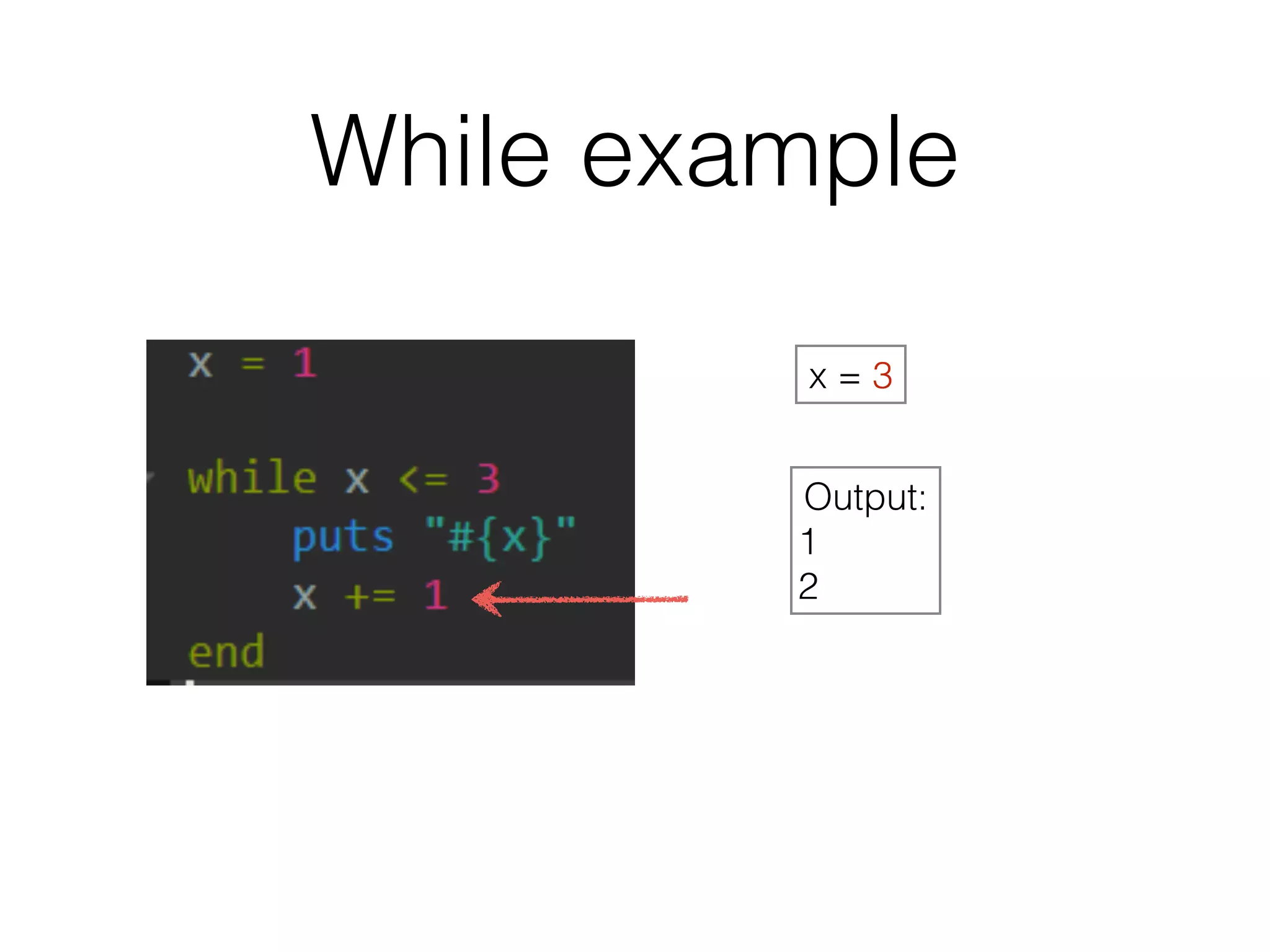
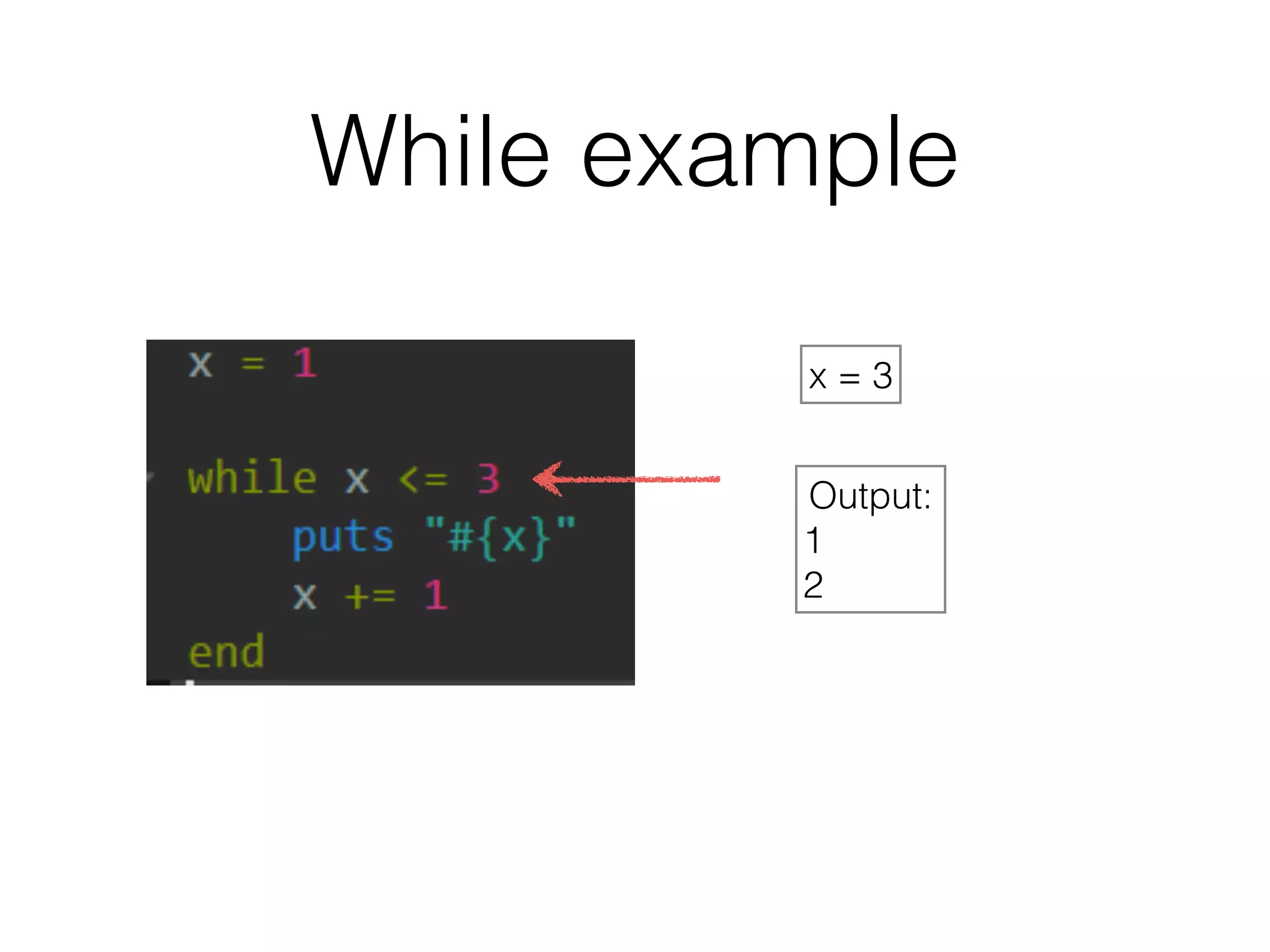
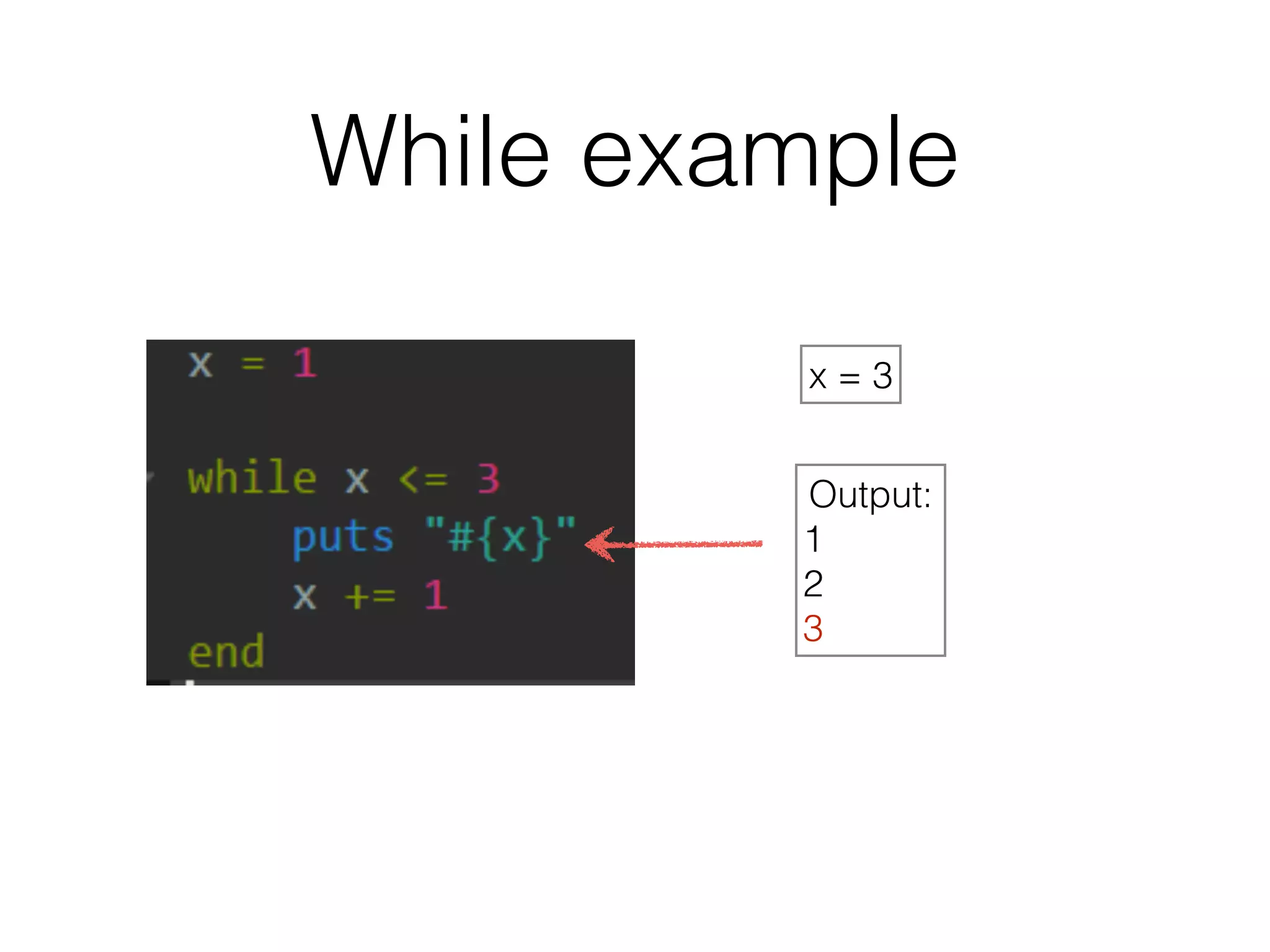
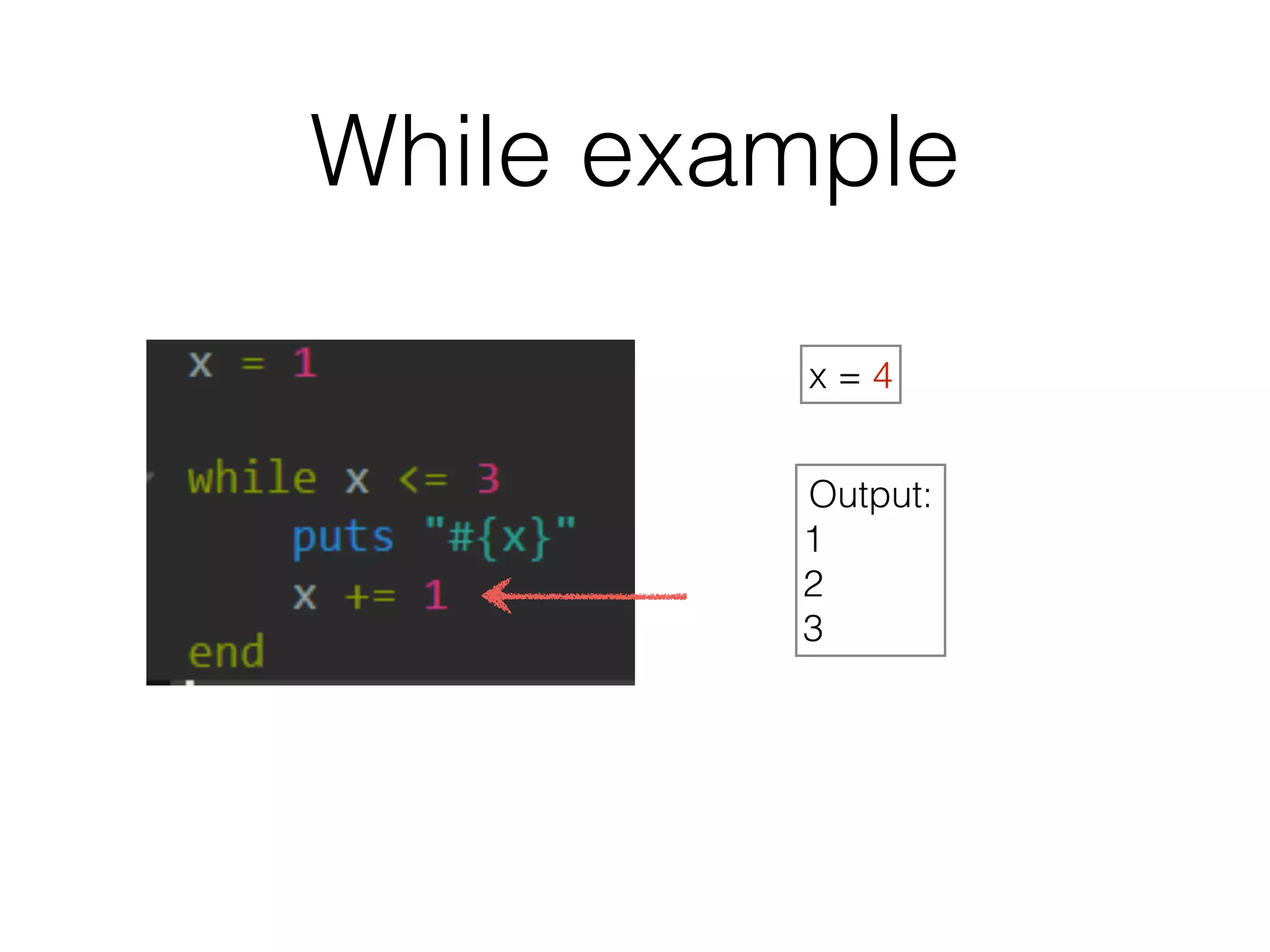
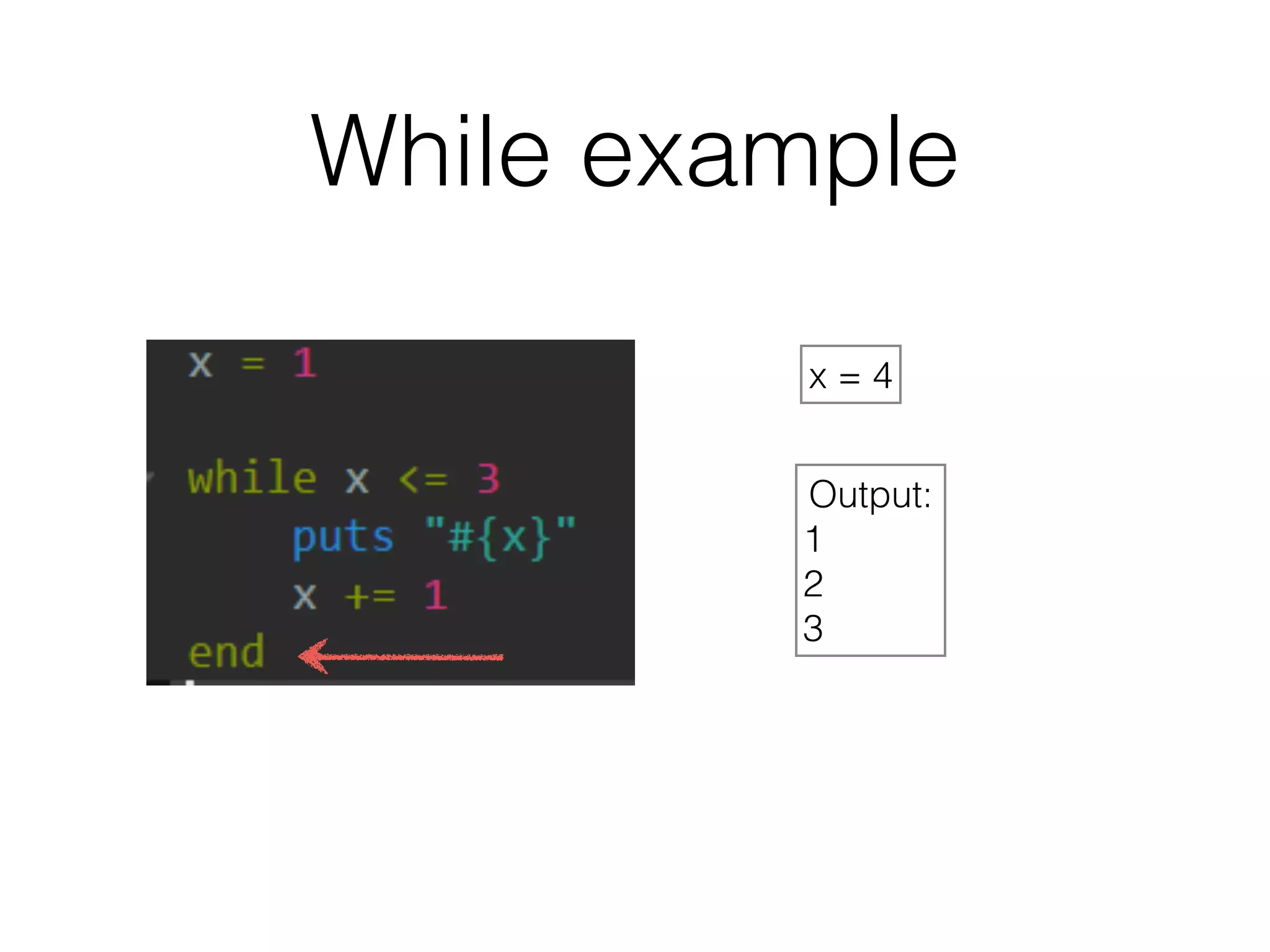
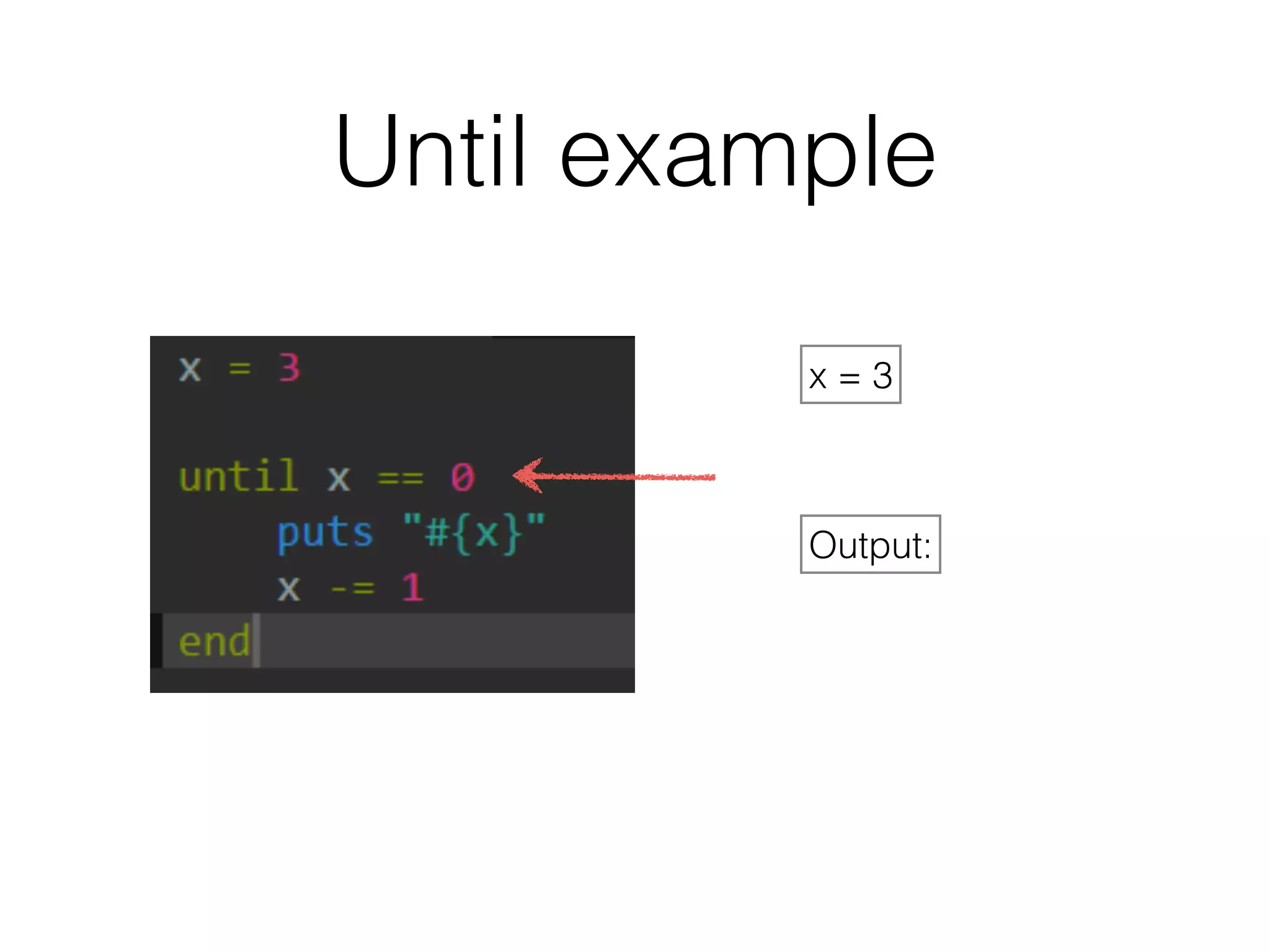
