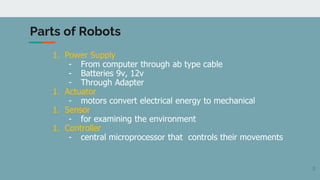
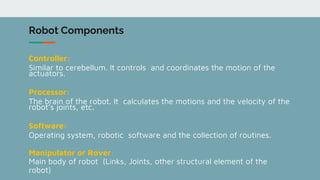
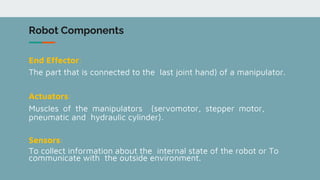
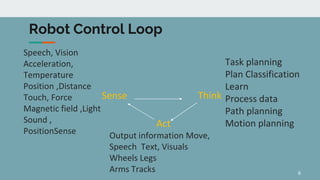
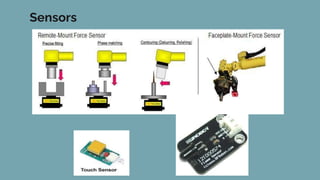
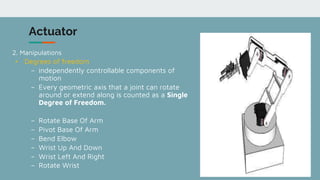
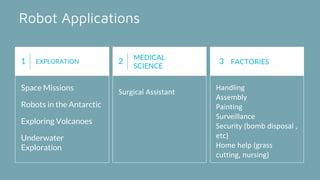
Robot architecture consists of several key components. The main components include a controller that coordinates movement, a processor that calculates motion, software that operates the robot, and manipulators or rovers that form the robot's main body. Robots also include end effectors, actuators, and various sensors. The robot control loop involves sensors sensing the environment, the processor planning actions, actuators moving the robot or manipulating objects, and feedback to continuously monitor and make adjustments. Robots are used in a variety of applications including exploration, medical science, factories, and more. Their development involves defining processes to automate and constant monitoring once deployed.