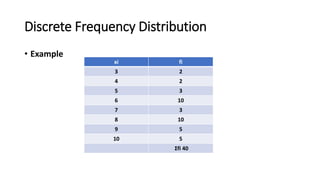
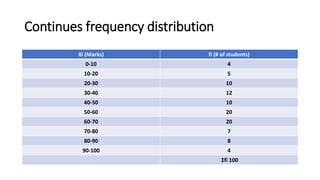
This presentation introduces various topics in social statistics. It defines social statistics as a set of procedures to organize, arrange, and communicate data. It discusses grouped and ungrouped data, including discrete and continuous frequency distributions. Descriptive statistics are defined as data presented in words, while inductive statistics are used to draw conclusions and predict future behavior. Different scales of measurement are also introduced, including nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio scales.