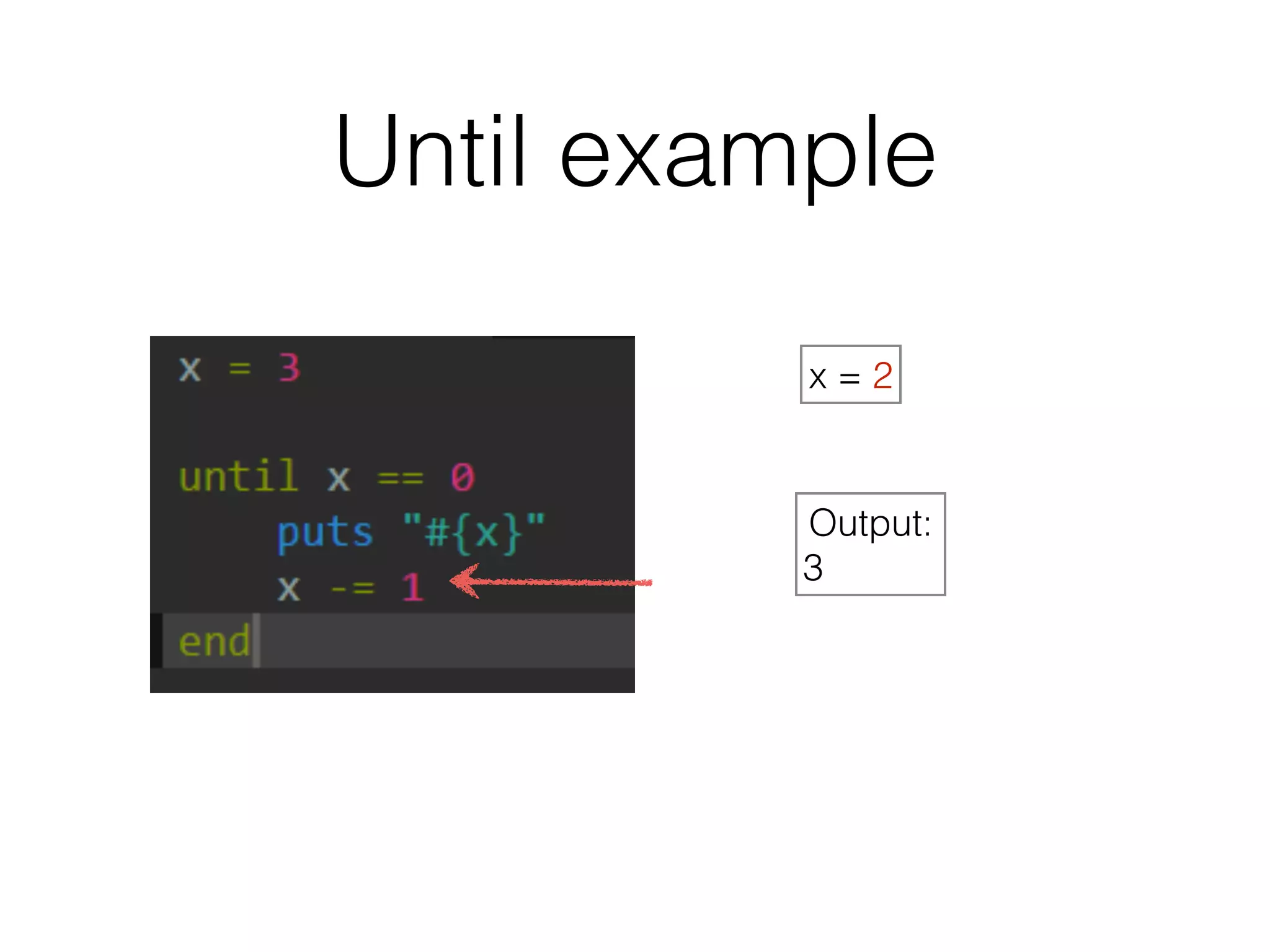
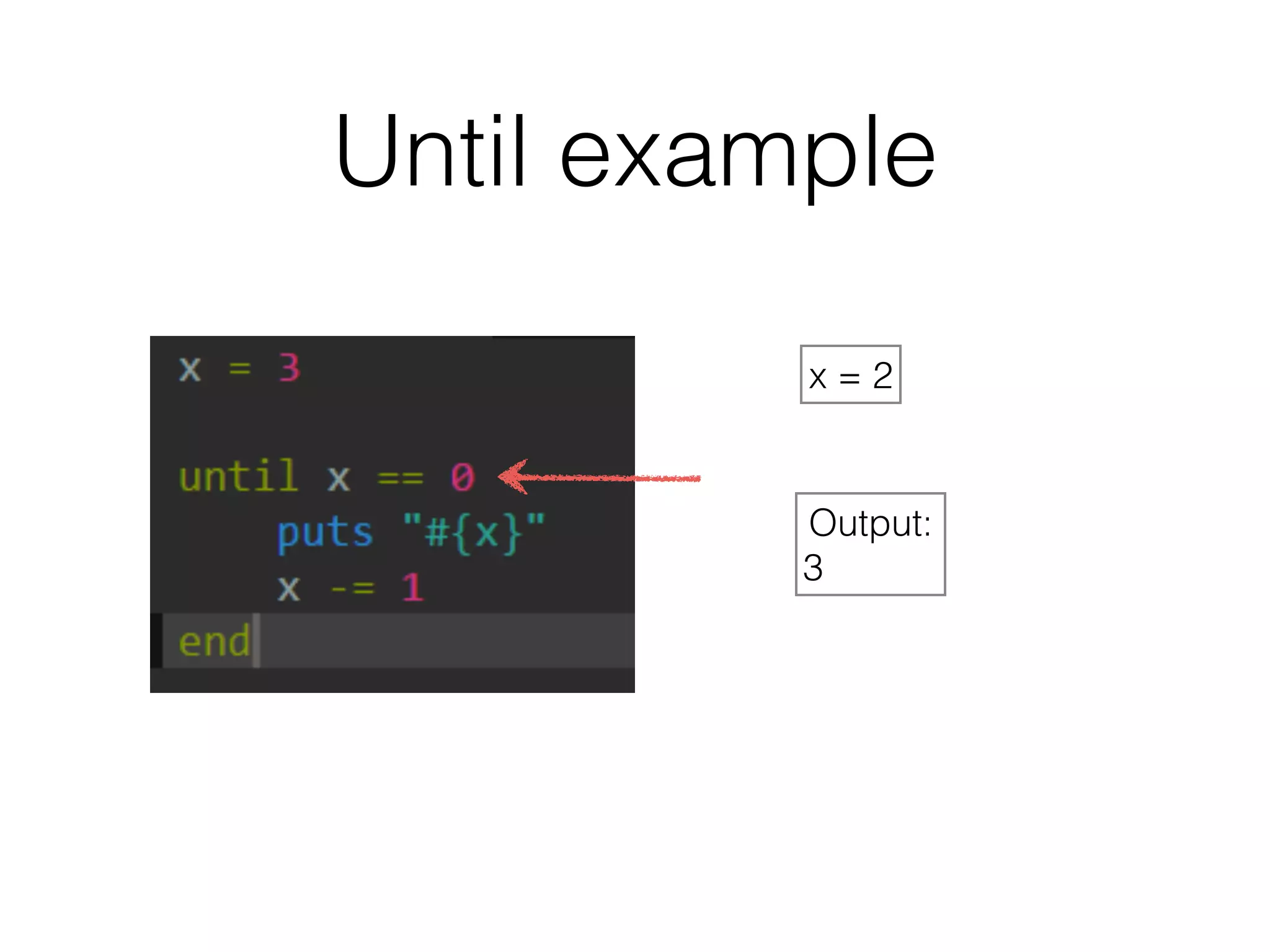
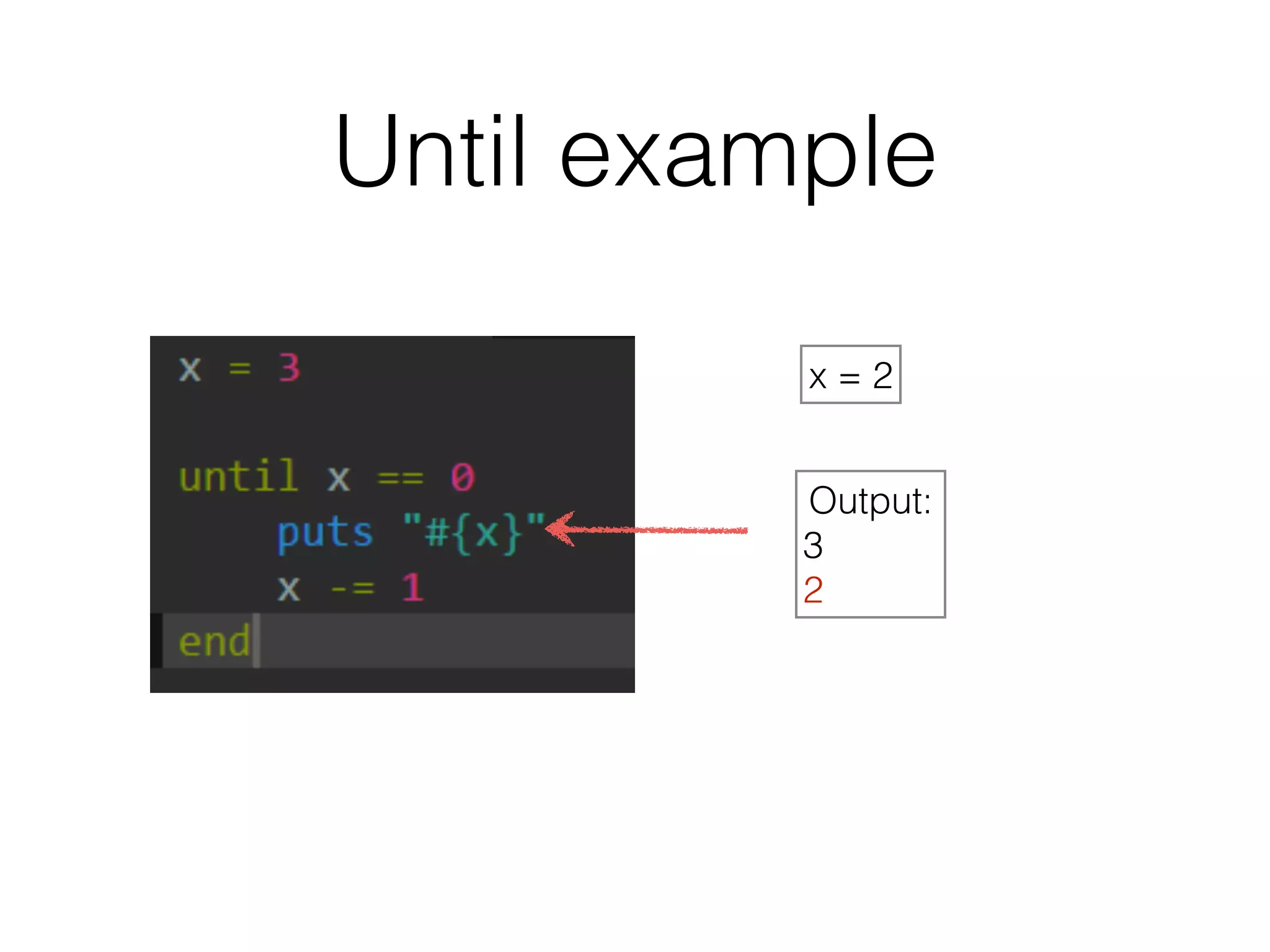
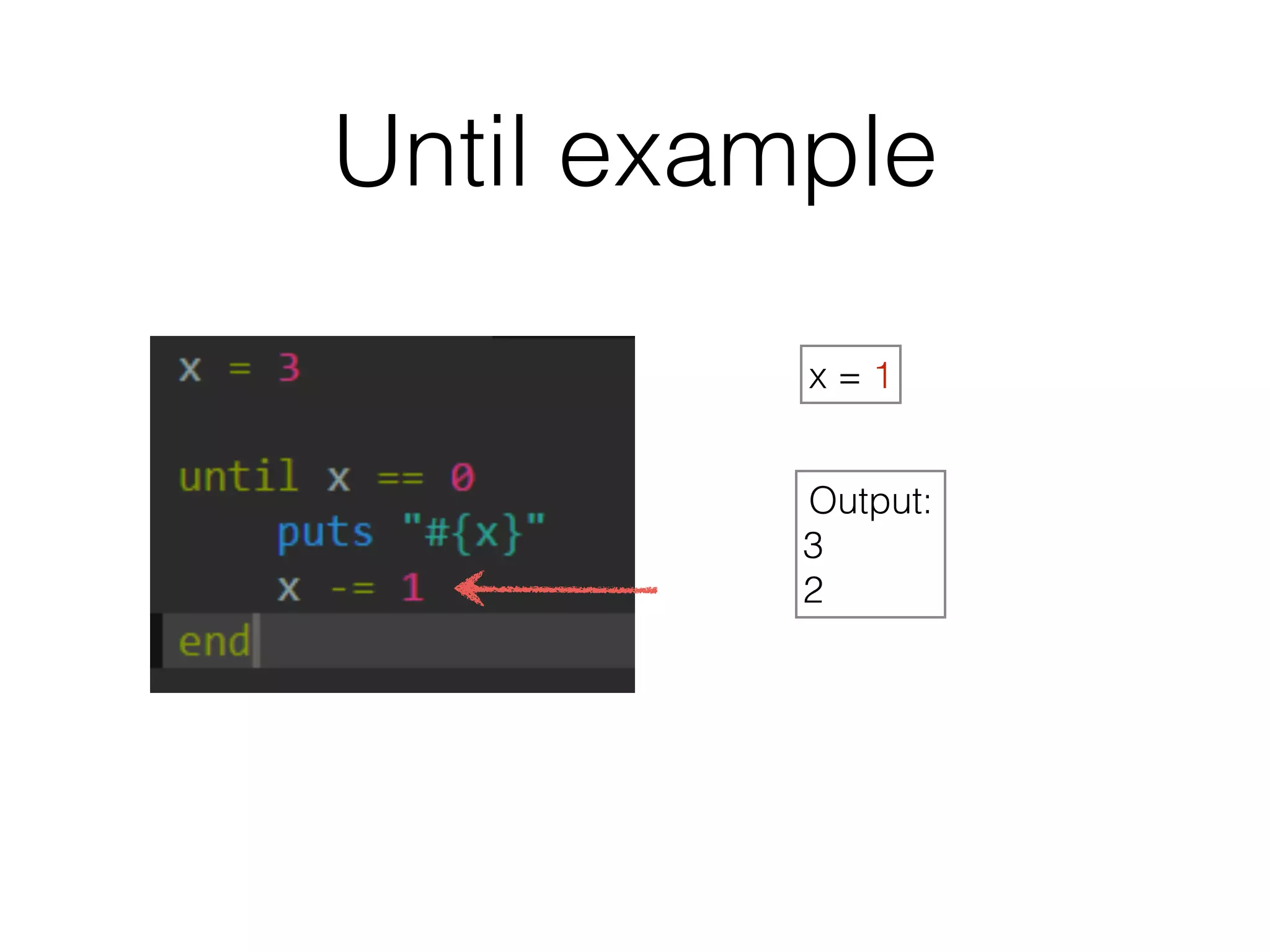
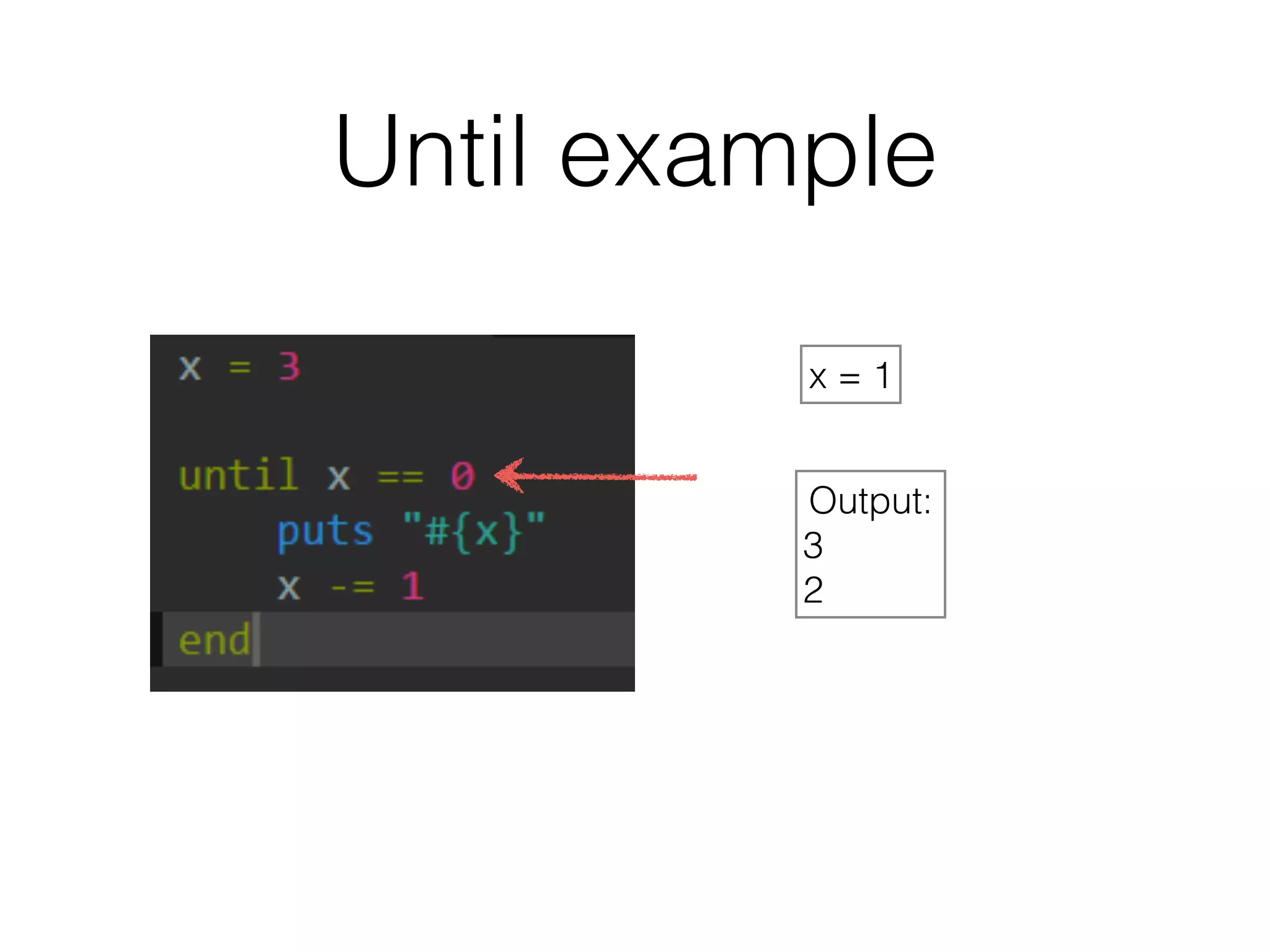
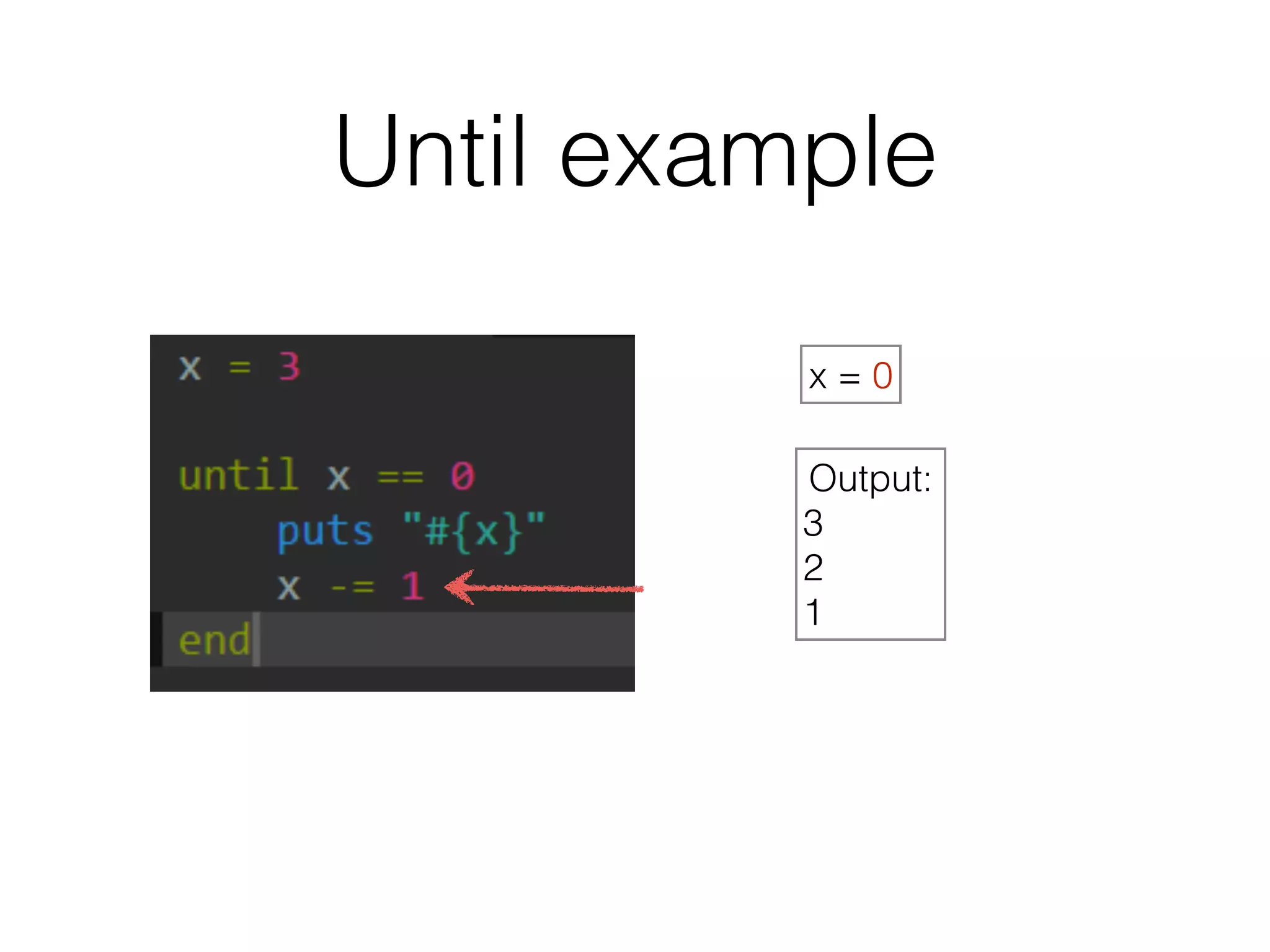
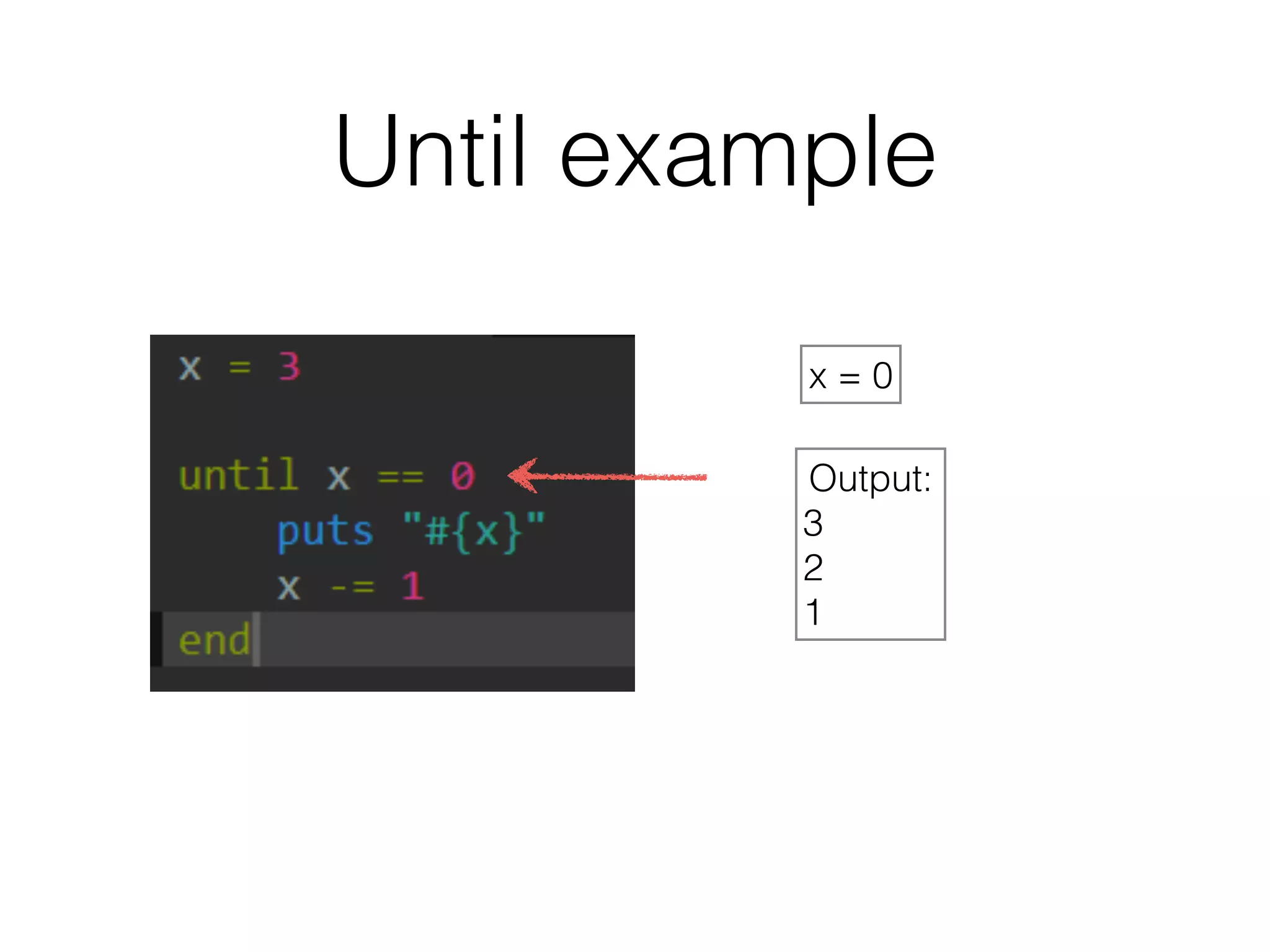
