- Recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL), defined as two or more pregnancy losses, is a serious problem that impacts women psychologically and socially.
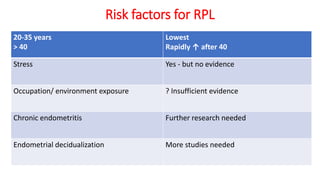
- The causes of RPL are often unknown, but can include genetic factors, anatomical abnormalities, endocrine/metabolic issues, autoimmune disorders like antiphospholipid syndrome, and lifestyle factors.
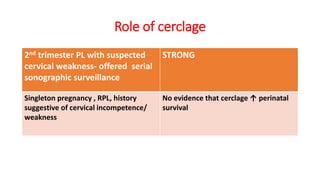
- Evaluation of RPL involves screening for causes like thyroid abnormalities, luteal phase defects, hyperprolactinemia, antiphospholipid syndrome, uterine anomalies, and counseling regarding lifestyle modifications. Treatment depends on the underlying cause but may include thyroid supplementation, progesterone, low-dose aspirin, anticoagulants, and surgery.