Root Cause Analysis (RCA) Concept and Applications:
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a methodology used to identify the fundamental causes of problems, aiming to prevent their recurrence rather than just addressing the symptoms. RCA helps improve processes, increase efficiency, and minimize losses across industrial, medical, and administrative fields.
**Concept of RCA**
Instead of dealing with problems superficially, RCA delves deeply into the factors that led to an issue, helping to find sustainable solutions. It relies on systematic questioning and data analysis to uncover the root cause.
Steps of RCA:
- Identify the Problem: Clearly describe the issue, including details and effects.
- Collect Data: Analyze how and when the problem occurred and who was affected.
- Determine Possible Causes: Examine processes and factors that may have led to the problem.
- Analyze the Root Cause: Use techniques like 5 Whys and Fishbone Diagram to pinpoint the actual root cause.
- Propose Solutions: Develop corrective actions to address the root cause.
- Implement Solutions: Apply preventive measures and test their effectiveness.
- Monitor & Evaluate: Review results to ensure the problem does not recur.
Popular RCA Techniques:
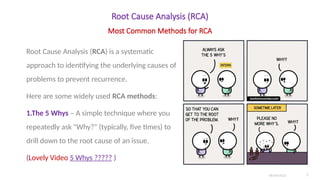
- 5 Whys: Asking "Why did this happen?" multiple times to reach the underlying cause.
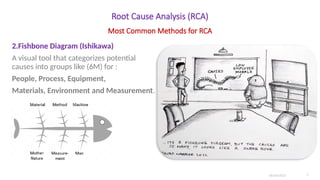
- Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa): Categorizes potential causes into groups such as equipment, people, processes, and environment.
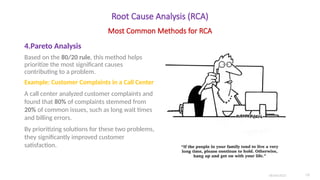
- Pareto Analysis: Identifies the most impactful factors using the 80/20 rule.
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA): Evaluates failure scenarios and their consequences.
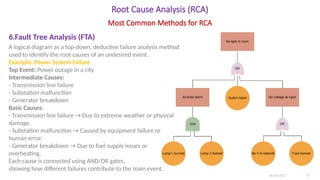
- Fault Tree Analysis (FTA): Logical analysis of events leading to the problem.
- Barrier Analysis: Examines the barriers that should have prevented the issue but failed.
Applications of RCA:
- Industry: Analyzing equipment failures and improving production quality.
- Healthcare: Identifying causes of medical errors and implementing preventive actions.
- IT: Enhancing system security and reducing recurring failures.
- Management: Addressing performance issues and increasing operational efficiency.
Practical Example: Factory Production Line Failure
Problem: Low productivity in a manufacturing line.
Data Collection: Increased rejection rate due to equipment malfunction.
Potential Causes:
- Outdated and poorly maintained equipment.
- Lack of worker training on machine operation.
- Poor routine maintenance procedures.
Using Fishbone Diagram:
- Root cause identified as the absence of an effective maintenance system.
Solution:
- Implement a scheduled maintenance system.
- Provide continuous worker training.
- Upgrade outdated machinery to ensure production quality.
Expected Outcomes of RCA:
- Reduced financial losses from recurring problems.
- Enhanced product and service quality.
- Improved operational efficiency and fewer failures.
- Higher customer satisfaction and better user experience.
a power.