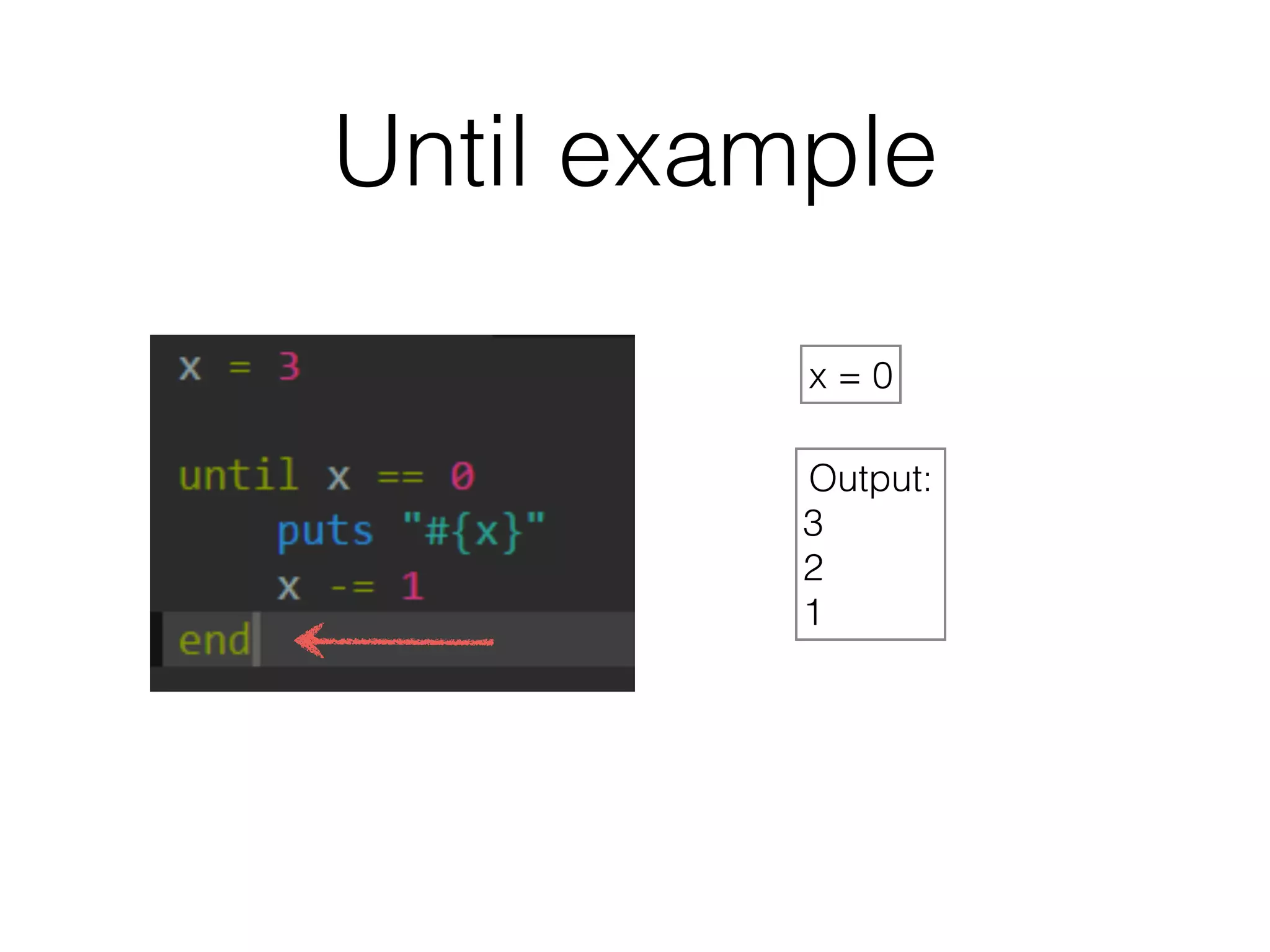
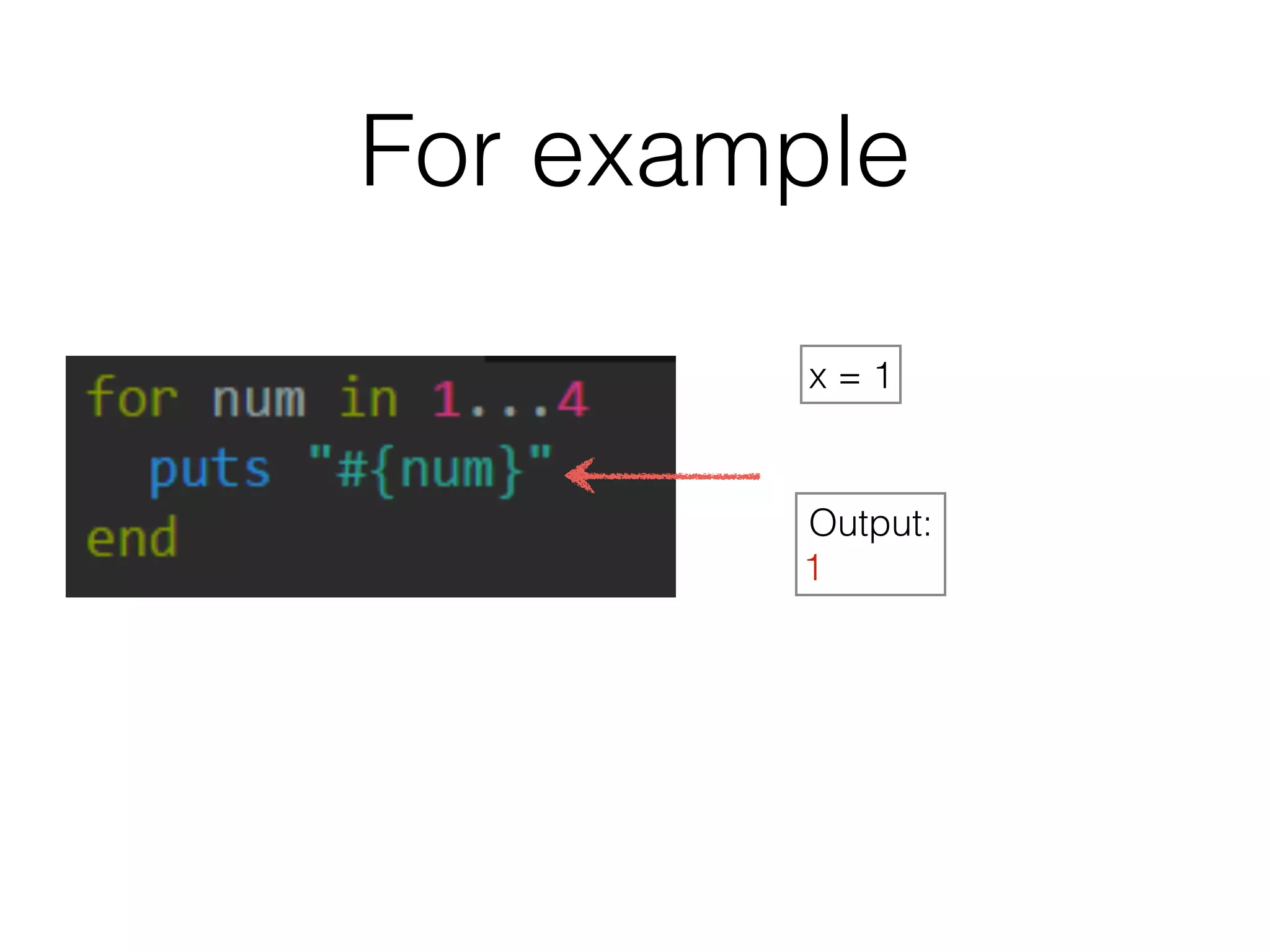
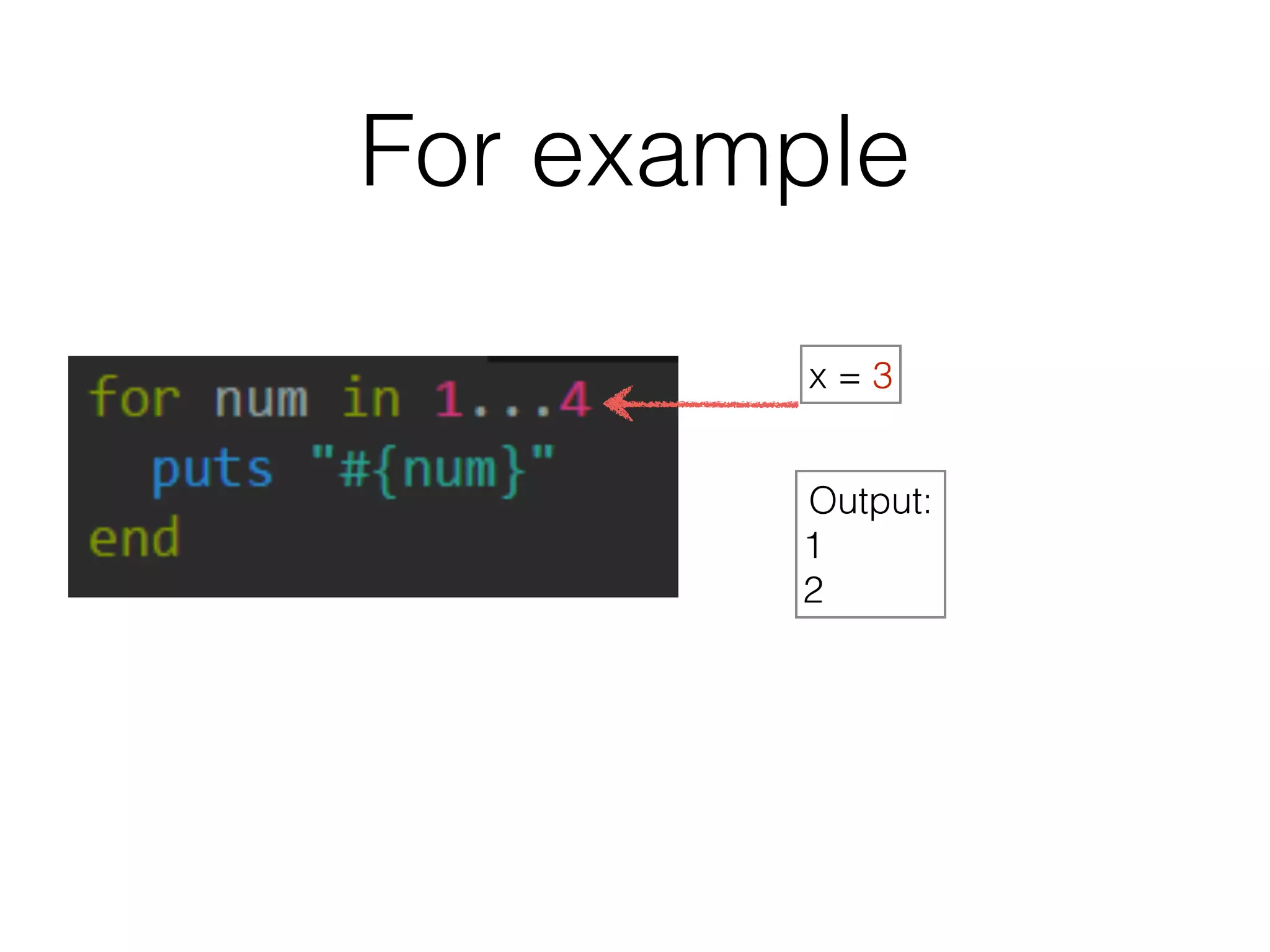
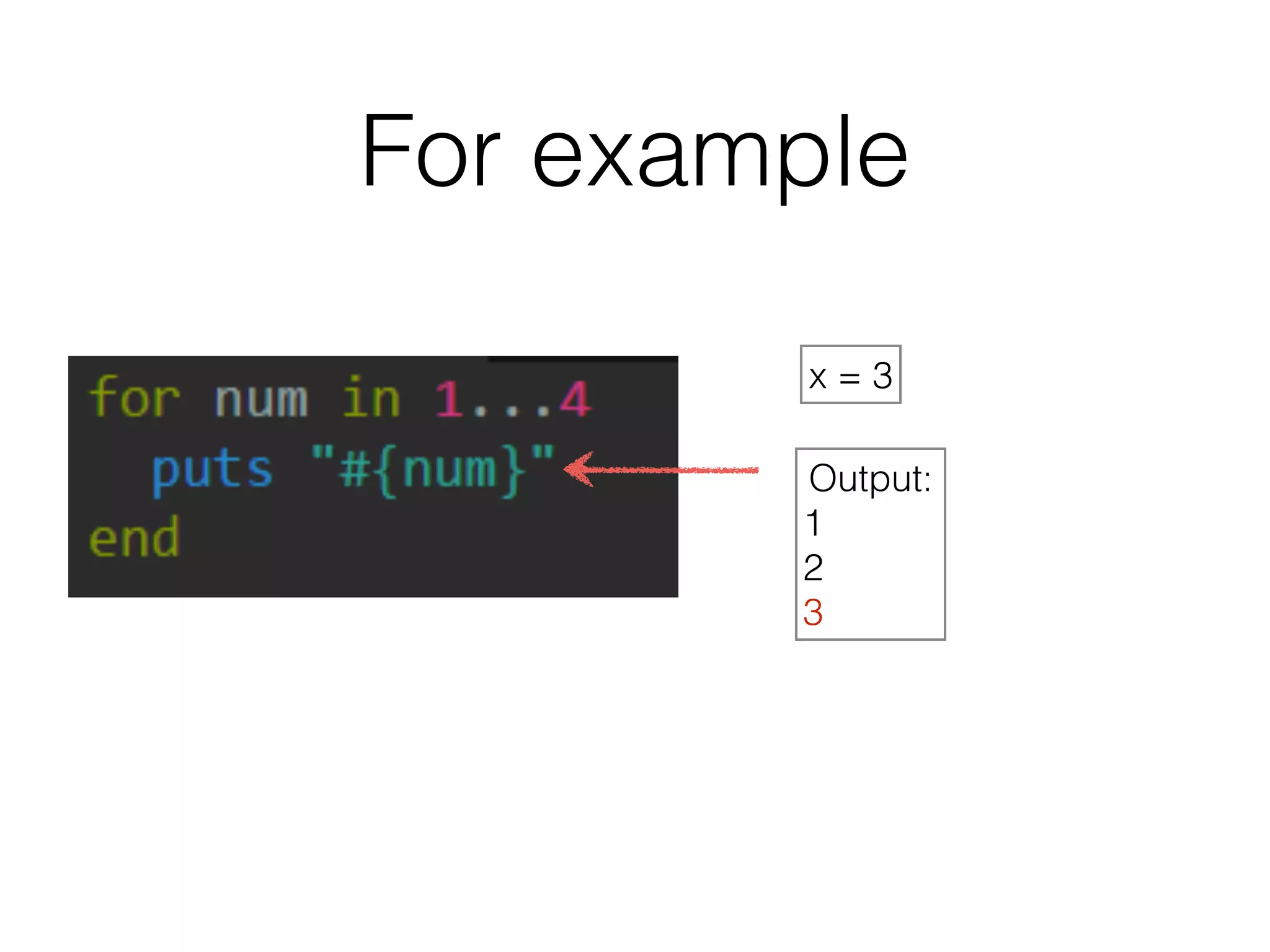
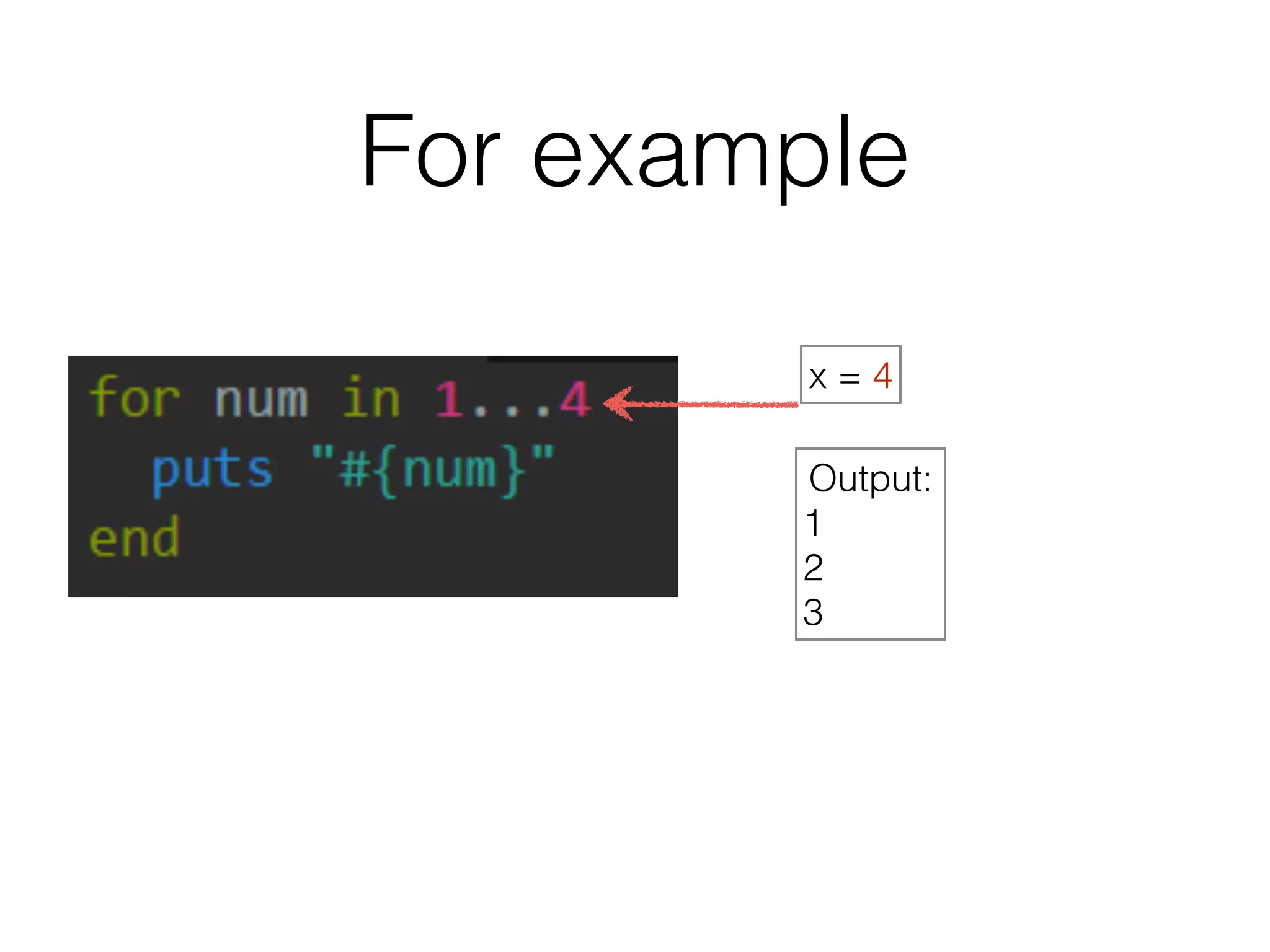
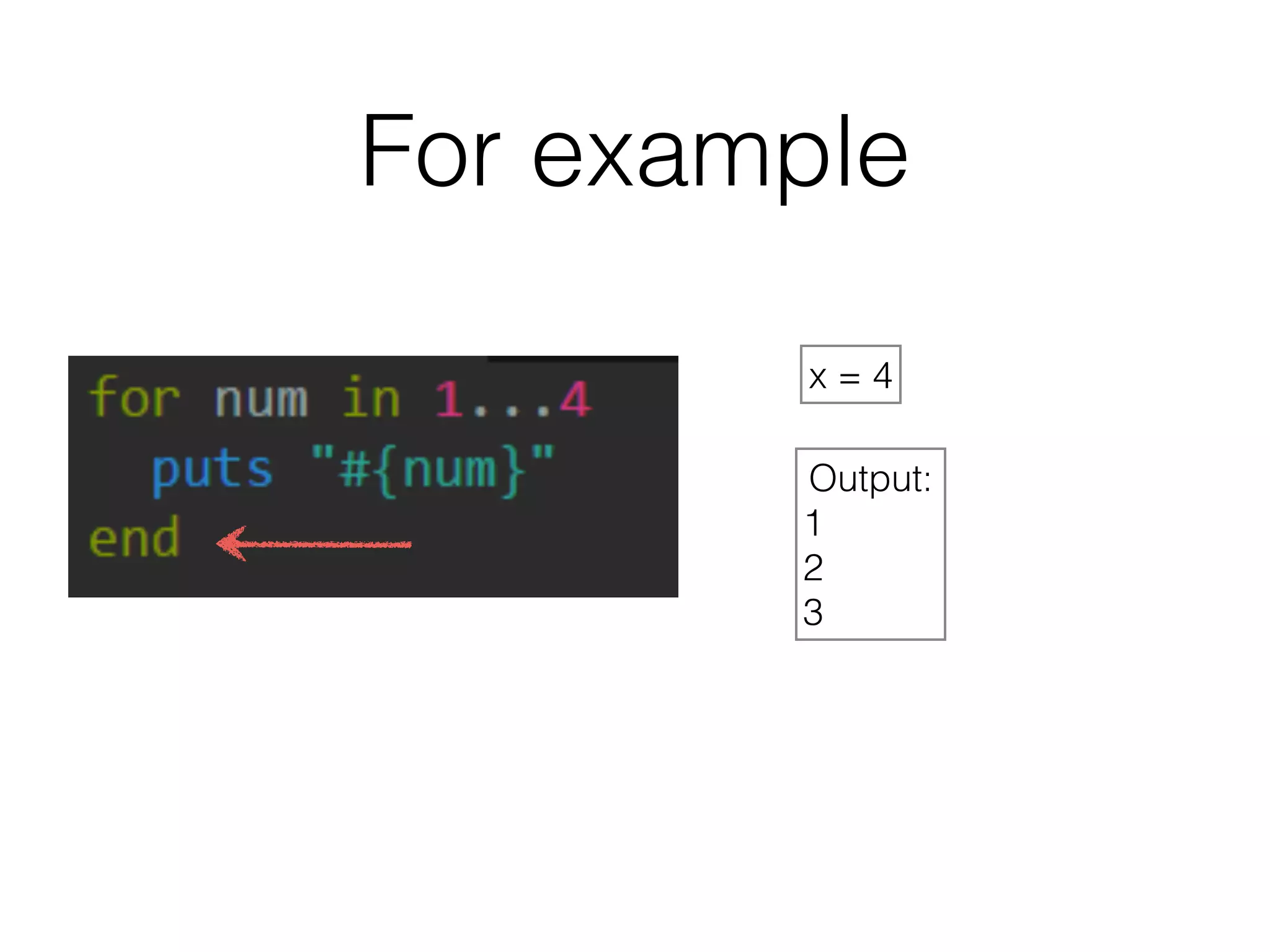
The document discusses loops in Ruby programming. It covers while, until, and for loops with examples. It also discusses arrays and sorting arrays. The homework assignment is to write a FizzBuzz program that prints numbers from 1 to 100, replacing multiples of 3 with "Fizz", multiples of 5 with "Buzz", and multiples of both with "FizzBuzz".


































![Array indices
What if we have the array {15, 27, 21, 13, 44, 17}?
my_array = [15, 27, 21, 13, 44, 17]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson3-141105204414-conversion-gate01/75/Init-Lesson-3-62-2048.jpg)
![Accessing Array Elements
How do we actually get to a specific element of an array? Let's
try to get the third number of the following array:
The third number's index is 2. Therefore, to get the third
element of this array we would type in 'my_array[2]'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson3-141105204414-conversion-gate01/75/Init-Lesson-3-63-2048.jpg)
![General Array Access
There is a general formula for accessing array elements:
array_name[element# - 1]
For example, if we have an array called 'string_array' and we
want to print out the fourth element we would type:
Will print out 'cheese'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson3-141105204414-conversion-gate01/75/Init-Lesson-3-64-2048.jpg)