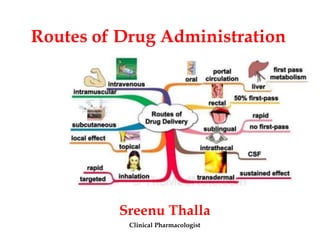
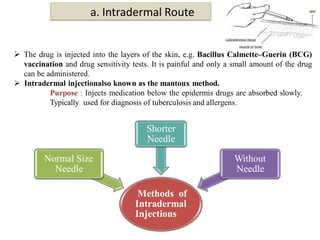
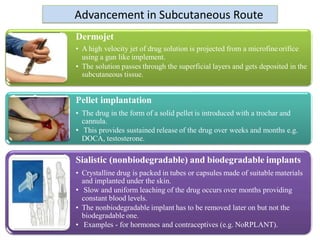
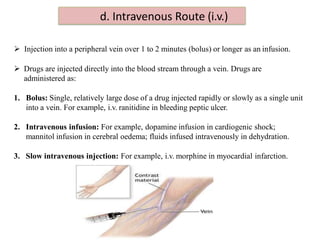
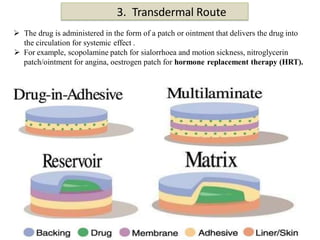
Routes of drug administration can be systemic or local. Systemic routes include enteral (oral, sublingual, rectal) and parenteral (inhalation, injection, transdermal) routes. The oral route is most common due to its convenience but has limitations. Sublingual and buccal routes provide rapid onset due to avoidance of first-pass metabolism. The rectal route can be used when oral is not possible. Parenteral routes have faster onset but require sterile techniques. Injections can be intradermal, subcutaneous, intramuscular or intravenous. Transdermal routes provide sustained delivery for select drugs. Choice of route depends on drug properties and patient factors.