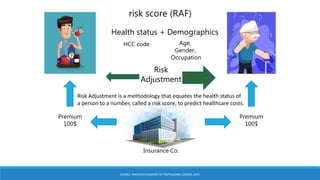
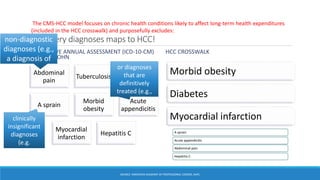
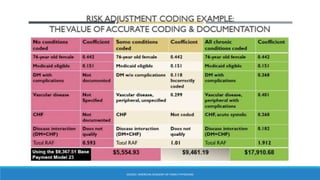
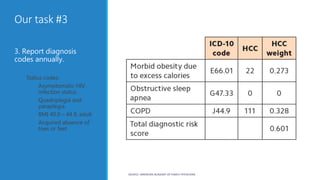
The document discusses risk adjustment factors (RAF) in relation to healthcare costs and risk selection, presenting methodologies for calculating risk scores based on health status and demographics. It outlines the CMS-HCC model's focus on chronic health conditions while emphasizing the importance of accurate diagnosis coding for effective risk adjustment. Key tasks include selecting diagnosis codes related to treatment and reporting them annually to ensure proper financial risk assessment.