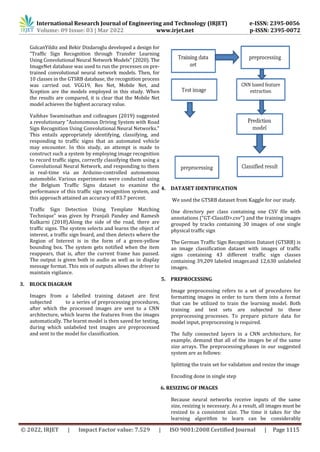
This document presents a method for detecting and recognizing road signs using convolutional neural networks (CNNs). The method uses the German Traffic Sign Recognition Benchmark (GTSRB) dataset to train and test a CNN model for classifying images into 43 sign categories. The images are preprocessed by resizing to 30x30 pixels and splitting the training set into train and validation portions. The CNN is implemented in TensorFlow and achieves over 95% accuracy on both the training and test sets. The document concludes the proposed method provides an accurate and robust approach for automatic road sign detection and recognition.

![International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 03 | Mar 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 1117
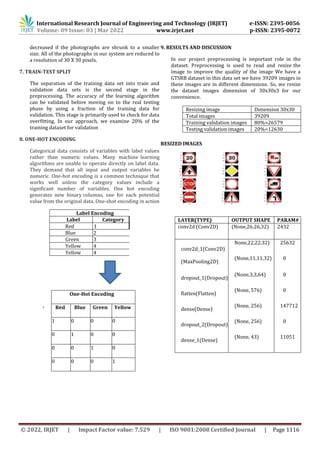
Neural Network Output
Total params: 242,251
Trainable params: 242,251
Non-trainable params: 0
After data preprocessing is to read and resize the
image the second step is to split the training data set
for train and testing data set for test. We have taken
80% for training and 20% for testing in our project
road sign detection and we get accuracy from
training and validation loss.
Finally, we get the output of Training accuracy and
Validation accuracy is 98.93% and 94.32% with loss ,
when we increase the training and validation accuracy
and loss will be decreased.
10. CONCLUSION
In the proposed work we use to know about
convolutional neural networks and how they can be
used in neural image recognition. We made a traffic sign
recognizer with the use of convolutional neural
networks by splitting up images into two categories as
testing and training validations. In this implementation,
we fixed 15 epocs for execution and got an accuracy of
94.32% in testing validation (20%) and98.93% in
training validation (80%). This type of road sign
detection is advisable for future use in autonomic self-
driving cars systems.
REFERENCES
[1] H. S. Lee, & K. Kim, “Simultaneous Traffic Sign
Detection and Boundary Estimation Using Convolutional
Neural Network”, vol. 19, no. 5, pp. 1652-1663, 2018
[2] Y. Yang, H. Luo, H. Xu, and F. Wu, “Towards Real-
Time Traffic Sign Detection and Classification”, Vol. 17,
no. 7, pp. 2022-2031, 2016
[3] Yuan Yuan, ZhitongXiong, Qi Wang, "An Incremental
Framework for Video-Based Traffic Sign Detection
Tracking and Recognition", vol. 18, no. 7, pp. 1918-1929,
2017
[4] Dongdong Wang, XinwenHou, JiaweiXu, ShigangYue,
Cheng-Lin Liu, "Traffic Sign Detection Using a Cascade
Method with Fast Feature Extraction and Saliency Test",
vol. 18, no. 12, pp. 3290-3302, 2017
[5] HengliangLuo, Yi Yang, Bei Tong, Fuchao Wu, Bin Fan,
"Traffic Sign Recognition Using a Multi-Task
Convolutional Neural Network", vol. 19, no. 4, pp. 1100-
1111, 2018.
[6] Jia Li, Zengfu Wang, "Real-Time Traffic Sign
Recognition Based on Efficient CNNs in the Wild", vol.20,
no. 3, pp. 975-984, 2019.
[7] CY Wang, "Research and application of traffic sign
detection and recognition based on deep learning",2018.
[8] T Chen and S Lu, "Accurate and Efficient Traffic Sign
Detection Using Discriminative Adaboost and Support
Vector Regression", vol. 65, no. 6, pp. 4006-4015, 2016.
[9] M Xing, M Chunyang, W Yan et al., "Traffic sign
detection and recognition using color standardization
and Zernike moments", 2016.
[10] Y. L. Pierre Sermanet, "Traffic sign recognition
with multiscale convolutional networks",pp. 2809-
2813, 2011.
S.NO TOTAL IMAGES
(39209)
ACCURACY LOSS
1 Training images
(80%=26579)
98.93 0.1776
2 Testing images
(20%=12630)
94.32
0.1296](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/irjet-v9i3202-220917103133-8f3abd4b/85/ROAD-SIGN-DETECTION-USING-CONVOLUTIONAL-NEURAL-NETWORK-CNN-4-320.jpg)