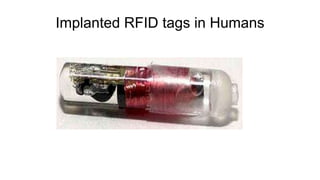
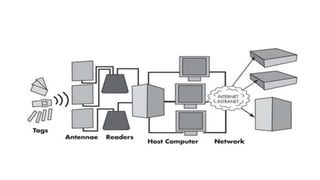
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is an automatic identification method utilizing radio waves for various applications, including asset tracking, medical uses, and wildlife monitoring. RFID tags, which can be passive, active, or semi-active, transmit data to readers without contact, offering advantages such as reusability, varied read ranges, and support for reading multiple tags simultaneously. However, the technology also faces risks, including reverse engineering and eavesdropping, necessitating careful consideration of security measures.