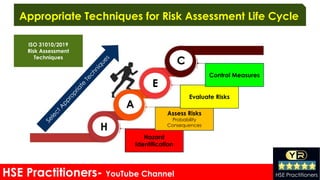
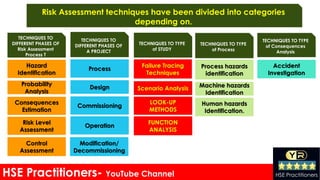
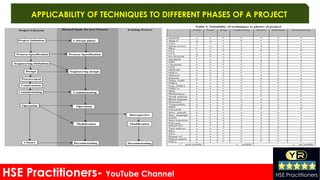
The document discusses risk assessment in the workplace, outlining its definition, types, and techniques for identifying and evaluating hazards that could harm workers. It emphasizes the importance of systematic risk evaluation and the various categories of hazards including mechanical, chemical, biological, psychological, and ergonomic risks. Additionally, it addresses the processes for hazard identification and control measures necessary to maintain safety in work environments.