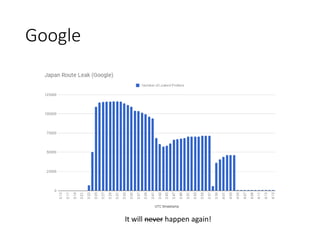
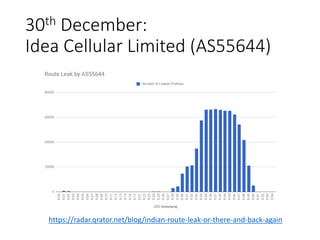
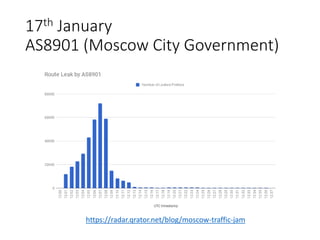
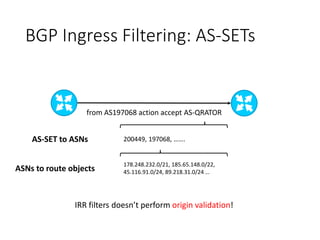
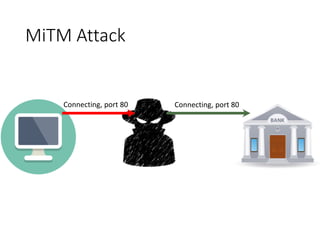
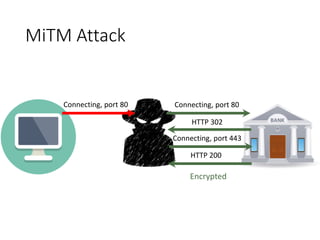
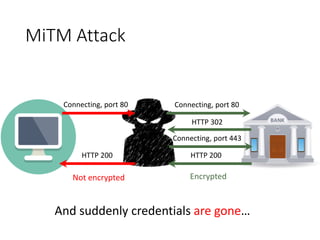
This document discusses BGP route leaks and hijacks, and issues with using AS-SETs and IRR filters to prevent them. The key points are:
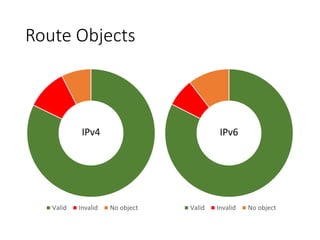
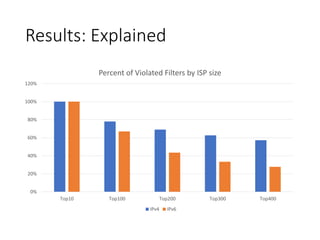
1. The document analyzes routing data and finds that at least 7% of IPv4 ISPs and 1% of IPv6 ISPs have problems with invalid BGP route advertisements violating their advertised filters.
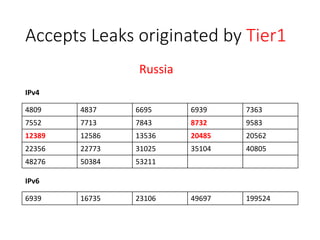
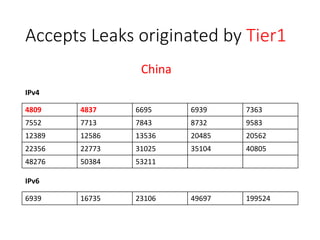
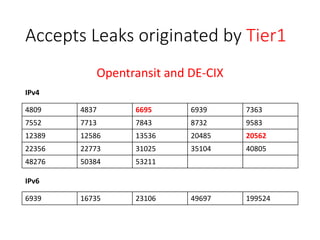
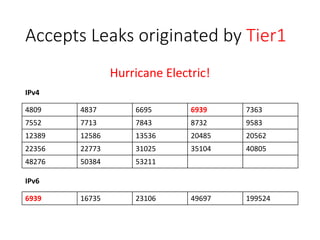
2. Major tier 1 and tier 2 networks are found to accept route leaks not originating from their own networks, failing to properly filter routes according to their AS-SETs.
3. Properly configured and maintained AS-SETs and IRR filters could help reduce route leaks and hijacks, but many networks have poorly maintained filters or