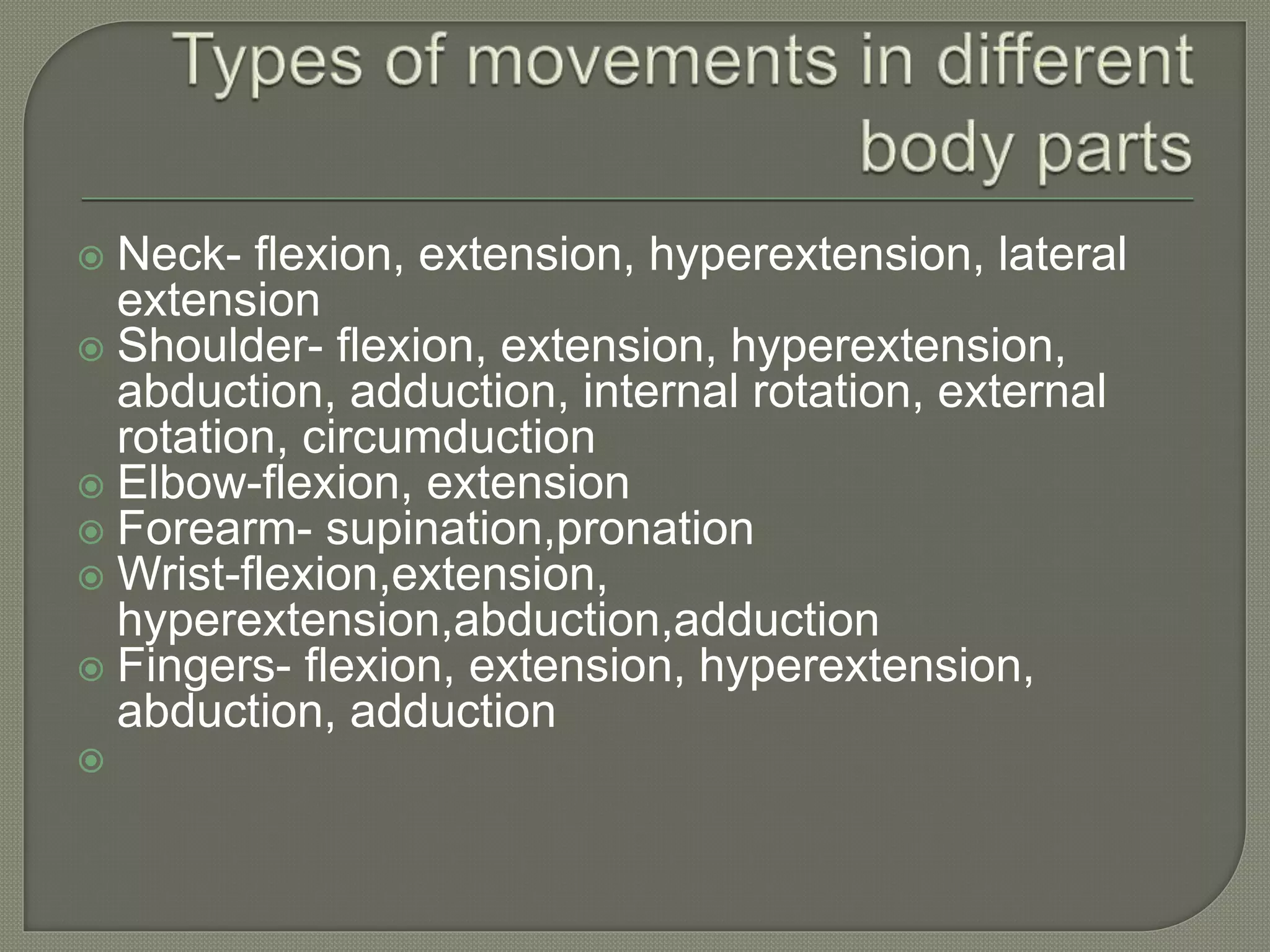
The document defines different types of exercises including active, passive, active assistive, aerobic, isometric, and isotonic exercises. It also lists the benefits of exercises such as improving cardiovascular function, mobility, and reducing blood pressure. The document provides general rules for exercises and defines different types of movements including flexion, extension, abduction, and rotation. It lists examples of movements for different body parts like shoulders, elbows, wrists, fingers, hips, and ankles.