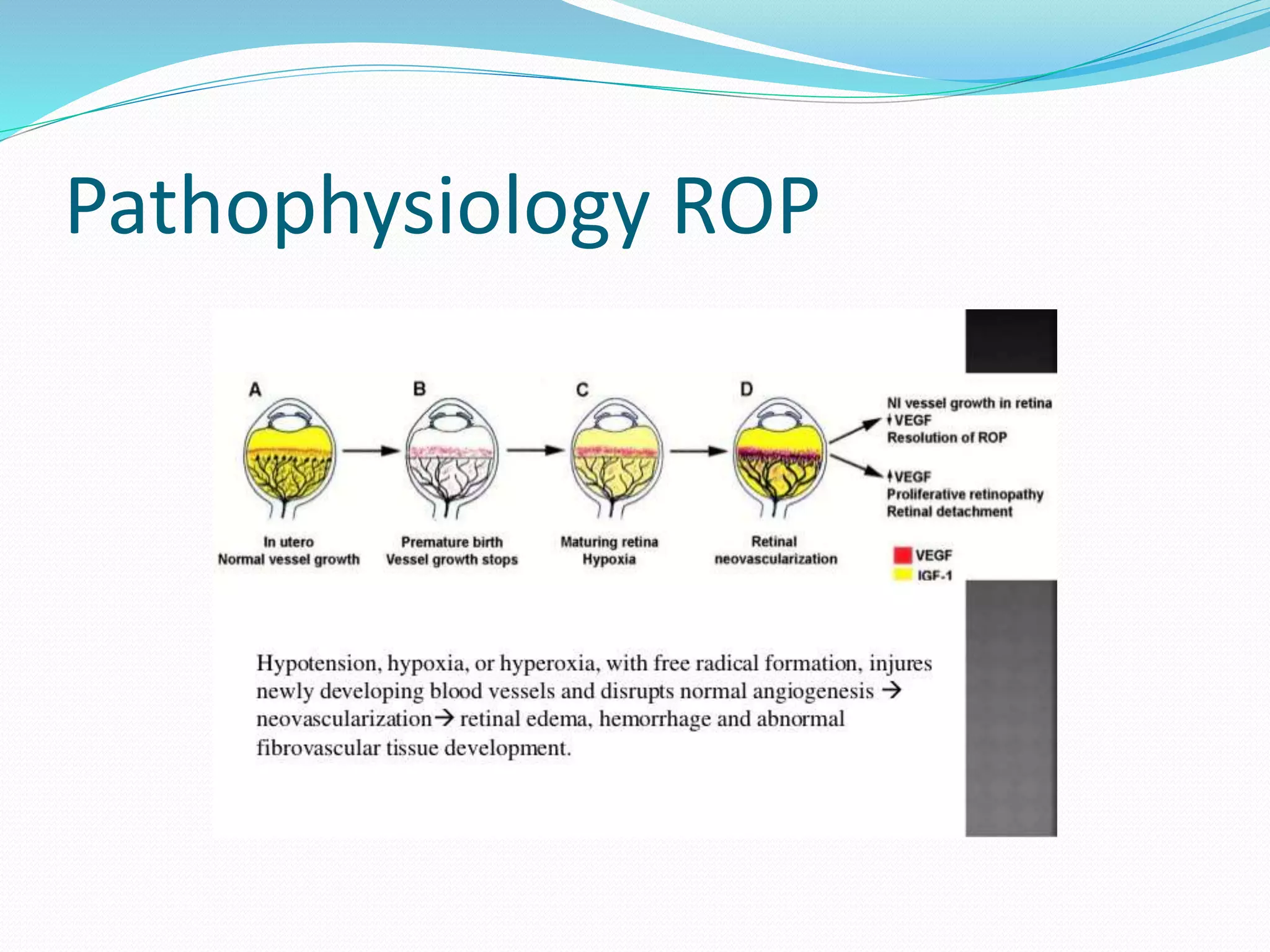
This document discusses retinopathy of prematurity (ROP), a retinal disorder primarily affecting preterm and low birth weight babies. ROP is a leading cause of childhood blindness globally. Key risk factors include prematurity, low birth weight, and prolonged oxygen therapy. The document outlines screening guidelines for ROP, including which infants should be screened based on gestational age and birth weight. It describes the examination procedure and classification system used to stage ROP based on location and severity. Treatment thresholds and follow up schedules are also discussed.