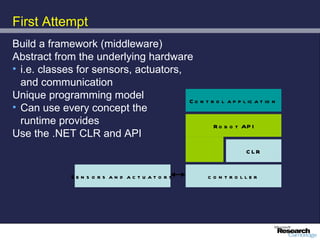
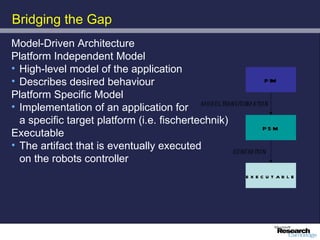
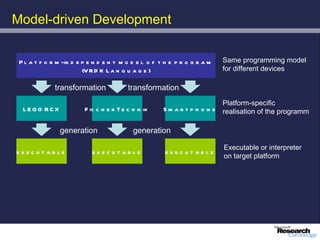
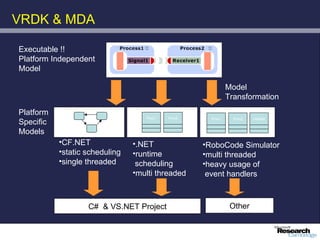
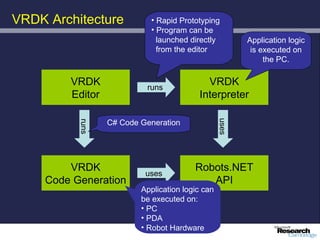
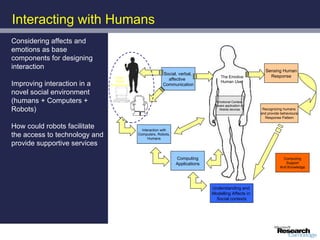
The document discusses advancements in robotics, emphasizing the development of personal and home assistant robots that enhance daily living and interaction. It highlights various projects, such as the robotcub initiative aimed at creating learning robots, and addresses the need for improved programming environments to facilitate robot interaction in everyday life. The text concludes with considerations on the emotional interaction between humans and robots, underlining the importance of social dynamics in robotics.