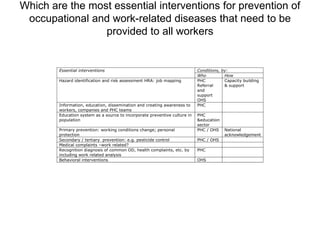
This document outlines the agenda for four parallel working sessions at a conference on occupational health and safety. Roundtable 1 focuses on universal healthcare coverage strategies. Roundtable 2 discusses people-centered care and the roles of primary care and occupational health. Roundtable 3 addresses participatory governance and considering worker health in healthcare reforms. Roundtable 4 explores integrating worker health into non-health policies and national occupational health programs through primary care.