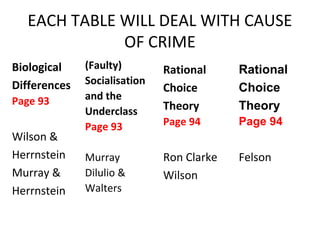
Right Realism seeks practical crime control measures rather than finding the causes of crime. It acknowledges crime is a real problem that destroys communities. Right Realists argue crime results from biological differences, faulty socialization leading to an underclass, and rational choice. They propose preventing crime through proactive policing, broken windows policy, strong communities, target hardening, and deterring crime through certainty of punishment like imprisonment. The goal is controlling crime rather than solving its root causes.








![Bennett, Dilulio & Walters (1996)
Crime is the result of
‘growing up surrounded by deviant, delinquent
and criminal adults in a practically perfect
criminogenic environment – that is, [one] that
seems almost consciously designed to produce
vicious, predatory unrepentant street
criminals’.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rightrealismpowerpointdef-130930093701-phpapp01/85/Right-realism-powerpoint-def-10-320.jpg)














